Table Of Contents
Safe Harbour Meaning
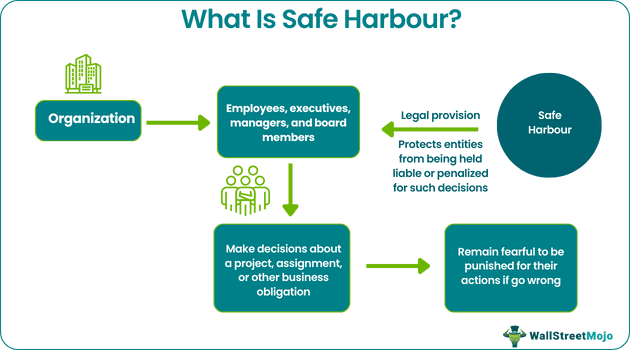
Safe harbour refers to a legal provision that shields an individual or entity in certain circumstances from being held liable or penalized for activities that go wrong. It gives business executives and managers the freedom to make decisions without fear of being held accountable in the future.
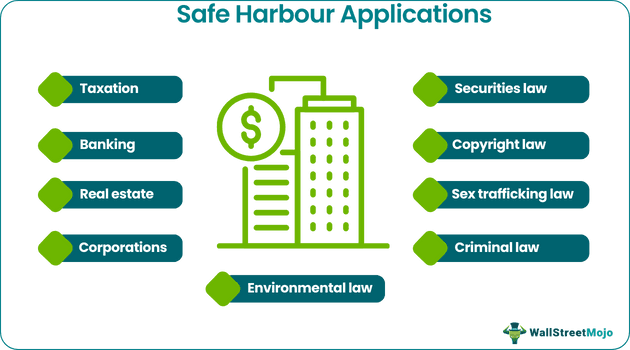
This statute, also known as the business judgment rule, helps prevent a hostile acquisition where a company takes over a severely regulated or loss-making firm to appear less attractive for acquisitions. The safe harbour rules are relevant in several fields, including taxation, banking, real estate, and corporations. It also applies to various laws, such as environmental, securities, copyright, sex trafficking, and criminal.
Key Takeaways
- Safe harbour is a legal provision that protects an individual or business from being held accountable or penalized for activities that go wrong under specific circumstances.
- It provides a safe haven for management and directors when deciding how to proceed with a project, assignment, or other corporate duty.
- The law allows taxpayers to get a break on how much they have to pay, avoid legal or tax constraints, and calculate the tax impact on meeting certain criteria.
- The Digital Millennium Copyright Act shields Internet Service Providers from liability for copyright infringement. In India, the rule applies to transfer pricing audit.
Understanding Safe Harbour Rules
Safe harbour rules apply to any entity irrespective of its size and structure. Whether a company is large or small, the decisions made by management, directors, or anybody in charge of a project directly impact the company's productivity and revenue. People stay fearful due to the liability they assume while taking on a corporate obligation, affecting their decision-making ability. In such a situation, the provision can be a lifesaver for individuals who make decisions solely in the organization's best interests.
In 2015, the policy was brought to light after a dispute between the United States and the European Union over citizen data transfer for law enforcement purposes (EU). As the name suggests, the term provides a safe haven for decision-makers while proceeding with a project, assignment, or other business obligation. However, certain circumstances must be followed for the safe harbour provisions to protect the company leaders' decisions.
Even if a decision is proven to be incorrect, the statue may protect the person in charge from being held accountable or fined for the loss if it is:
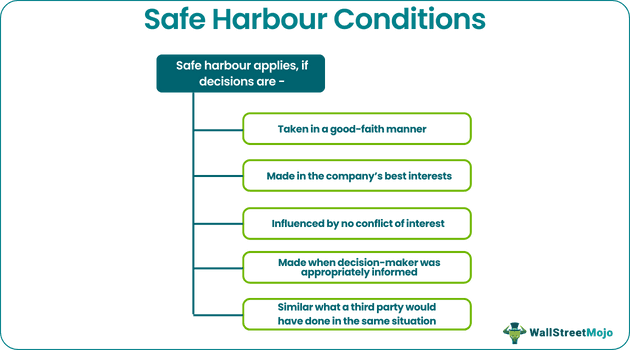
- Taken in a good-faith manner
- Made in the company’s best interests
- Influenced by no conflict of interest
- Made when decision-maker was appropriately informed
- Similar to what a third party would have done in the same situation
Safe Harbour In Taxation
This rule also applies to taxation, where taxpayers get some relaxation on how much they must pay if they meet specific conditions. It also aids the entity in avoiding legal or tax restrictions and determining a tax consequence in accounting.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) waives or reduces the underpayment penalty for the taxpayers if they:
- Pay at least 90% of what they owe for the current year as tax, or
- Pay 100% of the tax owed for the previous financial year, or
- Owe a tax amount less than $1,000 after deducting withholdings and credits
Safe Harbour In Real Estate
In 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) introduced a new regulation, known as the 199A deductions, allowing a 20% deduction. The provision came into existence to enable partnership, S corporation, and sole proprietorship businesses to take advantage of the deductions. The IRS issued Revenue Procedure 2019-38 in September 2019, outlining the safe harbour rule that classified an investor's real estate rental enterprise as a business or trade and hence making it eligible for the 199A deductions. The eligibility criteria to be met include:
- Having a separate book and record for a real estate enterprise
- At least 250 rental service hours during the year, such as rent or lease advertising, verifying tenant application, collecting rent, negotiating leases, maintaining the property, etc.
