Since social impact and green bonds focus on different sectors, their characteristics also vary. Thus, let us look at the differences between them:
Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
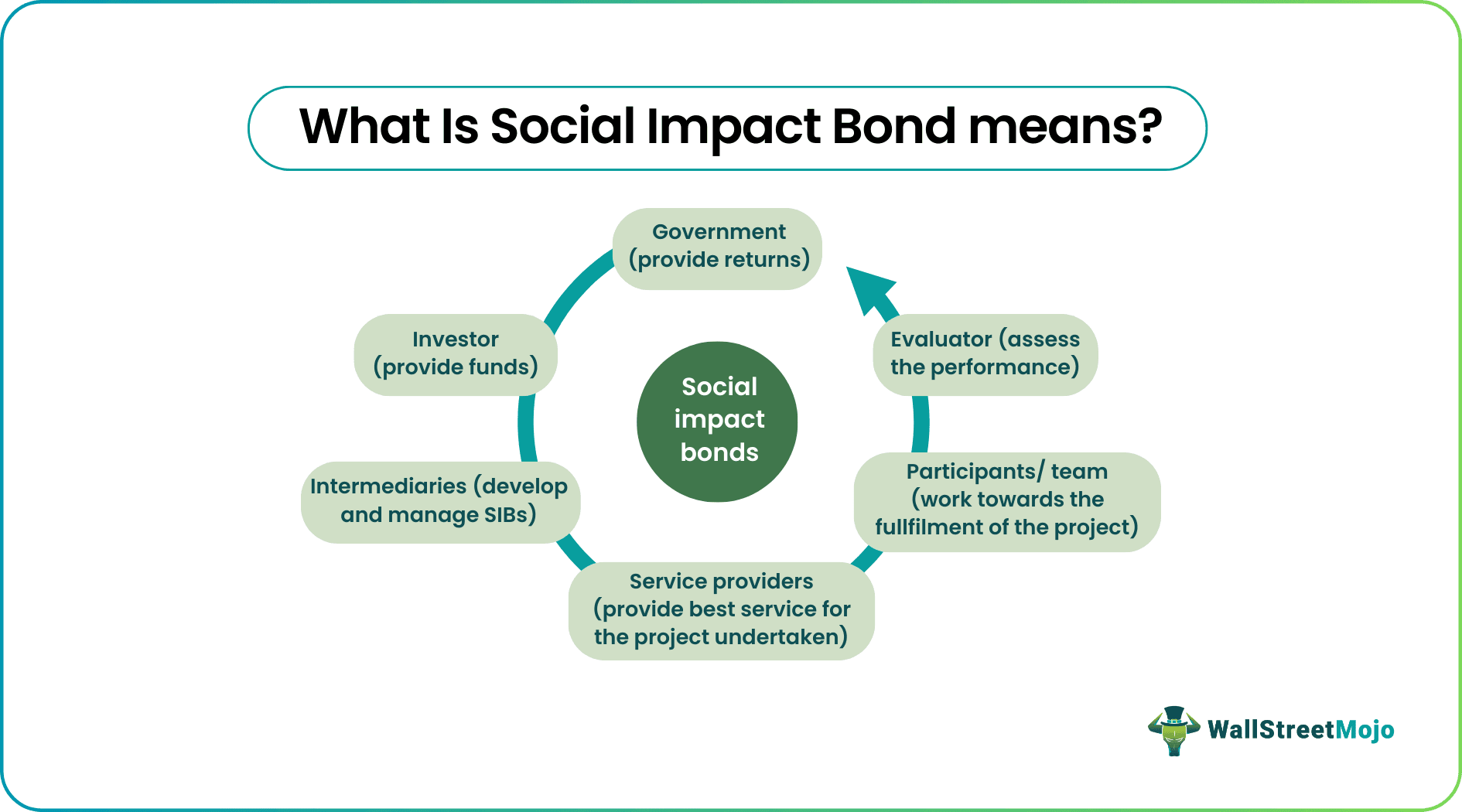
- Social Impact Bonds (SIB) are financial instruments that allow investors to invest in social programs and projects initiated by the government.
