Table Of Contents
What is a Short Sale in Real Estate?
A short sale in real estate is the sale of a property, which was held as a mortgage, at an amount less than the actual value of the property to repay the debts owed by the borrower. The property is sold to a third party, and the proceeds from the property sale are given to the lender. In such a scenario, the debt is not fully paid.
The lender can either choose to waive off the remaining amount or opt for a deficiency judgment against the borrower, which requires them to pay the lender a portion or all of the difference between the sale price of the property and the original value of the property that was held the mortgage.
Key Takeaways
- Real estate short sales occur when a property subject to a mortgage is sold for less than the property's market value to satisfy the borrower's debts.
- The borrower starts a short sale when they wish to sell the mortgaged property for less than the balance still owed on loan.
- Lenders cannot provide the short sale option if they believe they may make more money by foreclosing on the mortgage.
Short Sale in Real Estate Explained
A short sale in real estate refers to selling a mortgaged property at a price lower than the actual mortgaged value. In other words, the property's value did not rise as expected, and the borrower failed to make payments for the mortgage at the pre-decided intervals.
The remaining amount after a short sale is usually waived off looking at the borrower's financial circumstances and in some cases. In contrast, in some cases, the lender can get a deficiency judgment on the lender, which requires the borrower to make the payment for the difference in the sale price and the outstanding amount of the mortgage.
The cause of the financial distress should be new which can be deterioration of health, loss of a job, divorce, etc., which justifies the failure in making payments for the mortgage.
If the lender assumes that it can make more money by foreclosing the mortgage, the lender cannot allow the short sale option.
If the mortgage has a co-applicant, then the lender can hold the co-applicant responsible for default in the payment and may not allow a short sale.
The waived off of the remaining amount after a short sale is considered an income and can be taxable, which differs from country to country.
A deficiency judgment is a court order against a defaulted debtor or borrower on a mortgage or a secured loan which indicates that the sale of the property which was mortgaged did not cover the complete amount to pay back the mortgage.
Process
Let us understand the process of short selling in real estate through the step-by-step explanation below.
- Lender Consensus: The very first step towards selling a property that the owner is not able to afford is to convince the lender to agree with a short sell deal. The reasons must be a new financial difficulty such as a health problem or sudden unemployment. If the reasons were hidden from the lender at the time of the loan, more often than not, the lender would not be ready to support the borrower for obvious reasons.
- Professional Advice: It is important to understand the situation in terms of taxation, legality, and in absolute terms in the real estate domain. These professionals would advise the owner on the expenses, the best price to ensure potential buyers have the urge to buy, and the legal repercussions.
- Price Setting: In a short sale, it is almost certain that there would be a shortfall in the amount from the value of the property. However, it is important to account for the expenses of selling the property.
- Finding A Buyer: Having all documents relating to the property can help with the credibility of the owner and the property. Therefore, it is important to ensure all documents are in place before setting out to find potential buyers.
- Proposal To Bank: Once a buyer agrees to buy the property, the owner can gather documentation along with the offer for the property and explain the circumstances to the bank after which the bank authorities would carry out their due diligence.
Example
Let's discuss an example of the short sale in real estate for better understanding.
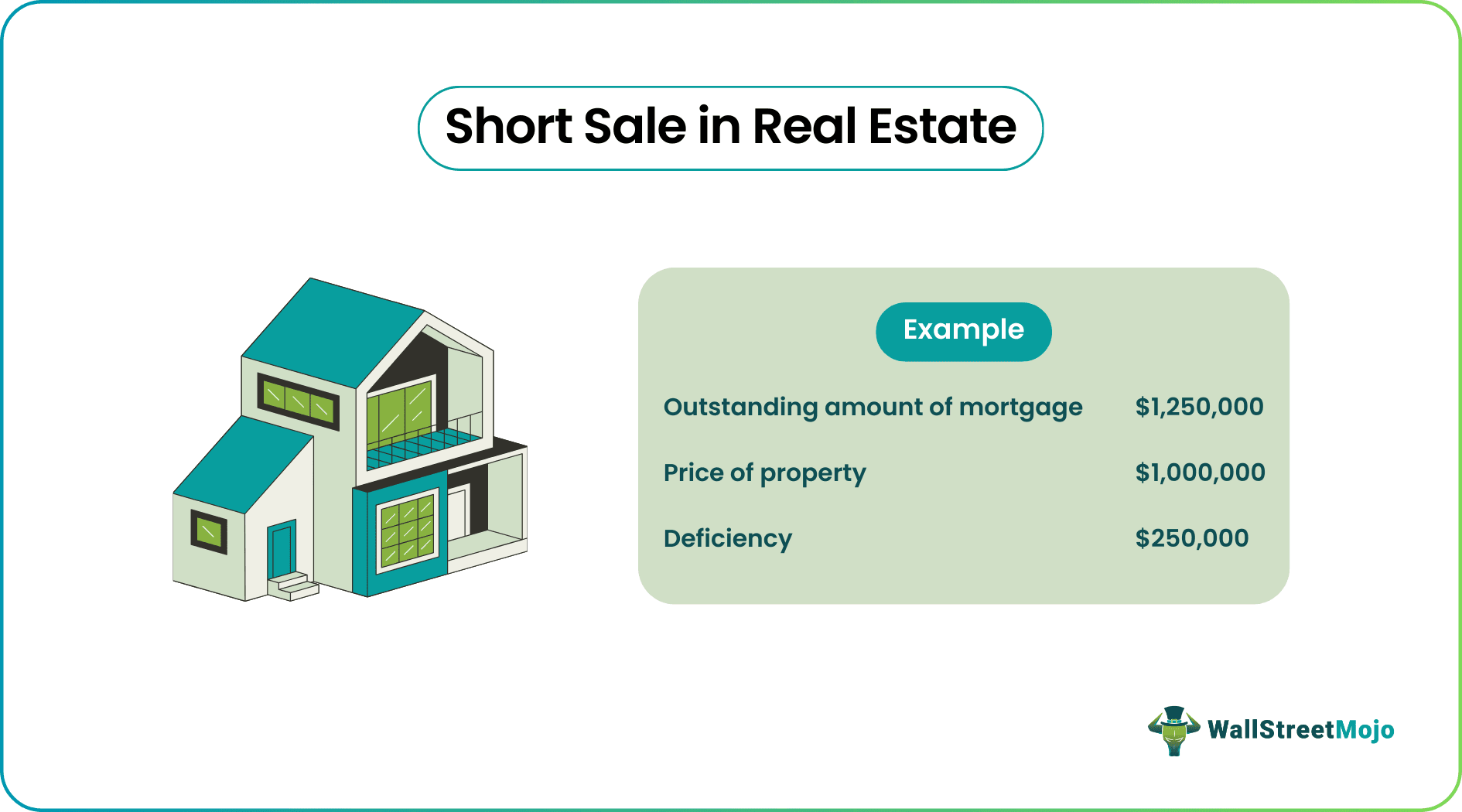
