Table Of Contents
Ring Fencing Meaning
Ring fencing is a mechanism to disintegrate the regulated public utility subsidiary from its parent corporation, which also performs non-regulated business operations, to safeguard the former from the unlimited risk involved in the latter. Thus, the entity needs to isolate a certain amount of its profits and assets financially.
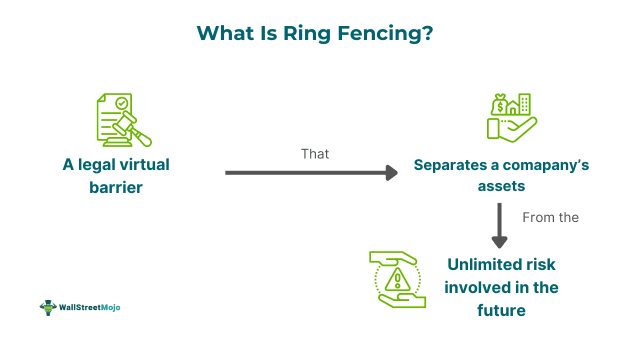
Such measures serve as a virtual barrier to protect public utility customers from the negative consequences of financial distress faced by these parent entities during economic crises or other such events. This is commonly seen in banks, which need to segregate their retail services from their investment banking business, which is highly risky.
Key Takeaways
- Risk sharing refers to the strategy undertaken by firms engaged in banking, finance, insurance, international trade, and partnerships to limit their potential financial losses through the distribution of uncertainties among various stakeholders.
- The government imposes bank ring fencing rules to ensure that these financial institutions separate their retail activities from their investment banking functions and safeguard the interests of retail customers, depositors, and investors.
- It is of four types, namely, legal, informatory, regulatory, and tax.
- It assists financial institutions in keeping their retail banking operations ongoing as well as minimizing the risk of losing assets.
- On the contrary, it also possesses some disadvantages, like interfering with the strategic objectives and growth initiatives of the organizations.
Ring Fencing Explained
Ring fencing is a method through which businesses, banks, and individuals shield their assets from unlimited risk exposure. It emphasizes segregating the regulated public utilities assets out of all the financial assets of a parent company (the one that also executes the non-regulatory activities). The purpose is to secure the interest of the public utility customers from not receiving basic amenities like water, electricity, telecommunications facilities, banking services, and other services when the providers face significant financial losses. Thus, it protects them from indirectly being exposed to the unlimited risk involved in the non-regulatory functions of the companies and banks.
Moreover, the ring fencing also ensures that the parent firms do not illegitimately use the personal information of these utility consumers for advertising or promoting their non-regulated services for profit-making. Further, the ring-fenced subsidiaries have more excellent creditworthiness and, therefore, are more preferred by investors and creditors. Also, they can avail of loans at a comparatively lower borrowing cost than non-fenced assets or firms. Notably, the need for ring-fencing in the banking sector has become significant after the havoc caused in the banking industry amidst the 2007-2008 financial crisis, especially in the UK.
Types
Ring-fencing is a method of securing wealth from exhaustion in certain financial circumstances. Given below are some of the different kinds of ring fences:
- Legal: It is a lawful method adopted by companies to restrict the movement of their respective financial assets outside or inside a country's geographical boundaries. It aims to preserve these assets for a specific purpose.
- Informal: In this measure, the company establishes informal procedures, practices, and policies to prevent its employees from disclosing or leaking critical information outside the company.
- Regulatory: As discussed earlier, in this type of ring-fencing, the banks are required to disintegrate their retail banking functions from their investment banking processes to safeguard the retail customers.
- Tax: Governments usually impose ring-fencing rules to prevent companies from consuming their losses in certain operations to curtail their taxable income from other activities.
Examples
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages
- Bank ring fencing helps these financial institutions keep their retail banking operations ongoing, such as extending loans and accepting deposits, even when they suffer financial distress in their investment banking sector.
- Also, it reduces the risk of losing all assets due to a financial crisis or insolvency of the business or other organizations.
- It helps banks and companies follow the government regulations for ring-fencing in taxation and assets.
- It shields utility or retail customers if a bank or business suffers bankruptcy during specific events.
- Further, it boosts the confidence of stakeholders, depositors, and investors in the banking system.
- The regulated public utility subsidiaries so formed have greater credibility due to limited perceived risk and enjoy credit facilities at a lower borrowing cost and other favorable terms.
- Such a mechanism prepares the banks for crises, making them more resilient towards such events.
Disadvantages
- However, ring fencing seems more like a restriction on businesses' ability to freely move their assets, resources, and funds between different operations and activities to ensure their optimal utilization.
- It also interferes with the strategic objectives and growth initiatives of the organizations by reducing the potential use of their assets.
- It further increases the operational and administrative burden and cost of separately managing financial assets.
- There are always certain legal loopholes that can make the businesses escape such rules.
