The usane and sight letters of credit are often mistaken for being the same. However, these are two different kinds of LCs due to the following reasons:
Table of Contents
Sight Letter Of Credit Meaning
A sight letter of credit (LC) refers to a financial instrument or document that serves as the buyer's assurance of immediate payment for the goods or services to the seller as soon as the latter presents the LC at sight at their bank with all the other relevant documents.
Such an LC is issued on behalf of the buyer by their bank. Sight LCs offer greater security to the seller in export transactions. Also, the seller will have sufficient working capital to fund its regular business operations. Moreover, as the buyers have a negligible credit period, they can negotiate and bargain to get a better discount from the seller.
Key Takeaways
- A sight letter of credit is a financial instrument issued by a buyer's bank to initiate the payment for importing the products right after the exporter submits the LC with all the related documents at their bank.
- A sight letter of credit is a financial instrument issued by a buyer's bank to initiate the payment for importing the products right after the exporter submits the LC with all the related documents at their bank.
- The other is irrevocable sight LCs, which cannot be changed or terminated once issued.
- It guarantees quick payment to the exporter even prior to the buyer's receipt of goods.
Sight Letter Of Credit Explained
A sight letter of credit is a type of negotiable payment tool that the importers use to make payment to the exporters immediately when they submit the LC with the bank together with the other shipment, ancillary, and other documents. It is one of the quickest and most secure ways of LC payments, facilitating international trade worldwide. It is a payment mode that ensures the exporter receives the sales amount even before the consignment reaches the importer. The issuing and negotiating or advising banks play a critical role in the process. At the same time, they ensure that their parties, the buyer and the seller, fulfill all the relevant terms and conditions mentioned in the letter of credit.
However, such payments are quick; it may take up to 5 business days for the review of the documents and two more business days for the money to reach the seller. There are majorly following two types of sight LCs:
- Revocable Sight Letter Of Credit: Such an LC can be terminated or altered at any point in time by the issuing bank without informing the seller or exporter beforehand.
- Irrevocable at Sight Letter Of Credit: Such LCs are more reliable since they don't allow the issuing bank or buyer to modify or terminate the LC after issuance.
A draft at-sight letter of credit shields the interest of both the buyer and the seller since it initiates the payment only when the exporter fulfills all the terms of the contract.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Process Steps
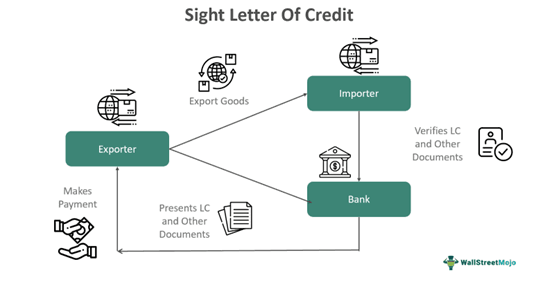
The sight letter of credit is a process that involves four parties, the importer, exporter, issuing bank, and advising bank, and the following critical steps:
- A buyer takes the quotation for the goods or services to be imported from the seller.
- Then, the buyer approaches their bank, where they have the LC facility (issuing bank) to prepare and issue a sight LC.
- The issuing bank then verifies the buyer's creditworthiness; if everything is good, then the bank issues the sight LC and provides it to the advising bank (i.e., the seller's bank) in the exporter's nation.
- The advising bank then informs the seller and sends the sight LC to them for cross-verifying.
- The exporter goes through the document and verifies if all the terms and conditions in the LC are correctly stated.
- On finding that everything is correct, the exporter ships the products to the buyer/importer and provides the shipping documents, like the dock receipt, to the advising bank.
- The advising bank then works out all the relevant documents and shares them with the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank then informs the buyer that the relevant shipping documents have been received. All these documents are required for the buyer to deliver the goods.
- The importer then cross-verifies the documents and, upon being satisfied, deposits the amount with the issuing bank to make the payment.
- The issuing bank then sends the amount to the advising bank, which further pays the seller, even before the consignment is delivered to the buyer.
Examples
Sight LCs are common in import-export transactions between buyers and sellers when they are located in different countries. Some of the relevant examples include:
Example #1
Suppose Mrs. Nancy, a New York-based importer, takes the quotation of goods worth $7500 from Mr. Andie, an exporter from Melbourne; however, Mr. Andie desired the payment through a sight LC. Hence, Mrs. Nancy initiated the process by asking her bank, XYZ Bank Ltd., to issue a sight LC in favor of Mr. Andie.
