Table of Contents
What Is Securities Valuation?
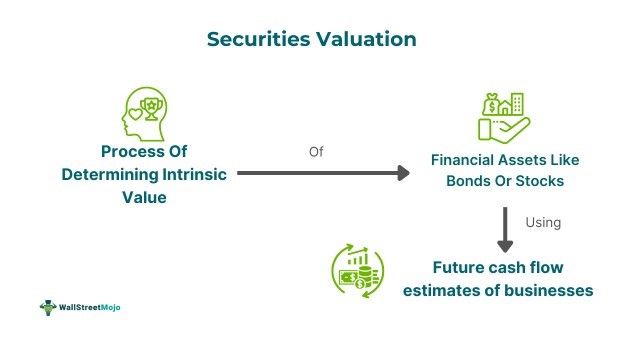
Securities Valuation refers to estimating the financial assets’ inherent value like bonds, stocks or any miscellaneous investment. It serves to evaluate the actual values of the securities based on their real worth as per different market conditions and multiple financial metrics.
It uses multiple methods to evaluate the net worth of securities having unique applications and strengths like the dividend discount model (DDM) and the discounted cash flow model (DCF). An accurate valuation of securities aids investors in identifying overvalued and undervalued assets, managing risks effectively, and making informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Securities valuation tries to estimate the intrinsic value of financial assets like bonds and stocks for evaluating their actual values based on financial metrics and market conditions.
- It has various methods like discounted cash flow analysis, comparative analysis, asset-based valuation, dividend discount model, option pricing models, and capital asset pricing model.
- Its importance is- aiding long-term investment strategies, identifying risks, ensuring credible financial reporting, assessing firms during mergers and acquisitions, providing clarity on returns, and improving portfolio management.
- Its challenges are- the company's financial performance, market trends, dividends, industry position, government policies, future growth, and company liabilities and debts.
Securities Valuation Explained
Securities valuation represents the procedure of finding the intrinsic value of financial instruments like bonds or stocks as per their future cash flows. Such valuation helps investors identify whether any security has been undervalued to overvalued in the financial markets, aiding them in making the right decisions. There are multiple methods to conduct the valuation of securities, as discussed in the next segment, mainly discounted cash flows or comparative analysis, etc. One of its types is mortgage-backed securities valuation, which consists of and is secured by numerous underlying mortgages.
Some countries like the USA have securities valuation offices related to the successor office or of the National Association of Insurance Commissioners. Its implication in making vital decision-making regarding investment, affecting investment strategies, corporate finance, along mergers and acquisitions. Any untoward mispricing could lead to major monetary losses or missed opportunities. The valuation has been utilized in assessing returns and risks of investment by financial managers, investors and analysts.
Investors also use it in risk assessment, strategic planning and portfolio management, enabling informed and profitable decision-making. It guides investor behavior, influencing market dynamics and affecting stock prices. It has an important role in retaining market efficiency because mispriced securities have either price corrected through informed valuations.
Methods
Many methods can be used for the valuation of securities, as follows:
#1 - Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis:
It calculates the present value of a security as per its estimated future cash flows for companies with regular fixed cash flows. The cash flows have to be adjusted to the current value after executing a discount rate accounting for the risk level of the investment.
#2 - Comparative Analysis:
It involves contrasting securities to equitable assets listed in the market, also termed relative valuation. It uses metrics like price-to-book value (P/B) & price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios along with other multiples for evaluating how any security compares with its peers.
#3 - Asset-Based Valuation:
It mainly centers on a company's assets instead of its market performance or earnings. It becomes crucial for company valuation to assess liquidation value or having large tangible assets.
#4 - Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
It works only for mature and stable dividend-paying companies by calculating their stock value per the current value of estimated future dividends.
#5 - Option Pricing Models:
It uses tools like the Black-Scholes model for valuing options and derivative securities. Such models take into account the expiration date, volatility and underlying price of the asset.
#6 - Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM):
It can be used for calculating security value as per expected return concerning the risk investors take while investing in such security.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An online article published on June 8, 2021, discusses the effect of a new rule of 2a-5 fair value of SEC effective since 2020. SEC has published the rule in a 200-page volume within the Investment Company Act 1940. The rule has set up detailed guidelines concerning fair calculations related to securities having no market quotations. The article highlights that the rule attributes important responsibility to pricing services and investment managers.
Moreover, the rule also needs to have rigorous oversight and transparency. Furthermore, boards should ascertain correct fair valuations, having comprehensive record keeping under the new 31a-4 rule. Additionally, pricing services have been monitored with enhanced transparency demanded by clients and deep-dive evaluation.
Example #2
Let us assume that a large firm called Stellary of Old York City issues a 10-year bond having $10000 as face value, providing a 6% annual coupon rate. An investor named Elenam from the same city decides to buy Stellary Bond. Hence, for making the final purchase, she decides to conduct a valuation of the bond by finding the bond's discounted future cash flows. For that, she determines:
Annual interest payment = $600
Principal repayment at maturity = $10000
Discount rate = 6% per the market conditions and Stellary’s credit rating.
Hence, after applying the method of discount rate, Elenam finds the exact current value of the bond, which comes out to be $10000.
Importance
It serves important roles for investors and companies, as shown below:
- Accurate valuation of securities helps in making informed decision-making regarding the selection of assets priced beneficially in contrast with their intrinsic value.
- Investors can avoid highly risky assets as proper valuation facilitates the identification of possible rewards and risks.
- Companies need to conduct correct valuation of securities because it helps in credible financial reporting and adherence to accounting standards.
- It becomes critical for assessing targeted firms and bargaining the best and fairest terms during mergers and acquisitions.
- It provides clarity on the extent of returns of investing in overpriced shares, reducing the risk of loss.
- Long-duration investment strategy derives benefits from valuation as it offers a transparent and helpful perspective on the value of a business during an extended period.
- Investors can undertake better portfolio management by using it to track the value of their investments over time.
Challenges
There can be multiple challenges to the valuation of securities, as listed below:
- The company's financial performance can affect how it can make a profit, grow its sales and stabilize its finances, affecting the valuation.
- Overall situation and trends of the market and industry affect the thinking of investors regarding the valuation of their shares.
- Dividends and profits profoundly affect how traders or investors can take the company's securities' worth for their calculation.
- The valuation of the company directly affects its position in the industry, market share and competitive advantage, thereby affecting the valuation of its securities.
- Any change in government policies, rules and laws tends to pose a challenge to the valuation of the securities.
- Investors bring in the aspect of future growth, entry not new markets and new product launches by companies, affecting the valuation of securities by investors.
- The level of liabilities and debts of a company directly impacts the valuation of its securities.

