Table Of Contents
What Is A Self-Regulatory Organization?
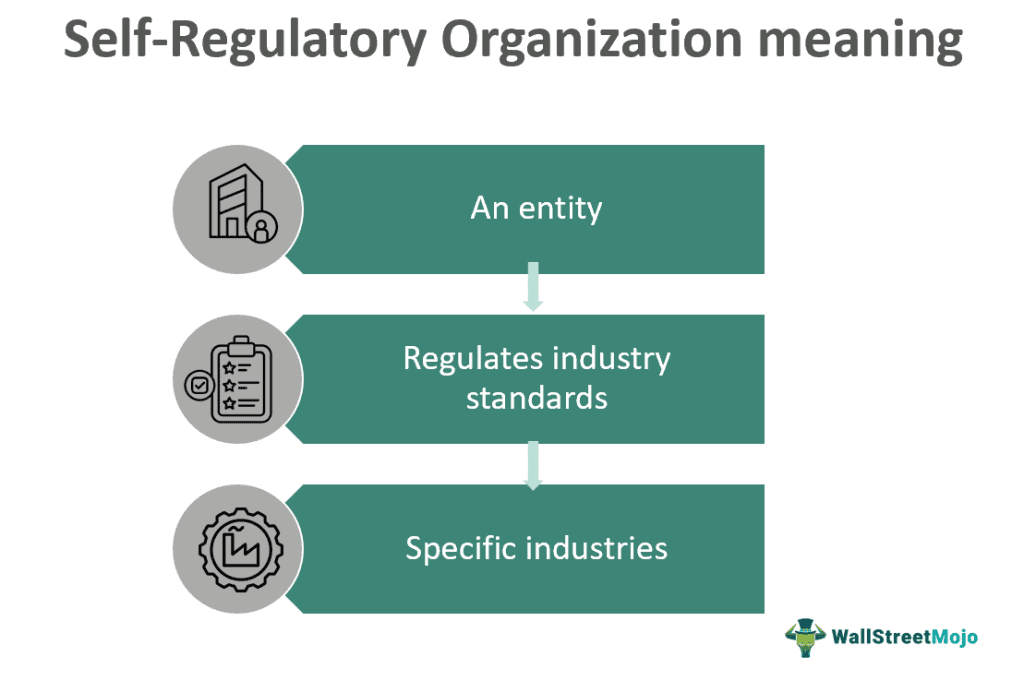
A Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO) is an entity established to regulate specific industries or professions. An SRO is responsible for developing the structure, system, guidelines, and code of conduct for operations, management, and business, creating industry standards and bringing order to the concerned profession or industry.
An SRO exists with government authority but operates as a nongovernmental organization. It serves as a higher authority for a particular industry that a person or society can trust, and it does not require any permission from the government to enforce its laws. However, any law regulated by the government will be considered primary and top priority, and the SRO regulations become supplemental.
Key Takeaways
- Self-regulatory organizations are nongovernmental entities that regulate certain industries and professions.
- In the US, the SEC ensures the establishment and mandates of the law under which FINRA operates as a self-regulatory entity for the rights and protection of brokers and firms.
- Industries can work together to form their SROs to ensure transparency, protect their rights and interests, maintain safety, and fulfill the supervision gap.
- The government can intervene and make broader policies for an SRO, including establishing new federal laws and guidelines.
Self-Regulatory Organization Explained
A self-regulatory organization manages, monitors, and regulates specific sectors, professions, or industries separately. It is generally created to fulfill the lack of order and structured framework in particular industries that require supervision and a code of conduct in their operations and management. These nongovernmental organizations have authoritative powers over their concerted action areas.
The self-regulatory organizations govern a particular industry, promoting its business and operations, improving at every level and bringing order by helping people and other associated members. Certain federal laws follow which any profession or sector can form an SRO form themselves to prevent fraud, manipulation and malicious practices and protect themselves from internal and external jeopardy.
