Table Of Contents
What Is Short Sale Vs Foreclosure?
The major difference between the Short Sale and Foreclosure is that short sale is a situation in which the property is sold at a price that is lower than the amount of the mortgage. In case of stocks, it is the process of selling borrowed shared at a higher price and buying them back a lower price, thus booking profit.
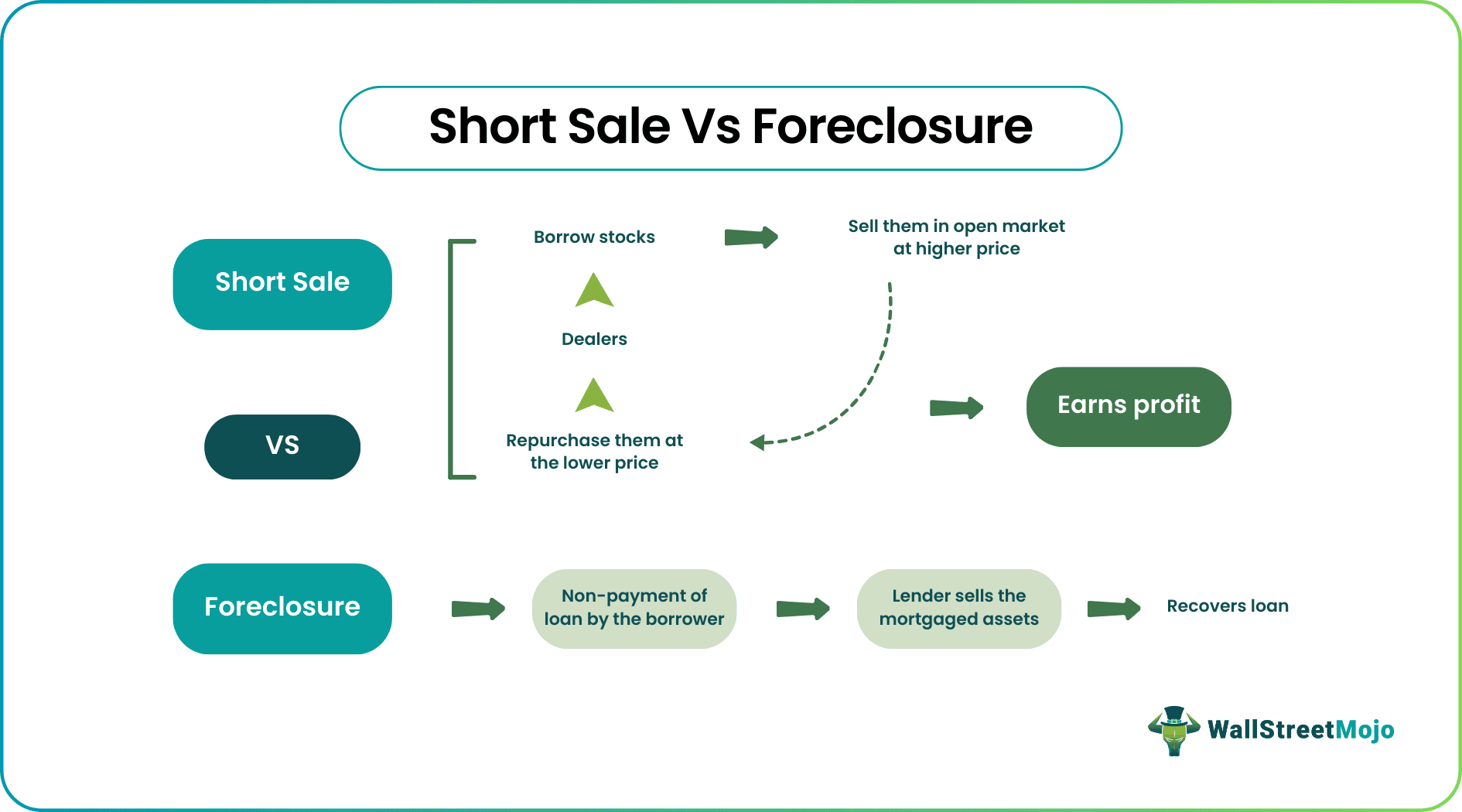
Whereas foreclosure is a legal process in which the borrower cannot repay the loan, and the lender has the right to sell the mortgaged asset to recover it. Thus it is a process of the debtor forfeiting the rights on the property that is mortgaged due to the failure to pay the outstanding debt taken; the property goes for foreclosure.
Key Takeaways
- When a debtor cannot pay their obligation, a short sale is when they sell real estate mortgaged to those who own the liens against the property.
- Foreclosure is a legal procedure in which a lender seizes ownership of a mortgaged property, evicts the borrower or homeowner, and then sells the mortgaged property once the borrower or homeowner cannot make full principal payments.
- A foreclosure often happens when the borrower or homeowner falls behind on their mortgage loan payments used to buy the mortgaged property.
- A short sale has some advantages over a foreclosure, one of which is that, if handled properly, it might not harm the owner's credit score as much.
