Table Of Contents
What Is A Sight Draft?
A Sight Draft refers to a bill of exchange in international trade, where the purchaser is obligated to pay the seller immediately upon the presentation or sight of the draft. It ensures the buyer pays before taking possession, securing the goods in international trade.
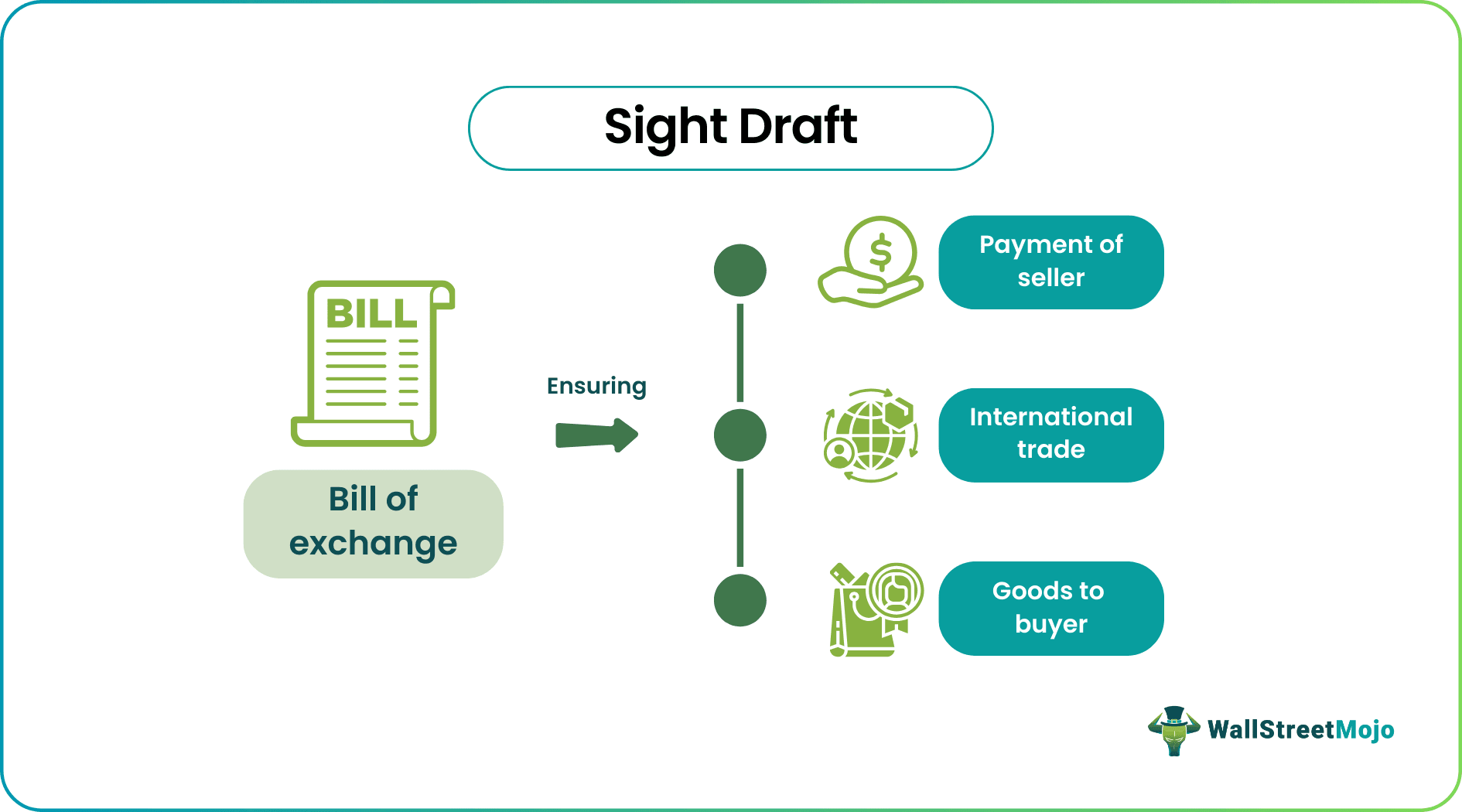
Typically, the seller creates this instrument and includes it with other shipping documents. It is then presented to the purchaser's bank. Once the buyer pays the bank, the shipping documents are released, allowing the buyer to take possession of the goods. Letters of credit and sight drafts are often utilized in tandem for secure and efficient international trade transactions.
Key Takeaways
- A sight draft definition states it as a bill of exchange that requires the buyer to pay the seller right away after receiving the goods in international trade.
