Table Of Contents
What Is Stakeholder Theory?
Stakeholder theory refers to the ethical concept that addresses the outcome of business decisions, trends, profits, etc., and its collective impact on all stakeholders, including the shareholders, employees, financers, government, customers, suppliers, etc.
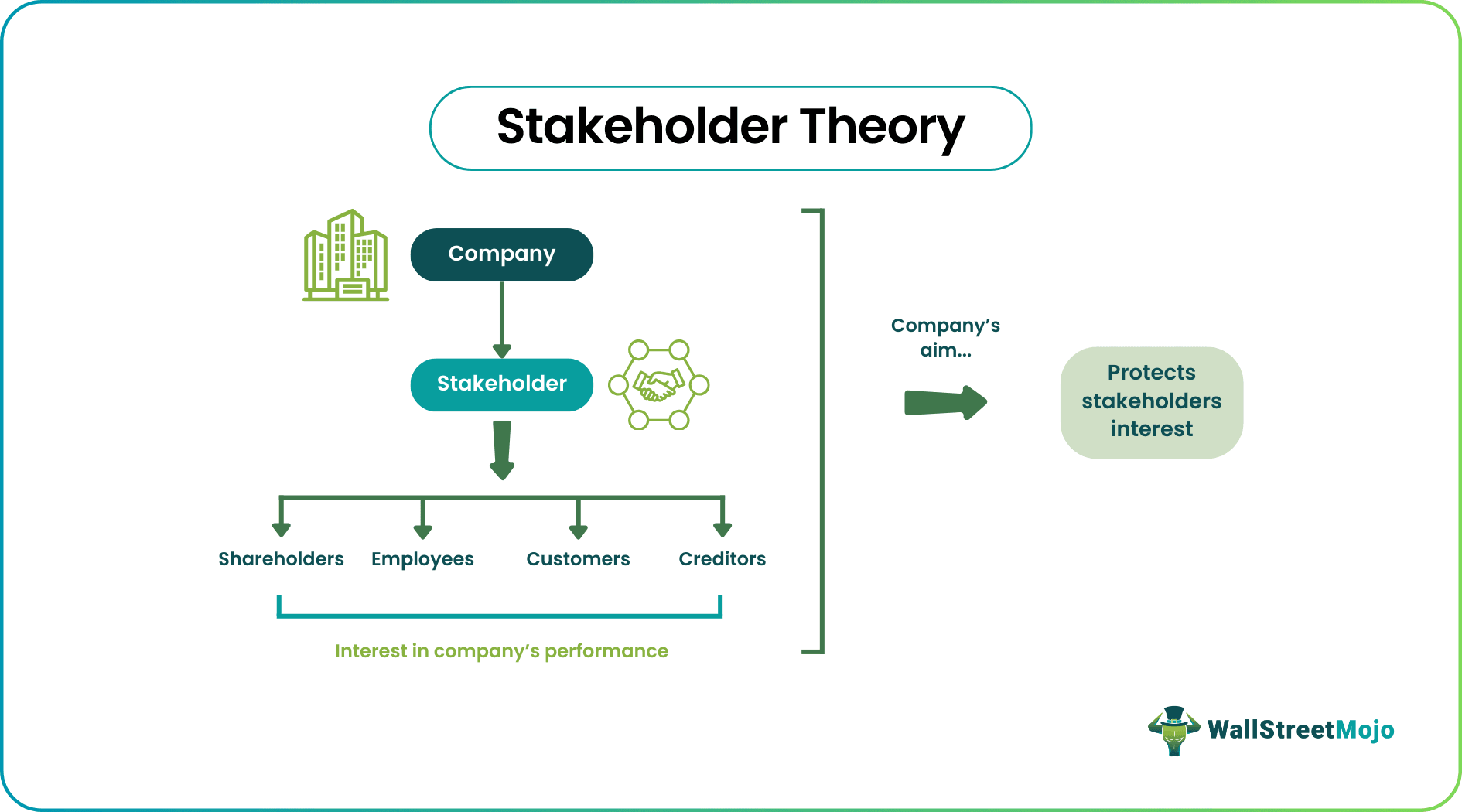
It highlights the importance of the relationship between the various stakeholders of an entity, and how the management should view, manage and treat them so as to make the maximum social and economic impact and achieve the best results through profit maximization.