The issuing bank first verified the creditworthiness of Mrs. Nancy and then issued and sent the sight LC to Mr. Andie's bank, ABC Bank Ltd. The advising bank then sends the LC at sight to Mr. Andie for verification and approval. Mr. Andie verifies the document and ships the consignment to Mrs. Nancy in New York. Then, he prepares all shipment documents and submits them with sight LC at ABC Bank Ltd. The bank then processes these documents and forwards them to XYZ Bank Ltd.
The issuing bank further informed Mrs. Nancy of the receipts for the required documents. Mrs. Nancy verifies the documents and deposits $7500 at XYZ Bank Ltd. The bank then processes the payment to ABC Bank Ltd. Who further pays Mr. Andie. Both banks, XYZ Bank Ltd. and ABC Bank Ltd., charged 0.5% as their fees for providing the sight LC services from their clients, I.e., Mrs. Nancy and Mr. Andie, respectively. However, Mrs. Nancy has yet to receive the delivery of the imported goods.
Example #2 - 45 Days At Sight Letter Of Credit
Suppose, in the above example, Mr. Andie agreed to accept payment worth $7500 through a 45-day sight LC from Mrs. Nancy on the sale of goods. Then, if Mr. Andie presents the LC with other documents on April 15, 2024, at ABC Bank Ltd., then Mr. Nancy would be liable to pay by May 30, 2024.
Example #3
According to these reports published on Feb 4, 2021, the letter of credit confirmation market size might reach $4.99 billion by 2027. Further downwards, the sight letter of credit segment might experience the highest growth as the degree of global activities pertaining to international trade has witnessed a sharp ascend. The growth in letter of credit market size, especially that of sight L/Cs, can also be attributed to technological advancements and improved business efficiency due to progress in digitization.
Advantages And Disadvantages
A sight LC is often considered to be more beneficial for sellers or exporters, and it is believed to have various drawbacks for buyers. Some of the prominent pros and cons of this type of LC are discussed below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The seller can expect quick payment from the buyer as soon as they export the goods or services and present the sight LC with other required documents at the bank. | A sight letter of credit deprives the buyers of availing credit period in import of goods or services, leading to an immediate payment burden on them. |
| It reduces the risk of payment default by the buyer in international trade. | The payment is usually made before the delivery of goods or services, resulting in the potential risk of non-fulfillment of obligations, fraud, receiving wrong goods, or quality issues for the buyer. |
| The seller can effectively manage their working capital as they have sufficient cash for their operations due to these cash-like transactions. | The seller may have to offer an additional discount or highly favorable terms on goods or services to make the buyer pay through a sight LC. |
| Also, such LCs provide liquidity to the seller; therefore, they don't need to rely upon working capital loans or overdraft facilities for their operations, which reduces their interest expenses. | There can be potential legal risks related to the regulations of international trade in different countries. |
| The banks charge a minimal fee on sight LCs, thus making it a favorable payment instrument in cross-border trade. | |
| The buyers also benefit from the sight letter of credit. As they don't get a favorable credit period, they can negotiate with the seller on price and other terms to prevent quick payment for imported goods or services. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Difference Between Sight And Usance Letter Of Credit
| Basis | Sight Letter Of Credit | Usane Letter Of Credit |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It is a type of LC that allows the exporter to receive sales proceeds from the buyer on credit sales of goods or services immediately after submitting the sight LC to its bank. | It is a kind of LC that provides an extended credit period to the buyer, who pays the seller in a specified time, usually after the delivery of goods. |
| 2. Payment Becomes Due | On submission of the sight LC by the seller at the advising bank with all other relevant documents, mainly before the goods reach the importer | After some days of presenting the time LC at the bank with the necessary document, I.e., post 15 to 360 days of such submission, usually after the importer receives the delivery of goods. |
| 3. Payment Condition | Verification of submitted LC and documents by the seller | After a specific tenure or fulfillment of credit terms |
| 4. Risk Involved | There is less risk of non-payment, unethical negotiation, or partial payment to the seller later. | Although it involves a higher risk of non-payment, the same can be offset by the strong creditworthiness of the buyers and the sellers' terms with them. |
| 5. Flexibility | It doesn't provide much payment flexibility or credit period to the buyer | Provides greater flexibility and a specific credit period to the buyer for the payment of the due amount |
| 6. Cash Flow Impact | It provides ample working capital availability to the supplier through quick credit sales conversion into cash. | It interrupts the cash flow for the supplier by blocking their working capital in credit sales. |
| 7. Cost | The banks charge lower fees on such LCs. | It involves higher costs or charges compared to at-sight LC. |

