Table Of Contents
What Is The Shrinkage Formula?
The shrinkage comes into play when there is a substantial difference in the number of items mentioned in the book of accounts than as present physical. Considering the case of inventory valuation, shrinkage is defined as the difference between the value of inventory mentioned in the book of accounts and the value of inventory that exists physically.
The inventory shrinkage formula is represented as below:
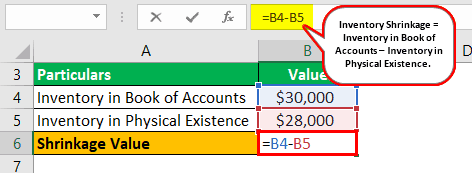
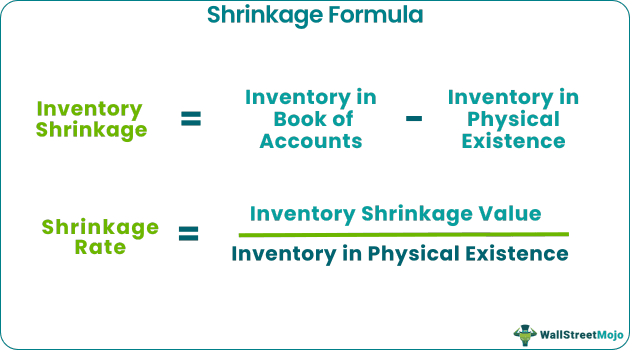
Inventory Shrinkage formula = Inventory in Book of Accounts – Inventory in Physical Existence.
- The inventory in the book of accounts formula is represented as follows:
Inventory in Book of Accounts = Beginning Value of Inventory +Purchase of Raw Materials – Sales – Adjustments.
- Similarly, from the above relationship, it is easy to derive the shrinkage rates observed in the inventory levels. The shrinkage rate formula is represented as below:
Shrinkage Rate = Inventory Shrinkage Value / Inventory in Physical Existence
Key Takeaways
- Shrinkage formula occurs when there is a significant discrepancy between the number of objects listed in the book of accounts and those there physically.
- Inventory shrinkage formula is represented = Inventory in Book of Accounts- Inventory in Physical Existence
- Inventory loss is a significant problem for manufacturing and retail companies. Business or inventory value loss may be the outcome of inventory shrinking.
- The company should closely scrutinize the management of the inventory daily. Stock shrinkage can arise due to errors the accountants make while stock valuation.
- If there is a discrepancy or shrinkage of any item in the book of accounts, it is usually considered an act of fraud, theft, or an accounting error.
- Inventory shrinkage is very common in retail and manufacturing businesses. Inventory shrinkage can result in business or inventory value loss. The business should be very critical in monitoring how the inventory is managed daily.
Explanation of Shrinkage Formula
The formula for shrinkage value and shrinkage rate can be calculated by using the following steps:
Firstly, Determine the value of beginning levels of the inventory.
Next, determine the costs of adjustments, if any, on the inventory levels.
Next, Determine the purchases made by the business for the financial year.
Next, Record the sales made by the business for the financial year.
Next, Add the beginning value of inventory and the purchases as recorded by the business.
Next, deduct the resulting value in step 5 from the sales achieved by the business and corresponding adjustments in inventory levels to arrive at the book value of inventory.
Next, deduct the actual value of the inventory from the book value of the inventory to arrive at the shrinkage value.
- Next, divide the shrinkage value determined in step 7 by the actual value of inventory to get the shrinkage rate.
Examples of Shrinkage Formula (with Excel Template)
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples of shrinkage formula to understand it better.
Shrinkage Formula Example #1
Let us take the example of a manufacturing business that had reported $30,000 as the final inventory value as per the book of accounts. However, the accountant observed that the business has $28,000 worth of finished products. Help the top management of the business determine the overall shrinkage in the inventory.
Solution:
Use the given data for the calculation of shrinkage value.

Calculation of shrinkage value can be done as follows:

Determine the value of shrinkage as displayed below:
Shrinkage Value = $30,000 - $28,000
Shrinkage Value will be -

Shrinkage Value = $2,000
Therefore, the manufacturing business has an inventory loss of $2,000 due to the shrinkage reported between the book of account and actual value.
Shrinkage Formula Example #2
Let us take the example of a manufacturing business that reported $50,000 as the final inventory value per the book of accounts. However, the accountant observed that the business has $37,000 worth of finished products. Help the top management determine the overall shrinkage and the shrinkage rate in the inventory.
Solution:
Use the given data for the calculation of shrinkage value.

Calculation of shrinkage value can be done as follows:

Determine the value of shrinkage as displayed below:
Shrinkage Value = $50,000 - $37,000
Shrinkage Value will be -

Shrinkage Value = $13,000
Calculation of shrinkage rate can be done as follows:

Shrinkage Rate = $13,000 / $37,000
Shrinkage Rate will be -

Shrinkage Rate = 35.14%
Therefore, the manufacturing business has an inventory loss of $13,000 due to the shrinkage reported between the book of account and actual value. It further accounted for a shrinkage rate of 35.14%, which is very high. The management, therefore, has to investigate whether the shrinkage is due to theft or accounting errors.
Shrinkage Formula Example #3
Let us take the example of a manufacturing business that had reported $50,000 as the beginning inventory value as per the book of accounts. The business purchased $20,000 through the financial year and achieved sales of $30,000 for the financial year. It additionally made adjustments in inventory levels by $2,000.
However, the accountant observed that the business has $37,000 worth of finished products. Therefore, help the top management determine the overall shrinkage and the shrinkage rate in the inventory.
Solution:
Use the given data for the calculation of shrinkage value.

Calculation of Inventory on Book can be done as follows:

Inventory in the book of Accounts = $50,000 + $20,000 - $30,000 - $2,000
Inventory in the book of Accounts will be -

Inventory in Book of Accounts = $38,000
Calculation of shrinkage value can be done as follows:

Shrinkage Value = $38,000 - $37,000
Shrinkage Value will be -

Shrinkage Value = $1,000
Calculation of shrinkage rate can be done as follows:

Shrinkage Rate = $1,000 / $37,000
Shrinkage Rate will be -

Shrinkage Rate = 2.70%
Therefore, the manufacturing business has an inventory loss of $1,000 due to the shrinkage reported between the book of account and actual value. However, the shrinkage rate is comparatively low at 2.70%, and hence this shrinkage may be due to accounting errors while reporting the values in the book of accounts.
Relevance and Uses
It is critical for the accountants and the audit experts to monitor the physical inventory levels. Further, it has to be compared with the inventory levels, as mentioned in the book of accounts. Once the value is determined, the shrinkage arising out of the comparison should be noted and reported to the top management.
Determining the shrinkage levels helps in better control over the inventory. For example, an inventory shrinkage may result from direct theft, which may have been done by either employees, vendors, or customers.
Inventory shrinkage may also arise due to errors made by the accountants while performing inventory valuation. Hence, it could be inferred that shrinkage determination indirectly helps control how it is managed on a day-to-day basis.