- Mandatory maintenance of contemporary records, including time data and other documents to support hours, dates, and descriptions, along with the prover details for the services performed. It came into existence in 2020.
- The taxpayer should attach a financial statement when filing the tax return every year and specify the rule.
The rule exceptions are exercised if:
- Property used by taxpayers as its residence for over 14 days in a year.
- The rental or leasing of real estate property is done on a triple net lease basis, i.e., a lease in which the landlord assigns the tenant's duty for real estate taxes and other obligations.
- Property rented to an entity with shared ownership.
- Any portion of the property is recognized as a specified business or service provider under particular rules whereby the real estate is provided for service to other trades or businesses.
Types of Safe Habour
The safe harbour provision appears to have different relevance in different parts of the world. Let us look at a few countries where these regulations are in effect:
#1 - United States
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is the U.S. safe harbour law that prevents Internet Service Providers (ISPs) from being held liable for copyright violations resulting from comments placed on their websites or other illegal activities carried out by customers. This 1998 provision introduced by Congress under the subsections of Section 512 becomes applicable if the below-mentioned conditions are found to be true:
- Communications made via a temporary digital network
- Information distributed on systems or networks directed at users
- Caching on the system
- A tool for finding information
Even if the situation does not meet the criteria mentioned above, holding the ISPs responsible for any copyright infringement is unnecessary. Instead, there needs to be solid proof of involvement to hold them accountable for copyright violations. Failing to do so will always protect them from harsh punishment.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) also recommended regulatory guidelines under safe harbour rules, which shield management from responsibility when making good-faith financial projections and forecasts.
#2 - Australia
A director is liable for the company's debts if it is approaching insolvency, according to Section 588 G of Australia’s Corporations Act. The safe harbour rule was introduced under Section 588 G (A) in July 2018, allowing and encouraging directors to make decisions and keep a business going while experiencing financial difficulties.
#3 - India
In September 2013, India's Central Board of Direct Taxes implemented the safe harbour provisions associated with transfer pricing. Transfer price is the arm's length cost for international transactions between two entities.
Under this provision, multinational corporations that report minimum operating earnings are exempt from transfer pricing audits. In Indian Tax Law, the rule is applicable when tax authorities accept the transfer price as disclosed by the taxpayer.
Examples
Let us consider the following safe harbour examples to understand the relevance of the concept even better:
Example #1
Jeff, a project in charge of a construction assignment handled by Max Constructions, decided to subcontract a few construction-related works to other entities to speed up the process. As a result, he invited proposals and selected the one through a well-defined corporate process, considering the quality of the product and the rates.
Five years later, the building collapsed because of the poor quality raw materials. Jeff was held responsible for everything, but the safe harbour provision was applied. It was observed that he had no self-interest involved in the deal and whatever he did was in good faith. In addition, anyone in place of him would have taken the same decision. As a result, Jeff came out clean.
Example #2
The EU Data Protection Directive includes rigorous privacy rights for EU citizens. In addition, it bans EU enterprises from transferring any personal data to entities outside the EU that have less stringent privacy rules.
Earlier, the EU allowed U.S. law enforcement agencies to transfer data about U.S. residents from the EU under an old safe harbour agreement. However, the clause created under the International Safe Harbour Privacy Policies was found invalid by the European Union's Court of Justice in 2015. The decision was made due to the U.S.'s lack of privacy protection against EU data snooping.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Safe harbour is a legal term that prevents a person or an entity from being held accountable for mistakes or fined for the loss if certain requirements are met. The provision affects many sectors, such as taxation, banking, real estate, and corporations. It also covers a wide range of legislation, including environmental, securities, copyright, sex trafficking, and criminal law. Even if a decision is proven to be incorrect, it may protect the person in charge if it is:
• Taken in a good-faith manner
• Made in the company’s best interests
• Influenced by no conflict of interest
• Made when decision-maker was appropriately informed
• Similar to what a third party would have done in the same situation
The IRS released Revenue Procedure 2019-38 in September 2019, outlining the safe harbour rule that allows an investor's real estate rental operation to be designated a business or trade and hence qualify for the 199A deductions.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) waives or reduces the underpayment penalty for the taxpayers if they:
• Pay at least 90% of what they owe in taxes for the current year, or
• Pay 100% of what they owe for the preceding financial year, or
• Owe a tax amount of less than $1,000 after withholdings and credits are deducted.