Not every nation has an SRO. Currently, the Canadian Investment Regulatory Organization (CIRO) is the only self-regulatory organization in Canada, which follows up after the Mutual Fund Dealers Association of Canada (MFDA) and the Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada (IIROC). The key aspect is that no SRO is above federal law, and the SRO guidelines become supplemental in front of any old or new federal policies.
It has the power and responsibility to educate professionals about the right practices and promote the industry internally. Apart from finance SROs, there are many other US SROs, such as the Institute of Nuclear Power Operations (INPO), Fixed Income Clearing Corporation (FICC), Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) and the American Bar Association (ABA).
Characteristics
The characteristics of a self-regulatory organization are -
- An SRO operates as a legislative body to create rules, policies and guidelines and enforce them in the concerned industry or profession.
- A self-regulatory organization remains transparent in its operations and framework with strong governance over its members and other representatives.
- It constantly monitors and does detailed supervision of every organization member, ensuring they all comply with the rules and regulations and follow industry standards.
- In case of conflict of interest and managerial disputes, an SRO comes forward to resolve matters and take the distinct process into its own hands to ensure each party receives justice.
- Another important characteristic of an SRO is to keep and maintain a regulatory database of the required persons and members of the profession. It shall include every minute detail along with the record of complaints and disciplinary actions.
- It helps protect the rights and interests of people, especially funds and monetary involvement of people belonging to the SROs underlying industry.
- It is also a characteristic feature of an SRO to work hand in hand with the government and introduce well-structured enforcement programs to seek any violations and make proper investigations of them.
- An SRO resolves disruption and process fair treatment of the accused.
Examples
Here are two separate SRO examples:
Example #1
In a fictitious town, all the doctors, healthcare workers, and associations unite to charter a self-regulatory organization that will devise the healthcare industry standards, regulate policies, and make laws and protocols that every hospital shall follow. It does not matter if a doctor is practicing in their clinic or if there is a big hospital; every single healthcare unit or personnel comes under this SRO.
Its members fund the SRO, and it operates like a nongovernmental organization. It protects the benefits, interests and rights of patients, hospital staff, and other healthcare employees and workers. At the same time, anytime a federal law is initiated regarding the industry, it supersedes the laws of the SRO, and the government has extensive rights to dictate broader policies. It is a simple self-regulatory organization example, but it takes time and processing in the real world.
Example #2
Adelle Nazarian and Alex Allaire, the CEOs of the American Blockchain PAC and the American Blockchain Initiative, respectively, have recently proposed to create a self-regulatory organization for the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector. The step runs parallel to the US President Joe Biden's executive order for the digital asset development.
This SRO will offer public protection and resolve issues regarding improperly funded regulators. At the same time, it will safeguard the consumers, not playing with the innovation factor and compliance costs. The self-regulation model in the cryptocurrency sector will be a smart move from both practical and reputational perspectives.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages of self-regulatory organization are -
- It operates individually apart and parallel to the government regulations.
- SRO builds and establishes industry standards and guidelines in certain professions or industries.
- Protects the rights and interests of members and representatives of the concerned industry or profession.
- An SRO advises people and related members on correctly promoting the business and operations.
- It makes the industry members or professionals aware of the potential risks and helps them understand the securities structure.
The disadvantages of the self-regulatory organization are -
- As they are nongovernmental organizations, the regulations have no statutory backing.
- Sometimes, between the guidelines of the government and separate protocols of the self-regulatory organization, it becomes complex and difficult to comply.
- Even with little supervision, there are times when government authorities can overpower the rules of an SRO, which often does not favor the industry members.
Self-Regulatory Organization vs Independent Regulator
The main differences between self-regulatory organizations and independent regulators are -
- Self-regulatory organizations are nongovernmental, but independent regulators are sanctioned government bodies or agencies.
- SROs represent the member's interests and rights to the government. In contrast, independent regulators exhibit government intervention and laws in the concerned professions.
- An entity can be independent and SRO when it receives government recognition and is powered and funded by members.
