Table Of Contents
What Are Silver Futures?
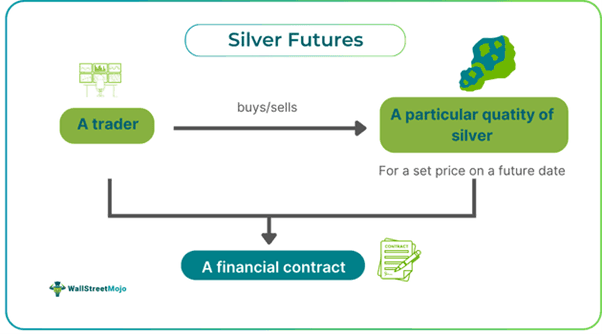
Silver futures are standardized financial agreements that involve two parties committing to buy and sell a specific quantity of the underlying asset, i.e., silver, in this case, for a prespecified price on a prespecified date. These contracts expose people to get exposure to the precious metal without actually buying/selling it.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
Hedgers often utilize silver futures contracts as part of their risk management strategy. They frequently use such contracts to mitigate the impact of inflation, decrease price risk, and make financial gains from favorable price changes. Speculators can also get exposure to the precious metal by paying a fraction of the actual price and profiting from the price fluctuations.
Key Takeaways
- Silver futures refer to a type of derivative contract that individuals purchase or sell based on their price predictions concerning silver.
- It serves as a hedging tool and also allows speculators to profit from price fluctuations concerning the underlying precious metal.
- There are some noteworthy disadvantages associated with these contracts. For example, they are prone to manipulation and carry significant financial risk.
- Three key benefits of these derivatives are price transparency, liquidity, and diversification.
- Some vital specifications associated with these legally binding agreements are contract size, first notice date, exchange, and daily limit.
Silver Futures Explained
Silver futures refer to a legally binding financial agreement that involves two parties who agree regarding the price of price on a specific future date and make a promise to ensure settlement of the trade on that predetermined date of expiration. These contracts enable people to mitigate risks and safeguard themselves from potential downturns.
With the increasing demand for silver across different industries, the futures market has been growing in popularity among traders who are seeking portfolio diversification and looking to profit from the price volatility of the underlying commodity.
One must note that silver prices are influenced by various factors, such as demand and supply dynamics, investor sentiment, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Hence, one must stay updated with the latest silver futures news to ensure they make well-informed decisions that can lead to significant financial gains. If one is not aware of the latest news, they may suffer significant losses after making a wrong decision.
Specifications
Let us look at the key specifications concerning these derivative contracts.
- Exchange: It refers to the exchange on which the trading of the contract occurs. For example, it can be the Commodity Exchange or COMEX.
- Contract Unit: The contract unit refers to a standardized size, which is unique to individual futures contracts. For instance, in the case of CME futures, it is 5,000 troy ounces.
- Exchange: The symbol for these contracts on an exchange. For example, it can be SI or SIL.
- Trading Hours: It is the time during which one may trade these contracts on an exchange.
- Minimum Tick Size: This refers smallest price increase permissible for any contract traded on a commodity exchange.
- Daily Limit: It is the maximum permissible price range for any silver futures contract in a trading session. For example, it can be 10% below or above the prior settlement.
- First Notice Date: This refers to the first day a short or long deliverable contract holder can possibly be forced to take delivery or make delivery of the underlying asset. It varies across exchanges.
- Settlement Period: Since these contracts have an expiration date, they come with a settlement period. The CME Group defines the settlement period for these contracts as 13:24:00 – 13:25:00 ET in the case of active months, while 13:10:00 – 13:25:00 ET in the case of calendar spreads.
- Settlement: This denotes whether the settlement needs to take place through liquidation or physical delivery.
- Expiry Date: It is the date on which the contract will expire.
How To Trade?
One can take a look at the pointers below to carry out the trading of these derivatives effectively.
- First, one must select a brokerage firm that is reliable and open a trading account. For this step, it is essential to check brokers’ track records, reviews regarding customer service, and the trading fees charged by them.
- Individuals need to activate the account by providing the necessary documents and making a deposit if required.
- Next, traders must conduct thorough research and analysis and be well-formed regarding the latest market trends and silver futures news. Additionally, they must assess their risk appetite and formulate trading strategies that can provide desirable results.
- Next, the trader needs to select a silver futures contract to enter a position. In this step, they must check the specifications of the contract before making a decision according to their requirements. Finally, they have to place the trade.
When trading silver futures, experts recommend using stop-loss and take-profit orders to minimize the losses and secure the gains, respectively. Also, one must remember to try and conduct both fundamental and technical analysis to develop effective strategies that can generate significant financial gains.
Examples
Let us look at a few silver futures examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose Trevor was an experienced commodities trader. He took account of the rising global uncertainties and political instability and realized that more and more people were buying safe-haven assets, such as gold and silver. Spotting this opportunity to make gains, Trevor purchased silver futures, taking a long position.
The contract size was 5,000 troy ounces, and the price at the time of purchase was $20 per troy ounce. He had to pay a certain percentage of the overall amount to fulfill the margin requirement. On the date of expiration, when Trevor closed his position to complete the cash settlement, the price had risen to $30 because of the growing demand. Thus, he could make substantial gains by trading this type of derivative contract.
Example #2
On September 24, 2024, silver prices on the Multi Commodity Exchange or MCX jumped to Rs. 89,617 per kg, representing an increase of Rs. 386 in the silver futures trade for December delivery.
According to analysts, the surge in the precious metal prices resulted primarily because market participants built up fresh positions on a domestic trend that was positive. In New York, silver traded at $31.20 per ounce, globally, the white metal traded 0.37% higher.
Benefits
Let us look at some key advantages of these derivatives contracts.
- Hedge against Risk: Individuals can use these derivatives to hedge against any unfavorable changes taking place in the market.
- Price Transparency: Traders can make informed decisions on the basis of the market patterns and price fluctuations because the pricing information that futures markets provide is crystal clear. This transparency plays a vital role in ensuring equitable and efficient trading.
- Liquidity: The market where the trading of such contracts takes place is extremely liquid. In other words, there are a large number of sellers and buyers in the market. This allows one to enter or exit trades easily just by paying a minimal amount.
- Diversification: Individuals can diversify their investment portfolio by getting exposure to silver futures contracts. Diversification, in turn, reduces portfolio risk and improves the overall performance of the portfolio.
Risks
Some risks associated with investments in such financial contracts are as follows:
- High Financial Risk: Trading silver futures involves a very high degree of financial risk because of the dynamic market environment and volatility associated with asset prices. If a trader or investor cannot predict the price changes with accuracy, they might suffer substantial losses.
- Margin Requirements: Trading these derivatives usually requires traders to make a deposit of a large sum as a margin. This amount acts as collateral for the position entered by them. If the price moves unfavorably, traders may have to deposit extra funds for the purpose of maintaining the position. This, in turn, results in higher capital requirements.
- Susceptible to Manipulation: Large institutions or some high net-worth traders can manipulate futures markets. As a result, individuals may end up suffering significant losses.
