Table Of Contents
Special Purpose Entity Meaning
A Special Purpose Entity is a separate legal entity created to fulfill certain objectives, including devising measures to appropriate financial risk and legal risk profile. This entity generally has a predefined purpose and limited activity scope and is sometimes used as a short-term solution to a current or potential problem. Also, their structure is accordingly devised.
Also known as a special purpose vehicle, it is the subsidiary of the larger corporation with different liability structures, asset structures, and legal status, which makes all its obligations secure. It is secure even if its parent company becomes bankrupt. It is also designed to serve as the counterparty for the swaps and the other types of derivative instruments that are credit-sensitive.
Key Takeaways
- Special Purpose Entity is an independent legal entity that meets particular needs. It also includes planning means for sound financial and legal risk profiles.
- Sometimes, it is called a special-purpose vehicle. It is a vast corporation subsidiary with distinct liability and asset structures and legal statuses.
- Moreover, it makes all the responsibility secure even if the parent company becomes insolvent. Often, it is used as a short-term solution to a current or potential problem and structured accordingly.
- On-balance sheet SPE and off-balance sheet SPE are the two types of Special Purpose Entities (SPE).
Special Purpose Entity (SPE) Explained
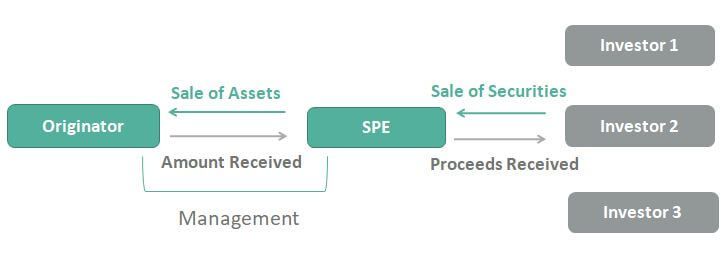
A special purpose entity (SPV) is a subsidiary company formed to facilitate the parent company's financial arrangements, which includes speculative investments and leverage, without compromising the whole group.
It means that if the special purpose vehicle becomes bankrupt, then in that case the parent company remains unaffected, and in case the parent company becomes bankrupt. The special-purpose entity remains protected and unaffected. Special purpose entities generally are used for securitization, and they are allowed to buy, sell, and finance the assets.
Although Special Purpose Vehicle is used for isolating the financial risk present because of the different accounting loopholes, at the same time, these entities may become CFO's financially devastating way for hiding the debts.
The parent company can form the SPE through trusts, corporations, limited partnerships, limited liability corporations, etc.
The documentation of the equity, assets, and liabilities is done by the Special-purpose entity (SPE) on a balance sheet of its own rather than the parent company's balance sheet as the equity or debt.
SPE may hide crucial information from its investors who might not completely know the company's financial situation. With this risk, the investors should analyze the balance sheet of the Special-purpose entity and the parent company properly before reaching any conclusion regarding investing in the business of any of them.
Reasons
Though these entities are not controlled or monitored by the central bank, they are still regulated based on the objective they have been created to serve. The reasons or objectives that these SPEs are formed to deal with or take care of include the following:
- It holds a pool of securities and assets, which can act as collateral for loans when required.
- It can pass the risks involved in holding the pool of assets to other investors or entities.
- These entities make it easier for a firm to have access to cash, thereby increasing the liquidity opportunities for it.
Types
The following are the two types of SPE.
#1 - On Balance Sheet SPE
In the case of Balance Sheet SPE, the financial results of the Special-purpose entity are consolidated with the parent company’s financial results. The incomes, in this case by some means, are transferred to the parent company.
#2 - Off-Balance Sheet SPE
In the case of off Balance Sheet SPE, the financial results of the Special-purpose entity are not consolidated with the parent company's financial results, and the incomes are also not transferred to the parent company by any means.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand what is a special purpose entity and how it works:
Example 1
There is a company named BCF limited which is famous for manufacturing the different types of equipment used for industrial purposes. The company uses a special purpose entity for financial risk leverage. Out of all the Special-purpose entities of the company, one of the SPE has independent members on the board, which consists of a commercial bank that provides the credit facility and the loan, different equity investors who have the tax free investments, government who provides the subsidies and also permits the company for the operation of the contracts of the Special-purpose entity, and the sponsor protecting the minority investors of the parent company and coverage to the technical risk.
The SPE Company formed acts as the equipment solution provider and other technical consulting issues. Also, the Special-purpose entity (SPE) offers construction engineering and maintenance.
The different advantages which the parent company BCF limited have when its BCF limited is operating involves the high-level project and risk management, which allows the company to collaborate with its stakeholders and the chain holders effectively. Apart from this, it is easy for the parent company to finance its operations using government funding, long-term debt or equity investors without any compromise to its main operations.
Example 2
KeyBank Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFI) Group offers a $20 million line of credit to support small businesses in the region with Lendistry, An SPE founded by BSD Capital, Inc. Lendistry is an entity that helps small businesses obtain loans when they do not fulfill the conventional lending criteria, be it with respect to cash or credit or collateral, etc. The SPE offers credit facilities and other financial services to small businesses across the United States and helps them deal with shortfalls effectively to enjoy uninterrupted progress and growth.
Advantages
Having a special purpose entity formed gives companies an opportunity to stay away from direct financial risks and losses. These firms are created to fulfill the temporary objectives of their parent company and offer a shield against the expected losses or risks. Some of the benefits of having the SPEs formed are as follows:
- By creating the Special purpose vehicle, the parent company will be allowed to legally isolate the financial risk associated with the project and share it with the other investors.
- SPE helps in the tax saving for the company in case the entity is created in the tax haven countries.
- It is easy to set up the SPE.
- The same rules and regulations do not bind the Special purpose vehicle and the parent company, so it offers more freedom to operate it.
- SPE helps keep secrecy concerning some projects from the competitors of a parent company or from the investors of the parent company whose company thinks may disapprove of the particular transaction.
- There is direct ownership in the special-purpose entity of the specific asset.
- The parent company can perform the high-risk transactions using the Special-purpose entity without endangering the solvency of the entire company.
Disadvantages
Undoubtedly, creating the SPEs is of huge benefit to the parent companies, but they are not devoid of flaws. Let us have a look at the limitations of these entities:
- It requires a substantial amount of capital to create a Special-purpose entity.
- The SPE has lower access to capital when compared with the parent company because the Special-purpose entity doesn’t have the same level of credit as the parent company.
- Suppose there are some unexpected changes in the rules and regulations in the market that apply to the particular Special-purpose entity. In that case, it can create a serious problem for the companies using these special purpose entities as they might not be able to meet the new rules and regulations that came into existence.
- The Accounting rules of Mark to Market could be triggered if the asset is sold, which will negatively impact the parent company's balance sheet.
- There are fewer options available to fund the special purpose vehicle.
Special Purpose Entity vs Single Purpose Entity
Special purpose entity and single purpose entity are terms that are synonymously used when it comes to referring to a newly formed firm taking care of the financial risks of a parent company. However, these two differ slightly in their horizon.
Both these entities can be used as a substitute as they have similar objectives to fulfill, but they still have one difference. While a single purpose entity is more expansive with a broader horizon, the special purpose entity is a part of it.
