Table Of Contents
Separate Legal Entity Meaning
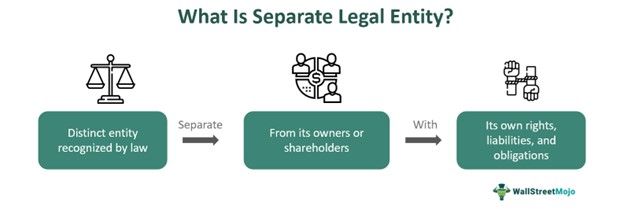
A Separate Legal Entity in company law is a legal concept acknowledging a company as an independent entity, distinct from its owners, shareholders, and directors. It means that a company is considered as a person in the eyes of the law and has legal rights and obligations just like an individual.
The purpose of a separate legal entity of a company is to provide legal protection to the owners, shareholders, and directors of a company by separating the business's liabilities from its assets. This protection ensures that if the company incurs debts or liabilities, the owners will not be personally responsible for paying them.
Key Takeaways
- Separate legal entity meaning refers to an organization, such as a corporation, that is recognized as having legal rights and responsibilities that are separate from those of its owners.
- The company has a perpetual existence, which means that it can continue to operate even if its owners or shareholders change over time.
- It can build a strong brand reputation that is separate from the reputation of its owners or shareholders, which can be valuable in attracting customers, investors, and employees.
Separate Legal Entity Explained
A separate legal entity occurs when a company is recognized as an entity distinct from its owners, shareholders, and directors. This principle signifies that the company possesses legal rights and responsibilities akin to those of an individual within the legal framework.
A company can own property, enter into contracts, sue and be sued, and carry out business activities independently of its owners. It can also incur debts and liabilities, which are separate from the personal finances of its shareholders and directors.
This concept is essential in limiting the personal liability of the company's owners and providing them with legal protection against business risks. Additionally, it allows the company to engage in business transactions and carry out business activities with legal independence, which would not have been possible without the recognition of the company as a separate legal entity.
In a partnership firm, the business is considered a separate legal entity, but the owners (partners) have joint and several liabilities. This means that each partner is personally liable for the partnership's debts and obligations. Additionally, each partner is responsible for the actions of the other partners in the course of the partnership business.
Examples
Let us look at some hypothetical and real-world examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
The About You Group has taken the step of spinning off its business unit, Scayle, into a new subsidiary, thus formalizing Scayle's status as a separate legal entity within the company's structure alongside its established online fashion store. Specializing in delivering a modern, cloud-based enterprise shop system, Scayle empowers brands and retailers with swift scalability and adaptability to evolving consumer needs.
With a current workforce of 300 based in Hamburg, Germany, Scayle's management team, under the leadership of Tobias Ring, René Dalock, Christopher Metz, and Sergio Sola, has transitioned from the former Scayle unit to assume responsibility for various operational functions. The strategic move to establish Scayle as a separate legal entity aims to grant it greater autonomy and drive further growth amidst challenging e-commerce market conditions.
Example #2
Suppose John and Mary decide to start a bakery together. They form a limited liability company (LLC) to operate the business. As a separate legal entity, the LLC can enter into contracts, hire employees, and own assets in its name.
One day, a customer at the bakery slips and falls, injuring themselves. The customer decides to sue the bakery for their injuries. The LLC is responsible for any legal liabilities arising from the incident, but John and Mary's assets are generally protected.
Assuming that the LLC has adequate insurance coverage or other assets to satisfy the judgment, the personal assets of John and Mary are not at risk of being seized to pay for any damages awarded to the customer.
In this way, the separate legal entity of the LLC provides John and Mary with a layer of legal protection for their assets while still allowing them to operate their bakery as a business entity.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of separate legal entities are as follows:
Advantages:
- It continues to exist even if one or more of its owners or shareholders dies, leaves the entity, or sells its ownership interest. This allows the entity to maintain its operations and business relationships over a long period.
- It is particularly advantageous for businesses that require significant upfront investments or ongoing capital expenditures.
- It provides tax benefits to its owners or shareholders, depending on the entity's tax classification and the tax laws of the jurisdiction in which it operates.
Disadvantages:
- It generally has higher startup and operating costs than other business structures. For example, incorporating a business or forming a limited liability company involves legal fees, filing fees, and other expenses.
- It can also be more complex to manage than other business structures. This is particularly true for larger entities with multiple owners or shareholders, which may require more formal governance structures and decision-making processes.
- Depending on the entity's tax classification and the tax laws of the jurisdiction in which it operates, it may be subject to double taxation.
