Table of Contents
What Are Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)?
Small and medium-sized enterprises, or SMEs, have different definitions in different regions of the world. However, the primary differentiator of the concept is that these enterprises have employees and revenues under a specific limit. It is also vital to note that SMEs have a sizeable contribution towards economic and job growth in the United States.
According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, or SBA, there are upwards of 30 million SMEs in the United States alone. Therefore, the growth in small and medium-sized enterprises such as healthcare, accommodation, social assistance, food services, and more lead to significant growth in the overall economy irrespective of the geographical location.
Key Takeaways
- Small and medium-sized enterprises are business establishments that fall under a particular limit. The limits vary based on different economies across the globe.
- These small companies account for a significant share of employment and revenue generation in major economies across the globe, including the United States, China, the EU, and Canada.
- These companies increase the competitiveness of the market and prevent large companies from forming monopolies in different sectors.
- As a result, consumers get products and services at a better price and quality.
- Innovation of products and processes is manifested through SMEs in different parts of the world.
Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises Explained
Small and medium-sized enterprises have various definitions in technical terms across different geographical locations. However, they are usually defined by the quantum of their revenue, assets, and the size of their workforce.
The exact numbers in terms of revenue, workforce, or assets differ from country to country. Nevertheless, the factor that shows a distinct difference between SMEs and other forms of business organization is that SMEs are more agile and flexible. They can adapt to market changes more effortlessly than some of the more prominent companies.
The prospects of small and medium-sized enterprises can be found in any industry. However, it is mainly found in industries that only require a few employees or a significant initial investment. Therefore, some of the most common SMEs are dental offices, legal firms, bars, and restaurants.
SMEs are also easier to run as enterprises than some large or even multinational companies. While the latter needs systems like enterprise resource planning for different functions, SMEs require smaller systems for their small scope of operations.
Another thing to recognize and acknowledge is that since these companies play a critical role in the economy, governments of different countries provide them with subsidies and incentives to run businesses, enhance innovation, and create more jobs.
Features
Despite the definitions of SMEs differing across the globe, there are a few standard features. They are:
- SMEs are driving factors of economies. They employ a large percentage of the country's workforce and generate significant revenues.
- They are typically small companies with below ten years from being incorporated.
- These enterprises are self-funded. They usually do not look for external sources of funding.
- Marketing in small and medium-sized enterprises have unique business concepts and limited resources compared to large corporations.
- Most successful SMEs have exemplary entrepreneurial qualities such as relationship building, governance structures, market diversification, and export characteristics.
- These companies might also face difficulties in terms of market share and day-to-day activities.
SMEs in the US
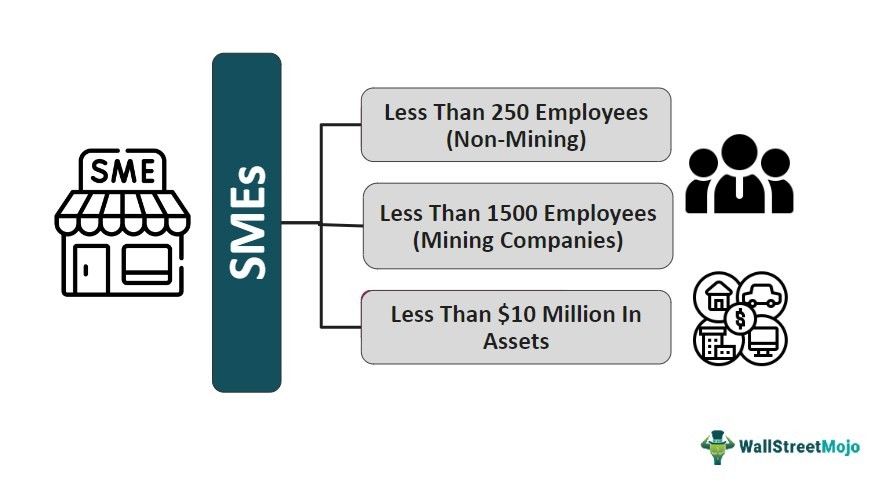
Small Business Administration (SBA) classifies SMEs in the United States of America. The classification is based on the number of employees, structure of ownership, industry, and earnings.