John bought a villa in a new project on the outskirts of the city and took a mortgage to pay for the property. John owned the villa on which he procured a mortgage of $1,500,000, and due to the loss of the job, he is currently selling it for $1,000,000. The outstanding on the mortgage is $1,250,000. John has already delayed making the mortgage payments and fears his property will be seized or foreclosed. He decides to sell the property and finds a customer for his villa, Joe, who is willing to buy the property at $1,000,000.
The difference between the outstanding amount and the sale price is calculated as below:
Outstanding Amount of Mortgage – Sale Price of Property
= $1,250,000 - $1,000,000
= $250,000
In this transaction, John will pay his lender (the bank) for the mortgage which will be $1,000,000, and the remaining difference of $250,000 is the deficiency.
Banks usually waive off the remaining amount considering the borrower's financial condition, although this might result in the credit score of someone like John taking a hit.
In the United States, if the borrower is waived off completely from the repayment of the mortgage after a deficiency judgment, the debt that was forgiven or waived off is considered income by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) taxable as per the income tax slab.
Disadvantages
Let us understand the disadvantages of a short sale in real estate buying.
- The property's value is undermined and has to be sold at a lower value.
- The property buyer may not always make a good deal out of the property even though the property was bought at a much cheaper rate.
- A credit score will be affected adversely even though the mortgage is waived off.
- Since the credit score will be affected, no other banks will be willing to provide a loan shortly unless the credit score for the borrower is brought back in a good state.
- A short sale in real estate refers to a property that was once sold at a higher rate in a rising market, and since the market has fallen, it will not fetch even the initial investment made to purchase the property.
- Banks sometimes lend additional mortgages to borrowers over their limit in a rising market. When the market falls, neither the borrower nor a lender makes any money out of the transaction.
- Affects the surrounding properties adversely since the value of one property in a locality can decide the value of other properties.
Importance
In a situation where the owner is unable to pay the mortgage dues on time, short sale in real estate buying comes in as a savior for them. Apart from the owner, there are other parties who benefit from the sale as well. Let us understand the importance through the discussion below.
- A financially distressed borrower has two options to close the mortgage – (a) short sale and (b) foreclosure.
- A short sale is initiated by the borrower in which they decide to sell the mortgaged property at a rate that is less than the outstanding mortgage amount.
- A foreclosure is initiated by the lender in which the bank seizes the property after the borrower fails to make payments for the mortgage for a long period. This is usually the last resort for banks when they are convinced that the borrower is in no condition to make any payments for the mortgage.
- A short sale in real estate has a negative hit on the borrower's credit score; however, it is less than a borrower whose property was seized, and the mortgage was foreclosed.
- If the mortgage has a co-applicant, then the lender can hold the co-applicant responsible for default in the payment and may not allow a short sale.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Since agents get compensated from the short sale proceeds but are not compensated if the client loses the house to the bank by going through a full foreclosure, agents strongly advise sellers to pursue a short sale.
Although it is entirely doable, negotiating a short sale might take time. In addition, unlike regular sales, short-sale negotiations require the lender's approval when the seller and the buyer negotiate solely.
Short sales are voluntary decisions the homeowner makes; the lender must approve them. However, foreclosures are unavoidable for the homeowner since the lender files a lawsuit to seize and sell the property.
