Table Of Contents
What Is Self-Employment Tax?
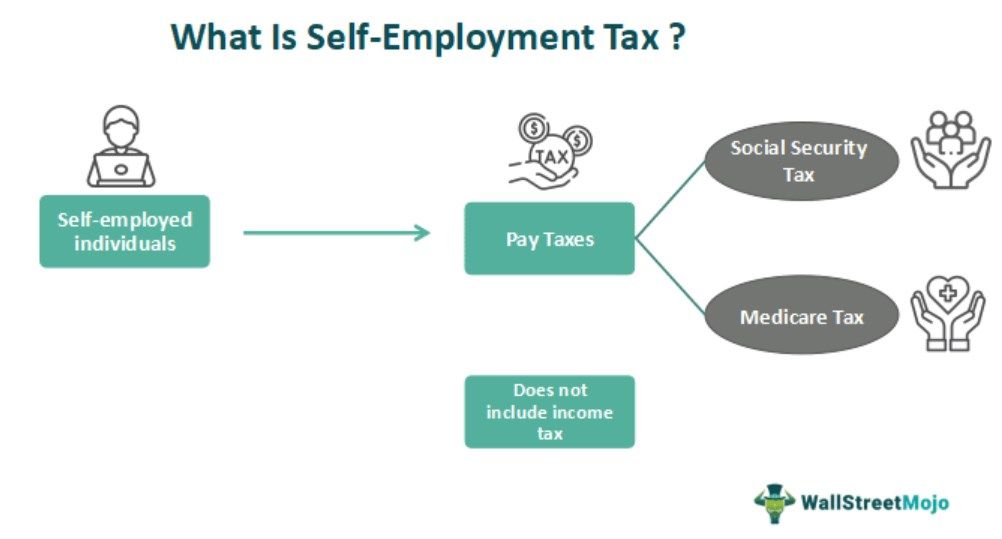
Self-Employment Tax refers to the tax payable by self-employed individuals toward Social Security and Medicare benefits. The ones to whom this taxation applies include sole proprietors, contractors and freelancers with net earnings of $400 or more for the concerned tax period.
This liability towards the federal government is reported through the file of Form 1040 Schedule SE. These taxes help self-employed individuals to fulfill their tax responsibilities and make sure to contribute in generating revenue for the economy.
Self-Employment Tax Explained
The self-employment tax includes only Social Security Tax and Medicare tax and no other taxes, including income tax. The basic tax structure is 12.4% for Social Security Tax & 2.9% for Medicare Tax, making it a total of 12.4+2.9= 15.3%
The Social Security tax also has two components – The employer pays social security tax of 6.2% & the employee pays social security tax of 6.2%. Thus, the self-employed person is required to pay for both rates. This makes the total social security tax rate 12.4%.
The breakup of the self-employment tax is available in the following table:

However, not the whole of net earnings is liable for the 15.3% self-employment tax rate. The first $ 137,700 is liable for social security tax only. Amount beyond $ 137,700 is liable for both social security tax as well as Medicare tax.
However, you are required to pay 0.90% for Additional Medicare in case the total earnings exceed $200,000 (in case of a single filer) or exceed $250,000 (in case of a joint filer).

In case additional Medicare tax is considered, the total Medicare tax becomes 2.9 + 0.9 = 3.8% in some instances. In that, the employment tax reaches 15.30+0.90= 16.20%
How to Calculate?
Let us consider the following examples to understand how to calculate self-employment tax:
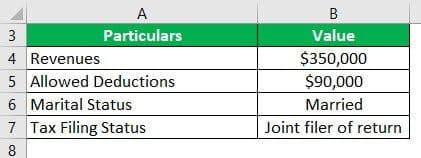
Example #1

Solution:

Example #2
The Taxpayer has provided the following details:

Solution:

Deductions
The IRS has logically framed the self-employment taxation system by allowing business-related expenses to be deducted from the earnings. The tax deductions have been specified as follows:
- Deduction for home office
- Deduction for health insurance premiums
- Meals
- Travel
- Interest expense
- Business Insurance
- Start-up costs
- Retirement Plan contributions
- Rental cost
- Education
- Advertising
- Vehicle use
How to Pay?
If one is sure to earn more than $ 400 a year, they should apply for a social security number (SSN), or taxpayer-identification number, or an employer identification number. These numbers help the federal government to identify them easily. The next step is to have the following self-employment tax forms.
- Form 1040-SR to quantify the benefits of social security programs.
- Form 1040 (Schedule SE) to report self-employed earnings.
- Form 1040 (Schedule C) to report the net income or loss
- Form 8959 to determine the liability for Additional Medicare Tax
- Form 1040-ES to pay for the estimated tax
- The payment for the taxes can be made through any of the available methods:
- The most convenient & reliable method is “IRS2Go Mobile Application.”
- Online payment through the website
- Wire transfer through a bank account
- The EFTPS (i.e. Electronic Federal Tax Payments System)
- Through cash with some additional fee
- Through check with details such as name, tax identification number & the year for which tax is being paid.
Benefits
The advantages of the self-employment taxes are as follows:

- Self-employment tax shows the sensitivity of the person towards society.
- It builds the nation with a higher quality of infrastructure.
- The government can fund the expenses of a needy person through such a collection.
- The tax rate is also the average and nominal.
- Computations are easy for a layman with no ambiguities.
- The individual is helping to build the nation.
Drawbacks
The disadvantages of this taxation system are as follows:
- Disposable income of the individual decreases.
- Risk of fraud of public money by politicians.
- The tax is a cost for the tax paper. It should have been as per the slab rate system to be more beneficial.
- Currently, the tax considers every earner on equal grounds which may be correct to assume.