For instance, in the manufacturing sector, SMEs can have a maximum of 500 employees. However, for copper and nickel ore mines, the employee count can go up to 1,500 employees to still qualify as an SME.
For tax-related purposes, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) does not differentiate businesses on the basis of SMEs or non-SMEs. However, they distinguish small businesses and self-employed taxpayers (Assets less than $10 million) and mid and large companies (Assets above $10 million) into another group.
According to the SBA data, there are over 33 million SMEs in the U.S., and 82% of these companies do not have a single employee.
SMEs in Canada
The Canadian Industry Statistics issued by the government of Canada clearly segregates businesses based on the number of employees. According to these statistics, the companies are segregated as:
- 1-4 employees = Micro Business
- 5-99 employees = Small Business
- 100-499 employees = Medium Business
- 500+ employees = Large Business
98% of all employer-based businesses in Canada are small businesses. In fact, small businesses employ over 10.3 million people, which is over three times what medium businesses employ.
SMEs in EU
The EU or European Union also has defining factors that make a business entity an SME. According to the EU, a small enterprise is a company that has a company with fewer than 50 employees. On the other hand, medium enterprises have more than 50 but fewer than 250 employees. Additionally, micro-companies have a maximum of 10 employees.
Therefore, like other countries, even the EU has SMEs that account for about 99% of all businesses within the region. Within the European Union, SMEs employ and empower over 100 million individuals. Moreover, these SMEs generate over 50% of the EU's GDP.
SMEs in China
In comparison to other countries, the classification system in China is complicated. The classification is different for different industries or sectors. Classifications for SMEs are in China:
- Retain companies within China are considered part of SMEs if they have 10-49 employees and generate annual operating revenue of $1 million or above.
- Agriculture and its related companies in China are considered small enterprises if they have an operating revenue within the $0.5 million-$5 million range.
- Real estate developers of Chinese origin would be considered small enterprises if their annual operating revenue is between $1 million-$10 million. Additionally, they shall be considered an SME if their assets are between $20 million-$50 million.
Examples
With the basics and overview of SME classifications across the globe, it is time to understand the practicality and real-life application through the examples below.
Example #1
ABC Construction Company has been in the industry for close to 5 years. They recorded a revenue of approximately $23.8 million in 2023. Therefore, they are classified as a prospect of small and medium-sized enterprises because the SBA's limit is $39.5 million annually.
Moreover, there are no employee limits for these companies anyway. Hence, ABS Construction Company was still able to avail of all SME incentives and subsidies.
Example #2
In December 2023, SMEs brought a fantastic opportunity for banks to do business. In times when rising interest rates led people to park their funds elsewhere, banks saw a great opportunity in SMEs.
In the United States, over 60 million employees are employed by SMEs, generating over $150 billion in revenue each year. The number of workers employed by SMEs accounts for about 47% of private sector jobs.
Incentives Offered
Governments across the world help with the growth and marketing of small and medium-sized enterprises. The help and support are commonly referred to as incentives. Moreover, in most countries, there are even private organizations that help SMEs achieve their true potential.
In the United States, 79(a) loans are provided to SMEs that give them a guaranteed portion of the total amount, limit processing and other fees, and cap interest rates in favor of such enterprises.
Financial institutions also provide small or microloans of about $50,000 to start operations and scale from zero to one. In fact, the loans processed and sanctioned through SBA can start from as low as $500 and go up to $5.5 million for these enterprises.
Importance
The importance of different prospects of small and medium-sized enterprises within an economy are as mentioned below:
- The growth of small, medium, and micro-organizations within an economy improves the competitiveness among different sectors. As a result, consumers can enjoy better pricing, quality, and efficiency.
- Without SMEs, large corporations would manipulate prices and take advantage to create monopolistic markets and complete monopolies in different sectors.
- Multiple SMEs are linked to being the flagbearers of innovative products and processes in different sectors.
- Despite the increasing competition between large companies and SMEs, the latter provides excellent assistance to the former with functions that they are not able to efficiently fulfill.
