Table Of Contents
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic process automation (RPA) refers to software technology that involves utilizing robotic applications to replace or augment human efforts within the financial sector. This kind of business process automation streamlines the accounting and finance space by standardizing maintenance and official documentation of crucial customer records and data.
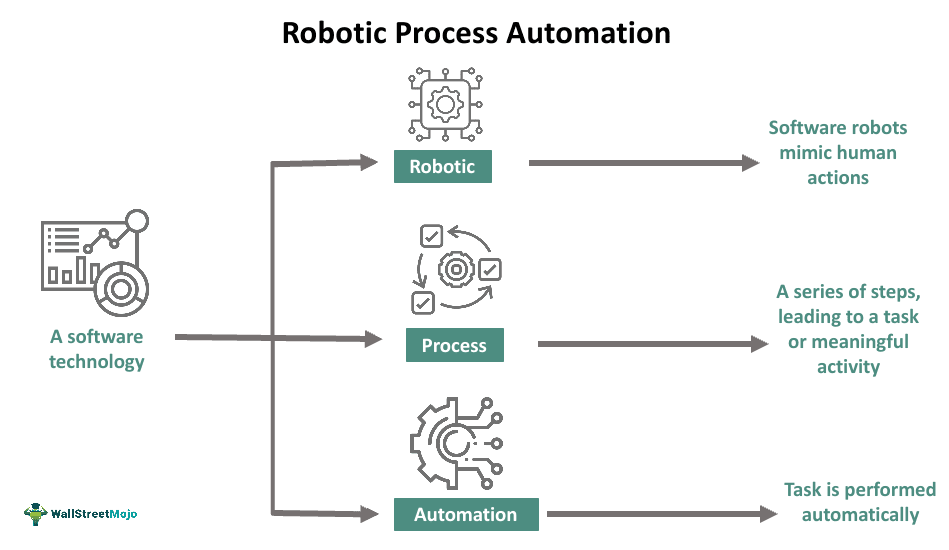
The optimization method utilizes virtual bots, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to perform tasks carried out by humans otherwise. Typically, it automates repetitive, computer-based tasks, minimizing errors and costs besides boosting a business’s operational efficiency. This, in turn, increases results in increased flexibility within the organization and higher profits. There are three types of RPA — attended, hybrid, and unattended.
Key Takeaways
- Robotic process automation refers to a procedure through which software bots utilize a combination of computer vision, automation,
- and machine learning to automate high-volume, repetitive tasks that are trigger-driven and rule-based.
- Unattended, attended, and hybrid are the three kinds of RPA that businesses may consider implementing.
- Some key benefits of robotic process automation are reduced operation costs, higher revenue, improved efficiency, and better compliance.
- A noteworthy challenge of robotic process automation is the possibility of significant job losses.
- A key difference between RPA and traditional automation is that the former mimics human actions to perform tasks.
Robotic Process Automation In Finance Explained
Robotic process automation refers to an application of technology that involves utilizing software robots to mimic human workers’ back-office tasks, for example, filling in forms, moving files, extracting data, etc. This software technology is ideal for tasks that involve high-level human data processing. It can significantly minimize labor costs, positively impact efficiency by greatly reducing human error, and help meet compliance mandates.
This advanced type of business process automation combines user interface (UI) and application programming interface to carry out and integrate repetitive tasks between productivity applications and enterprise.
RPA tools complete the autonomous implementation of multiple transactions and activities across unassociated software systems. This kind of automation utilizes software based on specific rules to carry out a high volume of business procedure activities. This frees up human resources and allows them to focus more on complicated tasks. For organizations looking to ensure regulatory compliance across their automated processes, employing PRA services can provide additional oversight and security, further enhancing the benefits of RPA in digital transformation efforts.
RPA allows chief information officers (CIOs), besides other key decision makers of any organization, to accelerate efforts concerning digital transformation to boost return on investment (ROI) from the workforce.
Let us look at some key aspects to consider when determining potential RPA fits:
- A rule-based process.
- Tasks need to have adequate volume.
- There must be defined outputs and inputs associated with the process.
- The repetition of the process must occur at fixed intervals, or there should be a pre-defined trigger.
Types
Let us look at the different RPA types.
- Attended Automation: This kind of bot is available on a user’s computer, and the user usually invokes it. This type of RPA is best-suitable for jobs triggered at points that are not easy to detect programmatically.
- Unattended Automation: This involves bots that automate processes without any human interaction. In other words, it enables users’ robots to get triggered automatically to finish the whole process.
- Hybrid Automation: In this case, a combination of unattended and attended RPA bots ensure front-office and back-office activities’ automation, which allows for end-to-end business process automation.
Examples
Let us look at a few robotic process automation examples to understand the topic better.
Example #1
Suppose Company ABC, a financial institution, implemented RPA in its business. The organization had data related to customer behavior automatically sent to certain persons within the organization. Machine learning models helped the company in grouping customers into specific categories on the basis of their behavior. Hence, the most appealing services or products could be recommended to them. The identification of cross-selling opportunities for different financial planning products resulted in a surge in revenue for Company ABC.
Example #2
In July 2023, a leading provider of automation solutions for financial services, SMA Technologies, announced robotic process automation or RPA capabilities for its financial services automation platform. The OpCon RPA allows clients to record and automate user interfaces or UI-specific workflows on the web or in Windows. This ensures the smooth implementation of financial services workflows conventionally requiring manual intervention.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Let us look at the benefits and limitations of RPA in finance.
- This optimization method streamlines the finance space by allowing for the maintenance of crucial consumer records. It also plays a vital role in standardizing official documentation.
- Using RPA results in process transformation; the efficient business functions and processes translate into gains.
- Automation is ideal for rule-based procedures populating mortgage and insurance organizations. RBA bots can carry out all the comparing and searching, less the costly mistakes.
- RPA increases the accuracy and speed of fraud detection.
- Another key benefit of robotic process automation is that the smart bots are able to carry out financial data entries correctly. As a result, they automate redundant jobs.
Disadvantages
- A key challenge of RPA is that the setup procedure can be time-consuming.
- Sometimes, RPA robots might not be able to detect obvious errors.
- Even small changes in an organization’s setup can lead to significant disruption from the RPA robots.
- A large number of workers can lose their jobs because of RPA.
- Organizational misalignment and process standardization are among the noteworthy challenges in executing RPA in the banking space.
- The slow technological development in the banking space is a key obstacle to adopting RPA.
Robotic Process Automation vs Traditional Automation vs Intelligent Automation
The concepts of traditional automation, RPA, and intelligent automation can create confusion if individuals are unfamiliar with them. Here are the differences between them:
| Robotic Process Automation | Traditional Automation | Intelligent Automation |
|---|---|---|
| RPA utilizes semi-structured and structured data inputs. | It uses structured data inputs. | This form of automation utilizes semi-structured and unstructured data inputs. |
| RPA replicates human actions to finish tasks. | It does not involve mimicking human actions. | Intelligent automation mimics human actions. |
| RPA automates tasks only when it has been programmed for the same. | It cannot automate a task via cognitive decision-making capabilities. | Intelligent automation can automate tasks via cognitive decision-making capabilities. |