- It guarantees that buyer ownership does not occur prior to seller payment and facilitates the safe transfer of products in international trade.
- It protects buyers and sellers alike, but it needs to provide the buyer with more flexibility.
- A time draft postpones payment until a predetermined date in the future, but a sight draft demands payment right once upon sight.
Sight Draft Explained
A sight draft is defined as a negotiable instrument that obliges the buyer to pay the seller upon the receipt of goods, with the presentation of the draft serving as a means to claim ownership of the goods from the seller. International traders commonly utilize this instrument for various payment transactions in import-export agreements. Following the shipment of the product, the seller prepares this instrument for presentation to the bank and subsequently forwards it to the buyer's bank after receiving confirmation.
Upon the goods reaching the buyer's destination, the buyer's bank presents this instrument to the buyer for payment. Once the buyer's bank receives the payment, it releases the goods to the buyer. Subsequently, the payment is forwarded to the seller's bank for reimbursement. Importantly, along with letters of credit or bills of lading, this instrument is typically presented together, assuring payment to the exporter.
Sight drafts offer security and prompt payments to both the seller and the buyer, thereby reducing credit risk. To prevent delays and streamline the process for both the exporter and the recipient, the exporter meticulously checks paperwork to ensure alignment with customer expectations and order agreements. This diligence fosters trust between the buyer and seller and results in a faster transaction. These are commonly employed in documentary collections for all international trade transactions.
This instrument has become a convenient choice for businesses engaged in international trade, ensuring the accurate delivery of goods to the importer before any payment is made. Additionally, the sight draft can facilitate an auto loan and serve as a payment check in certain countries. Consequently, it has contributed to increased global financial transactions, fostering global growth and revenue generation for companies involved in international trade.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Suppose Captain Amelia Silver, the famed explorer, obtains a sight draft template in the bustling city of Arcadia from Mr. Orion Blackwood, a mysterious businessman. The template details a transaction involving a trunk filled with exotic spices from the fictional country of Marakanda, traded for the legendary Sunstone of Eldoria. The delivery of the sight draft is witnessed by the supposed Dragon Empire Ambassador Li Wei, a renowned diplomat.
Acting as the interim issuing party, Silver Star Enterprises, a reputed trade corporation, embellishes the template with elaborate seals and signatures, symbolizing peaceful cooperation and fostering trade and cross-cultural interaction. As Captain Silver embarks on a new journey, the template serves as a representation of trust and prosperity, vividly illustrating the interconnectedness of the globe.
Example #2
Sight draft, or demand draft in India, has come to the fore. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) announced that it would no longer accept a demand draft for fees associated with its Informal Guidance Scheme. It added that the payments for requests for informal counsel must now be submitted directly to Sebi's bank account, using NEFT, RTGS, IMPS, or the Sebi payment channel, for a maximum of ₹25,000.
This modification is in line with Sebi's determination to remove demand drafts as a method of payment for requesting regulatory compliance advice. Under the amended Informal Guidance Scheme, the emphasis is now on direct credit mechanisms for meeting fee commitments.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Sight draft has several benefits but also has many demerits. Hence, it is necessary to know the advantages and disadvantages using the table below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It provides security for both seller and buyer. | Need for more adaptability for specific purchasers. |
| It ensures prompt payment upon submitting the draft. | Potential loss if the draft disappears or is stolen. |
| It reduces credit risk for both parties. | Demands a high degree of confidence between vendor and buyer. |
| It empowers the vendor with increased authority. | It is only appropriate for some kind of transaction. |
| It is an easy-to-use method for cross-border transactions. | It has no bank guarantee to support the buyer's commitment to pay. |
| It is a widely recognized payment option for international trade. | The buyer's capacity or desire to pay might change. |
| It shields the exporter from the risk of importer defaulting. | Risk of a shift in the importing nation's policy. |
Sight Draft vs Time Draft
Both are an integral part of international trade. Let us understand the differences from the table shown below.
| Basis | Sight Draft | Time Draft |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Requirement | It mandates immediate payment from the buyer upon sight. | Payment is set for a future specified date. |
| Timing of Payment | Payment on presentation of documents or sight of documents. | The date of payment is set in the future. |
| Control Over Payment Timing | Payment timeliness is not under the buyer's control. | The buyer takes charge of the payment date. |
| Ownership During Transaction | Ownership remains with the seller until payment. | The buyer may receive prepayment for products. |
| Risk Level | Reduced risk because payment is made right away. | There is an increased risk when payments are delayed. |