- There are two types of SIBs, namely individual SIBs and SIB funds. Further, the former is categorized into direct, managed, and intermediary SIBs.
- The concept has its origin in the year 2010. Social Finance Ltd was the sole firm to issue SIBs to investors.
- The only difference between SIBs, development impact bonds, and green bonds is that the former focuses on social programs. While the other two aim to fund development and environmental projects.
History
The first social impact bond model was introduced by the United Kingdom (UK) in 2010. Social Finance Ltd developed the first social impact bond in the UK. However, implementation of this model occurred in Peterborough to reduce reoffending rates. Later, other nations also started implementing it. The social impact bond structure differs from the other bonds issued.
Since its origin in 2010, various names have been given in different nations. In Europe, it is called Social Impact Partnerships. Similarly, in the United States, it is called Success Schemes. And lastly, the Australian population refers to it as Social Benefit Bonds. Despite their different synonyms, they work the same. They intend to accelerate the desired outcomes through proper investment guides. However, the process for the same may differ.
Types
Based on the function, two types of social impact bond structures exist. It includes individual SIBs and SIBs funds. While the former can issue only a single contract, the latter has access to multiple contracts. However, the individual SIBs are further divided into three subcategories. Let us look at them:
#1 - Direct SIBs
In a direct SIB, the contract between the government (outcome payer) and the service provider is signed. Here, the latter is responsible for the execution of the social project and performance evaluation. In short, the service provider has a major role in social impact bonds.
#2 - Intermediary SIBs
The intermediary SIBs enable a third-party contract between the outcome payer, the intermediary, and the investor. Here, a mediator tries to control, assess, and monitor social development projects. In some cases, an intermediary can also invest in SIBs.
#3 - Managed SIBs
This SIB is signed between the bond-raiser (or outcome-payer) and the intermediary (prime contractor). Here, the intermediary is usually responsible for major activities. However, the only difference between the intermediaries SIBs and Managed SIBs is the investment type.
Examples
Let us look at the examples of social impact bonds to comprehend the concept better:
Example #1
Suppose Hellingston is a country situated among the Western countries. It has changed from an underdeveloped to a developing economy in the past few years. Further, it wishes to accelerate the social and economic development of the nation. Among the major issues, the Hellingston government wishes to improve the transportation infrastructure. Therefore, they issue SIBs to the investors. They successfully raised $300 million for the project for seven years. By the end of the tenure, the savings made by the government were transferred to the respective investors.
Example #2
A recent article dated January 2023 stated that Japanese local governments are boosting the spread of social impact bonds. Many local governments are turning into SIBs since they improve the overall efficiency of administrative services while reducing expenses. The companies who take up projects on behalf of the governmental bodies can implement creative changes on top of making a profit for themselves.
In addition, there are various awareness programs issued for the public interest. The success of SIBs has led to the increase of their popularities on a large scale securing these programs more support and funds.
Pros And Cons
Pros
- It encourages development and innovation in public sector services.
- SIBs allow collaboration of public sector and private partnerships.
- It considers the benefits of the stakeholders and investors and tries to outperform their expectations.
- SIBs provide returns in the form of savings to investors.
- The financial burden is transmitted from the government to different investors.
- Additional funds are generated for social development programs apart from the budget allocated.
Cons
- SIBs contain enough complexity from development to execution.
- There are various fees and high transactions involved in this process.
- The officials might find it difficult to evaluate the funding program for the project.
- A sudden or slight drift in the project's objectives can hamper the relationship between investors and service providers.

Social Impact Bond vs Development Impact Bond
Although development impact bonds (DIBs) have similar functions, they differ in their characteristics. So, let us look at their potential differences:
It refers to the contracts initiated by the governments or public sector for funding social programs.
Development impact bonds are an investment vehicle focusing on the nation's development.
To access capital from investors, fund social programs, and provide gains in return.
It is similar to SIB, but here, it aids economic development and growth.
Government authorities, investors, service providers, and intermediaries.
Service provider, investor, outcome funder or payer, and evaluator.
Here, the government or outcome payer pays the investor.
In this case, a philanthropic organization repays instead of the government.