Table Of Contents
State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) Definition
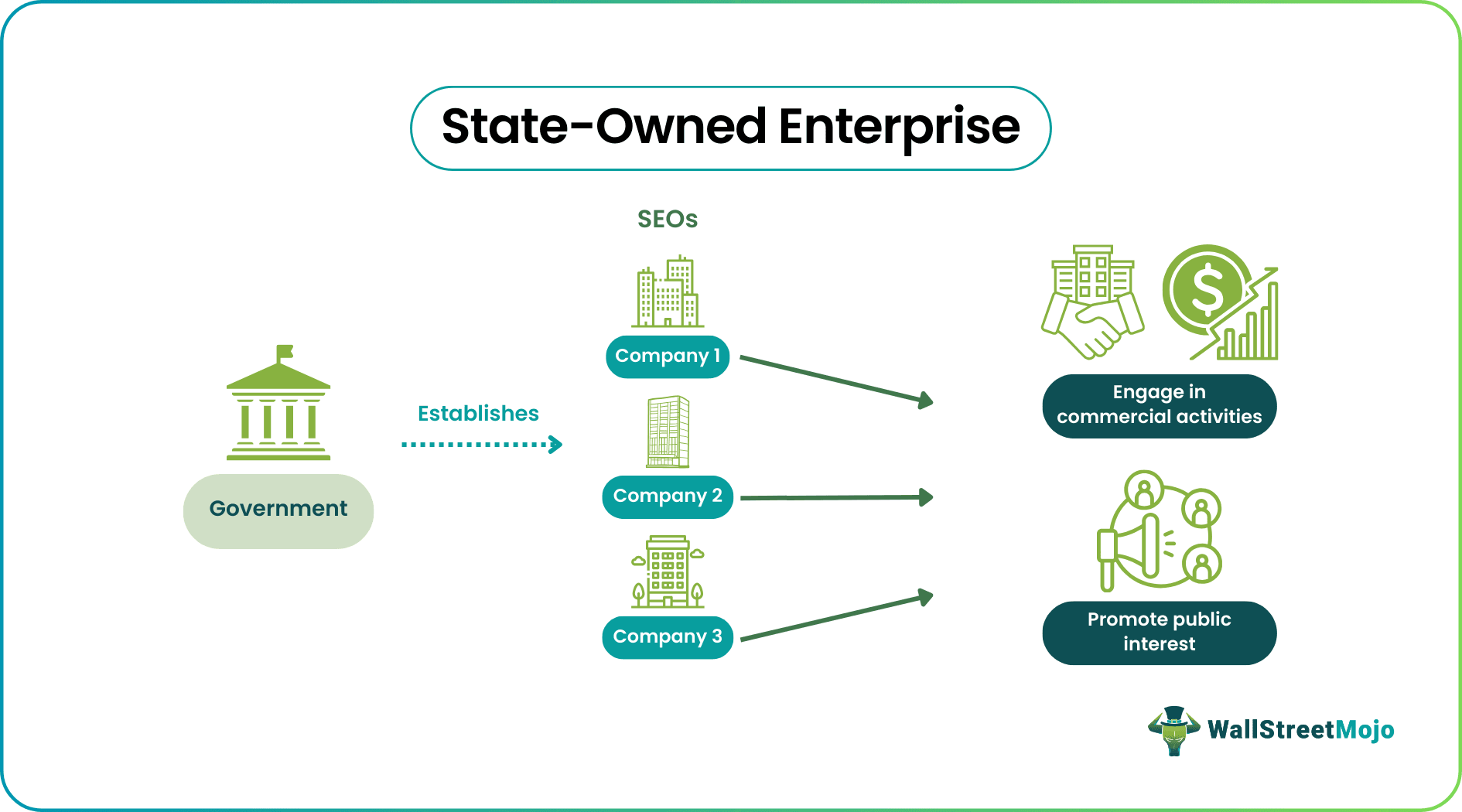
A State-Owned Enterprise (SEO) is a business venture with full or partial government ownership. This legitimate entity is primarily established to indulge in commercial affairs on behalf of the government. SEOs usually drive economic growth while preserving public interest.
Unlike state entities or government agencies that are primarily created for non-profit purposes, SOEs generate revenue for the government while furthering its public policy objectives. They are instrumental in modernizing the country and are usually set up in sectors like infrastructure, strategic goods and services, banking, healthcare, etc. United States Postal Services (USPS), Fannie Mae, and Freddie Mac are popular examples of state-owned businesses in the U.S.
Key Takeaways
- A state-owned enterprise is a fully or partially government-owned business undertaking that participates in economic activities on its behalf while promoting the public interest.
- SEOs usually contribute to the growth and development of a country. They serve different economic and social objectives.