Key Takeaways
- Stakeholder theory is the ethical concept that addresses the business decision's outcome, trends, profits, etc., and its collective impact on all stakeholders, including the shareholders, employees, financers, government, customers, suppliers, etc.
- The six principles of stakeholders theory are the principle of entry and exit, the principle of externalities, the principle of agency, the principle of governance, the principle of contract cost, and the principle of limited immortality.
- Freeman first coined the stakeholder theory concept in his article in 1983.
- "The Stakeholder Revolution and the Clarkson Principles" journal was published in 2002.
Stakeholder Theory Explained
The stakeholder theory of the firm explains the interconnected relationship between the different stakeholders of an entity like the suppliers, creditors, employees, community, etc.
The evolution of the theory dates back to 1983 when Freeman first coined the concept of the theory in his article. In 1995, Thomas Donaldson published an article named “The Stakeholder Theory of the Corporations: Concepts, Evidence, Implications” in the Academy of Management Review with Lee Preston.
Further, in 1999, he took forward the concept through a journal article, “Response: Making Stakeholder Theory Whole.”
In 2002, “The Stakeholder Revolution and the Clarkson Principles” journal was published.
When the concept matured, more people understood people’s relationships beyond, within, and outside the entity.
The stakeholder theory of the firm brings together the concepts of market and resource utilization and its socio-political impact of it. It defines how managers should understand and treat the stakeholders so that stakeholders’ interests come above all other interests.
Principles
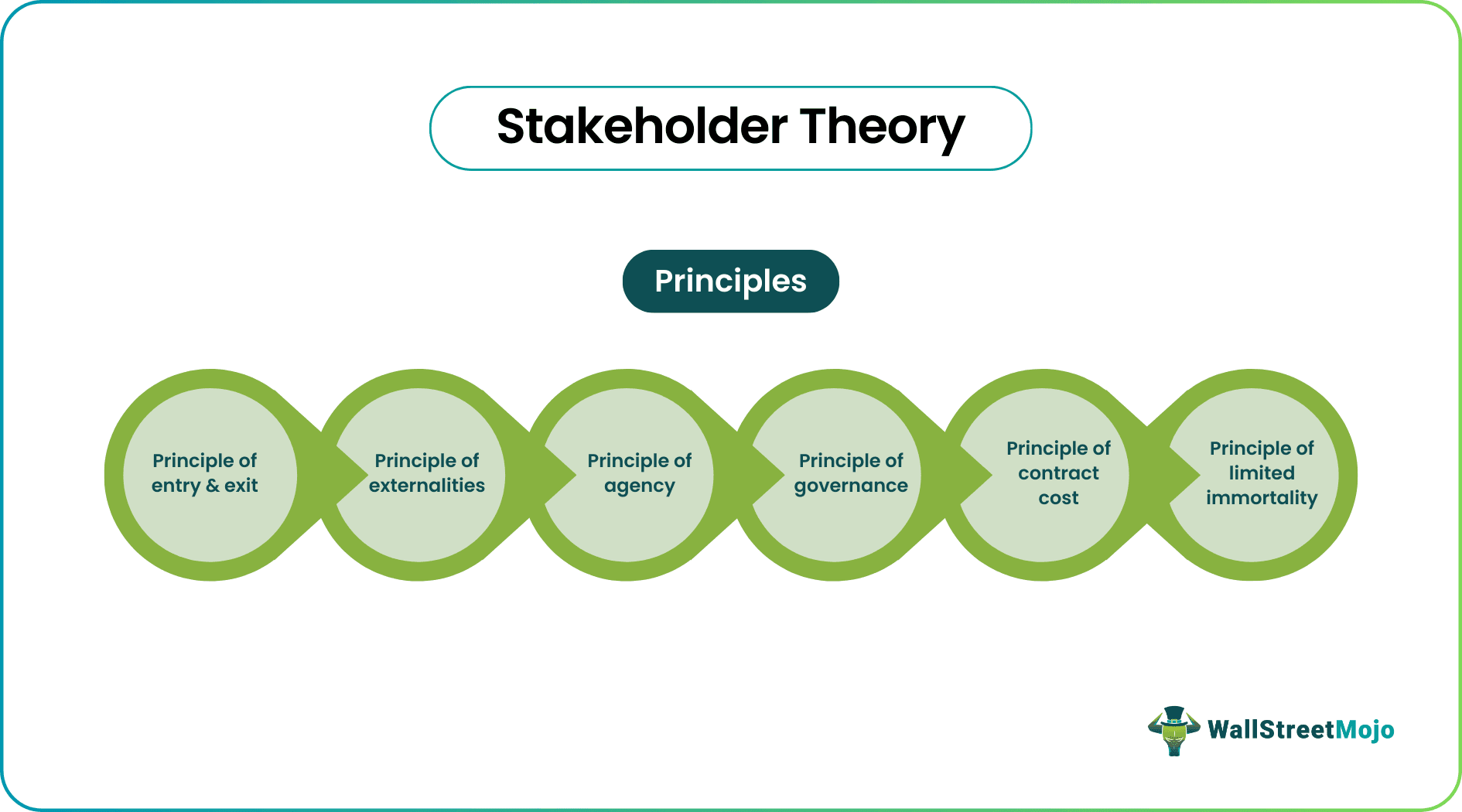
- Principle of Entry & Exit - An entity should have clear rules for hiring, firing, and the work profile of the employees with no ambiguity.
