Table Of Contents
What is Staggered Board?
Staggered Board, popularly known as Classified Board, refers to the particular set-up of the board members such that it contains directors that are stratified into different classes. In such a case, out of the several classes of directors, only one class of directors have to go through the process of elections at any given point of time.
Staggered board terms help companies to inculcate anti-takeover provisions and board continuity. These advantages are the major reasons why multiple levels or classes of directors are recruited. In situations such as hostile takeover, parties would find it extremely difficult to penetrate into a system such as this and gain control.
Key Takeaways
- A staggered board, known as a classified board, refers to the special Board members arrangement containing Directors layered into various classes.
- A staggered Board of Directors is a well-known practice in US corporations. It is usually created to govern the organization, corporation, or company's Board of Directors.
- In this arrangement, only a specific section of the Board members is elected at any time. Each Director's category is given a specific "class," Class I, II, III, etc.
Staggered Board Explained
A staggered board is a group of board of directors who serve different tenures as directors as they are split into different classes of directors. This arrangement helps companies drive anti-takeover strategies and overall continuity of the top-level management.
In the US corporations, a staggered board of directors is a very well-known practice, which is usually formed to govern the board of directors of an organization, corporation, or company. In this setup, only a certain section of the board members (instead of the entire board of directors) is elected at any given time each time. Each category of directors is assigned a specific "class," say Class I, Class II, Class III, etc.
Structure
Let us understand the structure in which a staggered board of directors is curated and how its implementation helps the company with different aspects of daily and long-term plans.
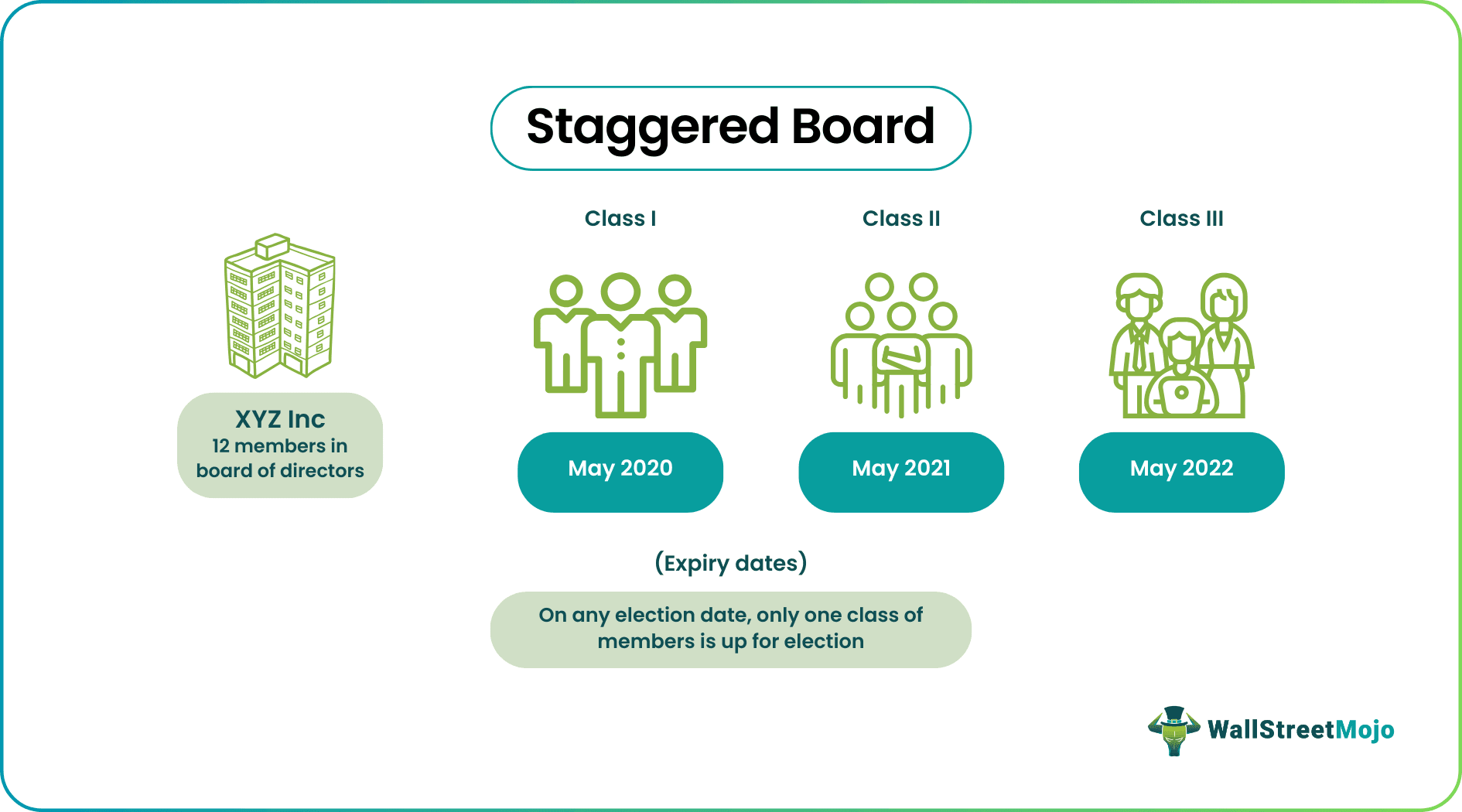
In a staggered board, the members are grouped into well-defined classes. Let us assume that there are 12 members on the board of directors of XYZ Inc., and they are grouped into three classes, say Class I, Class II, and Class III. Also, 25% (3 members), 50% (6), and 25% (3) of the members are there in Class I, Class II, and Class III, respectively. Now, the terms for Class I, Class II, and Class III are to expire in May 2020, May 2021, and May 2022, respectively. Therefore, on any election date, only one class of members is up for election, which is why the name is "staggered."