- The nation must practice SOE transparency to improve accountability, develop more partnerships, and guarantee better results.
- Several developing countries exercise the corporatization of SOEs wherein a government agency is converted into a profit-oriented venture aiming lucrative financial returns.
State-Owned Enterprise Explained
Also called Government-Owned Enterprises, SOEs are companies owned and controlled by the government. A majority of them dominate the public utility domains like water, electricity, transportation, etc. They are prevalent in South Africa, New Zealand, Brazil, Norway, India, and China.
Usually, the resource-rich nations employ them to capitalize on natural reserves and practice more authority over the sector for its betterment. Saudi Arabian oil company Saudi Aramco and state-owned Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) are well-known examples of SEOs controlling the oil sector in their respective countries.
Note that SOEs are different from listed companies with stocks partly owned by a government body. While SOEs are wholly or partially government-owned firms, listed companies are public corporations with the government acting solely as their shareholders.
SOEs strive to strike a balance between profitability and public accountability. In other words, it seeks to make the most of private sector efficiencies while ensuring public interest. Most SOEs are lawfully reckoned as business outfits, therefore enjoying all the related rights and duties. However, they must obey the specified regulations administering their performance.
The presence of SOEs has both positive and negative implications on a nation’s economic standing. While some have helped boost revenue generation and financial expansion, others failed miserably due to massive corruption and bribery.
Thence, countries must practice SOE transparency to boost accountability and foster new collaborations. Now, let’s discuss the merits and demerits of a state-owned entity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of State-Owned Enterprise
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Superior public service | More conflict possibilities in leadership |
| Ultimate security of resources | Increased burden of taxation |
| Rapid industrialization | Probable misuse of capital |
| Employment creation | Poor localization of industries |
| Inexpensive production of items | Management disorganization |
| Affordable services | Too much political interference |
| No more exploitation from private enterprises | Swift decisions are impossible |
| Assured protection to the Defence industry | Increased possibility of corruption |
| Stabilization of product rates | Less efficiency and productivity |
Examples of State-Owned Enterprise
List of State-Owned Enterprise in China
Here lies the list of 15 state-owned enterprises in China.
- China National Salt Industry Corporation (CNSIC)
- China National Gold Group Co Ltd (China Gold)
- China Eastern Air Holding Company (CEAH)
- Aluminum Corporation of China (CHINALCO)
- China Three Gorges Corporation (CTG)
- State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC)
- China Railway Group Limited (CRG)
- China Southern Power Grid (CSG)
- China Huaneng Group (CHNG)
- China First Heavy Industries (CFHI)
- China National Chemical Corporation (ChemChina)
- Nam Kwong (Group) Company Limited
- China National Administration of Coal Geology (CNACG)
- China Electronic Technology Group Corporation (CETC)
- China Communications Construction Company Limited (CCCC)
As per a recent Reuters article, Chinese SOEs in the real estate sector are acquiring properties from financially-strained private developers in a bid to save them from bankruptcy. This move aims to revive the crisis-laden property sector that contributes significantly to the Chinese economy.
List of State-Owned Enterprise in South Africa
Let’s check out the List of top 15 of South Africa’s 128 SOEs.
- Agricultural Research Council (ARC)
- Accounting Standards Board
- Airports Company South Africa (ACSA)
- Air Traffic and Navigation Services Company
- Armaments Corporation of South Africa (ARMSCOR)
- Alexkor Limited
- Brand South Africa
- Blind SA
- Broadband Infraco
- Breede-Gouritz Catchment Management Agency (CMA)
- Broadcasting Complaints Commission of South Africa (BCCSA)
- Central Energy Fund (CEF)
- Cape Town International Airport
- Commission for Employment Equity
- Commission for Conciliation, Mediation, and Arbitration
List of State-Owned Enterprise in India
In India, a state-owned business is known as Public Sector Enterprise (PSE) or Public Sector Undertaking (PSU). Here lies the list.
- ONGC (Oil & Natural Gas Corporation) Ltd
- Indian Oil Corporation Ltd.
- Coal India Ltd.
- NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) Ltd
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
- Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd.
- Gail (India) Ltd.
- Power Finance Corporation Ltd.
- Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
- India Post
- Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Ltd.
- State Trading Corporation of India
- National Textile Corporation Ltd.
- Orissa Mineral Development Company Ltd.
- Chennai Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
Corporatization of State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs)
“Corporatization” refers to a procedure wherein a state-owned entity is formed out of a government agency. It transforms the state-run agency into a for-profit business undertaking. Now, the agency functions in compliance with government objectives while being formally designated as a commercial enterprise.
Many developing countries adopt this practice to target the most profitable economic areas and advance their financial growth.