- Principle of Externalities - The decisions taken by an entity may affect people who have no relations with the entity. The theory suggests that people who may be affected by the findings of a business are also to be treated at par with other stakeholders.
- Principle of Agency - The shareholders appoint the company's management to run the entity's business. Management is not the owner of the entity but an agent acting on behalf of the company.
- Principle of Governance - Any changes affecting the relationship between stakeholders and the company need to be approved by them unanimously.
- Principle of Contract Cost - The stakeholder should bear any cost equally, i.e., one should not pay more than another. Furthermore, the cost-sharing should be similar or proportionate to the advantage gained.
- Principle of Limited Immortality - The firm should operate with long-term objectives at focus and not the motivation of short-term perks. Longevity ensures confidence in the stakeholders of the entity. A stakeholder is concerned with the long-term goals of the entity.
Example
As an example of stakeholder theory, we take highlights from the 2020 report of Domino's Pizza Inc.
- The company is concerned with corporate responsibility through which it ensures the satisfaction of its people and customers, the top quality of its products, the enrichment of its community, and the protection of its environment.
- The company runs with a CSR statement, "Do the right things because it's the right thing to do." It focuses on their approach toward the community.
- The Chief People and Culture Officer of the Company, David Klages, said, "This is a people business as much as a pizza business." That further shows their concerns about customers, suppliers, and employees.
- The report further states that a supply truck arrives at a Domino's Pizza Enterprises Ltd. store somewhere in the world every minute. It shows the level of procurement the company is involved in.
- Overall, the company is much concerned about the satisfaction of its customers. The customer is asked to provide feedback on their order for every delivery it makes. That makes the company responsible for each order and the stakeholder theory ethics strong.
Impact
- Normally, the owners are concerned with its profit when running a business. However, stakeholder theory takes the thought process further.
- It requires the management to re-align their focus from short-term profits to the long-term stakeholder theory sustainability in the business. In addition, stakeholders are concerned with the continued interactions since liquidated entities are a big turn-off for the economy.
- Many organizations take the concept seriously with the increased importance of corporate social responsibility. They have also made sufficient provisions to cater to the needs of various people connected with the entity.
Benefits
- Stakeholder theory benefits the organization and employees by increasing productivity, employee satisfaction, improved mental health, and lower turnover rates. That further helps easy talent acquisition in the future.
- Stakeholder theory sustainability in the organization depends on positive feedback from regular customers of the entity. Happy customers become unpaid marketers of the company products. This further increases overall sales.
- With the growing stage of cashflows, the finance providers are assured about the repaying capacity of the entity.
- The government also provides incentives for expanding the company's business in new sectors or areas of the country. In addition, it helps the entity to manage its cash flows.
Criticism
- Stakeholder theory focuses on all people who are or may be affected by the results or decisions of the entity. However, the view is majorly criticized, with the management focusing lower on the entity's shareholders.
- The shareholders have invested their money to maximize their returns. The administration is obliged to keep their interest in focus compared to others.
- The descriptive stakeholder theory is criticized since the entity cannot fulfill everyone's interests. You cannot provide a higher quality product by not increasing the prices. You cannot suffer to meet the hunger of various non-financial stakeholders. If there is a lower demand for the products, you cannot just pile up your inventory to please the suppliers. With an increase in your employees' pay, you cannot satisfy the finance providers concerned with the cash flows retained by the entity.