Examples
Let us understand the staggered board terms in depth with the help of a couple of examples. These examples would help us understand the intricate details about the concept and the practical implications and occurrences.
Example #1
Let us take the example of XYZ Inc. and ABC Inc. to illustrate their importance. Both the companies have 15 members in their board of directors, who each serve for a term of 3 years. XYZ Inc. uses a staggered board while ABC Inc. uses a normal set-up for the board of directors.
In the case of XYZ Inc., five directors are grouped into each of the three classes. The terms for Class I, Class II, and Class III are to expire in June 2020, June 2021, and June 2022, respectively. In the case of ABC Inc., the terms of all the 15 directors are to expire in June 2021.
Now, let us assume a situation of a potential hostile takeover of both XYZ Inc. and ABC Inc. by DFG Inc. in June 2021. DFG Inc. seeks to acquire either of the two companies to strengthen its market domination by having more market share. However, none of the companies are willing to join DFG Inc.
The takeOver of XYZ Inc: DFG Inc. will have to garner a board majority. Given the staggered nature of the board, the acquirer will be able to pocket a maximum of 5 seats in any election. So, in the election of June 2021, even if DFG Inc. acquires all five seats, it will still fail to achieve a board majority (5 out of 15). Therefore, the acquirer will have to wait until the next election to achieve a board majority. In this period, the target company might devise some other way to overcome the takeover attempt.
The takeOver of ABC Inc: DFG Inc. will have to garner a board majority. Given the normal nature of the board, DFG Inc. will be able to acquire all the 15 seats in the election of June 2021 and swiftly take over ABC Inc.
The above example shows how such a classified board can be useful to avoid such attempts of a hostile takeover.
Example #2
A Harvard Business School research paper studied the implementation of the Massachusetts law that was put into action in 1990. In their study they compared companies that were forced to adopt this law and form a staggered board of directors.
The result was that the companies saw an increase of 15.9% in their Tobin’s Q numbers in 15 years. The Tobin’s Q reflects the market value of the company’s assets divided by the replacement cost of the company’s assets.
Importance
The importance of staggered board terms can be acknowledged because it can be used as an effective measure to stop a hostile takeover, as illustrated in the above example. To gain control of the majority section of the board, the hostile bidder has to acquire the required seats across several elections planned for a specific director class. Because of a staggered board, a hostile bidder has to delay its attempt at least by one year or not more. In this way, it safeguards a corporation from outside influence.
Benefits
Other than tenures and takeover issues, there are other factors that prove to be significant advantages of forming a staggered board of directors through the discussion below.
- Members of such boards are offered longer overall tenure, and as such, they can focus on major business issues. They are not bothered by elections every year.
- The structure of a staggered board of directors is such that it inherently prevents any abusive or hostile takeover attempts.
- Long-term investors usually seek stability, and a classified board can provide that stability as there isn’t as much pressure on the board members to make uncertain decisions to make an evil profit.
Limitations
Despite having multiple advantages, there are several factors that prove to be hassles or hurdles. Let us discuss the disadvantages to completely understand the staggered board terms.
- A company’s value might become impacted due to a staggered board as the board members are there for an extended period irrespective of their performance.
- Only a certain section of the board is replaced in any given year through an election. In such a scenario, any change that the current board members are unwilling to make can’t be brought for the next couple of years until the majority of the members are changed.