Short Sale Vs Foreclosure Explained
The methods of short sale vs foreclosure for buyer can be explained elaborately as given below. A short mortgage sale can be defined as the sale of a property by the borrower who has become financially distressed for less than the outstanding balance due to the mortgage, where the lender will use the proceeds from the sale of the asset to repay the same. The lender will then accept the less than full repayment of the mortgage loan (and the borrower will be released from the mortgage obligation), the reason for the same being, to avoid what would amount to larger losses for the creditor or the lender, had it been to foreclose on that mortgage loan.
Foreclosure, on the other hand, is the legal process in which a lender will take control of the mortgaged property, also evicts the borrower or, say, the homeowner, and will sell the mortgaged property after the borrower or the homeowner is not able to make entire principal and interest on those principal payments on their mortgage loan, that was stipulated in the mortgage deed or the contract.
A foreclosure usually occurs when the borrower or the homeowner is behind the payments schedule on the mortgage loan used to purchase the mortgaged property. Foreclosure is something that no borrower or homeowner wants to experience the same. In most cases, the lack of payments on a housing loan is usually due to an unexpected dip in their finances or a change in the borrower or the owner’s circumstances. Thus, as given above, a strategic foreclosure vs short sale process has many details to understand.
Infographics
Let’s see the top differences between short sale vs foreclosure for buyer.

The above list given a detailed description about strategic foreclosure vs short sale.
Example
The following example will clearly show the short sale and foreclosure difference.
Let us look at an example where Max bought a property worth $2 million. He took a loan for the purchase which amounts to $1.5 million after keeping this property as mortgage. However, a few year, he is unable to pay the loan installments. The bank initiate a foreclosure, in which the property is sold and the bank recovers the pending loan amount.
Let us take the same example to understand short sale and foreclosure difference. Max is in financial distress after paying the loan for a few years. So he approaches te bank and informs them about his decision to short sale. The bank approves, and Max sells off the property at a price lower than his loan amount and pays back the loan to the bank.
Pros And Cons
Let us look at the pros and cons of both the cases.
Short Sale
Pros:
- This process needs less legal fees.
- The process initiation is at the borrower’s discretion.
- It is not reported in future loan applications.
- Owner’s credit score has less impact.
Cons:
- Lot of paperwork is required.
- It is a lengthy process.
- Lender’s approval is also required, who might counter or reject the process.
- Since it is a time consuming process, the buyer may miss the opportunity to geta better deal.
Foreclosure
Pros:
- Less paperwork is required.
- Lenders are eager to sell off the foreclosed property. So sale takes place faster.
- Buyers get property a lower price.
Cons:
- This process needs more legal fees.
- The process initiation is at the lender’s discretion.
- It has to be reported in future applications.
- Owner’s credit score is highly impacted.
Credit Impact
Both the short sale and foreclosure listings have an impact on the credit score of the borrower.
The negative impact on the borrower’s or the owner’s credit score is typically smaller in short sales than in a foreclosure. However, there are some benefits for a short sale that, if done rightly, may not do as much damage to the owner’s credit score as the foreclosure would.
Foreclosure has a higher negative effect because they reflect in the individual’s credit report continuously for seven years. However, because of this, the borrowers won’t have to wait as long to buy another house as they would have if they had gone through foreclosure.
Comparative Table
The table given below will give a comparative study of short sale and foreclosure listings.
| Basis | Short Sale | Foreclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Definition | A short sale is happening when a mortgage lender or the creditor allows the borrower or the owner to sell that mortgaged property for lesser than what’s owed on that mortgage. Property owners who attempt the step to initiate a short sale are usually those who are under financial stress, and the market value of their mortgage property must have substantially declined, relative to their borrowed amount. | A mortgage lender who is conducting a foreclosure will repossess the property that was mortgaged to collect for those unpaid debts. This will result in more liability and fees to the borrower or the owner compared to a short sale. |
| Fees and Liability | Comparatively fewer fees, penalties, and legal expenses and hence the liability than a foreclosure. | As mentioned, this process proves to be more expensive due to high fees. |
| Control | The borrower or the owner gets to stay in the mortgaged property and can retain a certain amount of control. | Foreclosures will end with the eviction of the borrower or the owner, who exercises no control over the entire process. |
| Used when | The borrower or the owner is not able to make those mortgage loan payments, owes more than the home’s current market value or say current worth, and the lender must agree. | When the owner or the borrower defaults. |
| Methods to execute | It’s done through Realtor | Auctioned at the Trustee Sale. |
| Impact on credit score | Drops almost 50 – 150 credit points. Also, it can be listed on the credit report if the lender or the creditor will report the reduction in debt to credit reporting agencies. | It impacts a lot and almost drops 200 – 400 credit points. Also, it remains on the credit report for almost seven years. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The foreclosure process is more expensive for the lender. However, in a short sale, the homeowner and the lender split the costs of selling the house quickly.
In some cases, lenders make money during the foreclosure process. Although it is not always the case, it is feasible for a lender to generate enough revenue from interest payments and a foreclosure auction to avoid suffering a loss.
Paying more than the property's current market is worthwhile; purchasing a foreclosed home is a frequent danger. This risk increases if you make an auction purchase since other bidders may "spite bid" to boost the price.
