Table Of Contents
Reverse Repurchase Agreement (Reverse Repo) Definition
A Reverse Repurchase Agreement is also called reverse repo, which brings into the implementation of an agreement between a buyer and seller stating that that the buyers of the securities who purchased any kind of securities or assets have the right to sell them at a higher price in the future, i.e., the seller who has to accept the higher price in the future.
The reverse purchase agreement is a substitute method to provide liquidity to a portfolio. It is a method to prevent liquidating a portfolio to face the unforeseen cash requirement. It is also used as an effective cash management practice. The reverse repo is a collateral deposit for the lender of funds provisioning itself with a short-term investment scope and, in this way, also creates a gateway of borrowing the security to get certain short positions covered.
Reverse Repo Explained
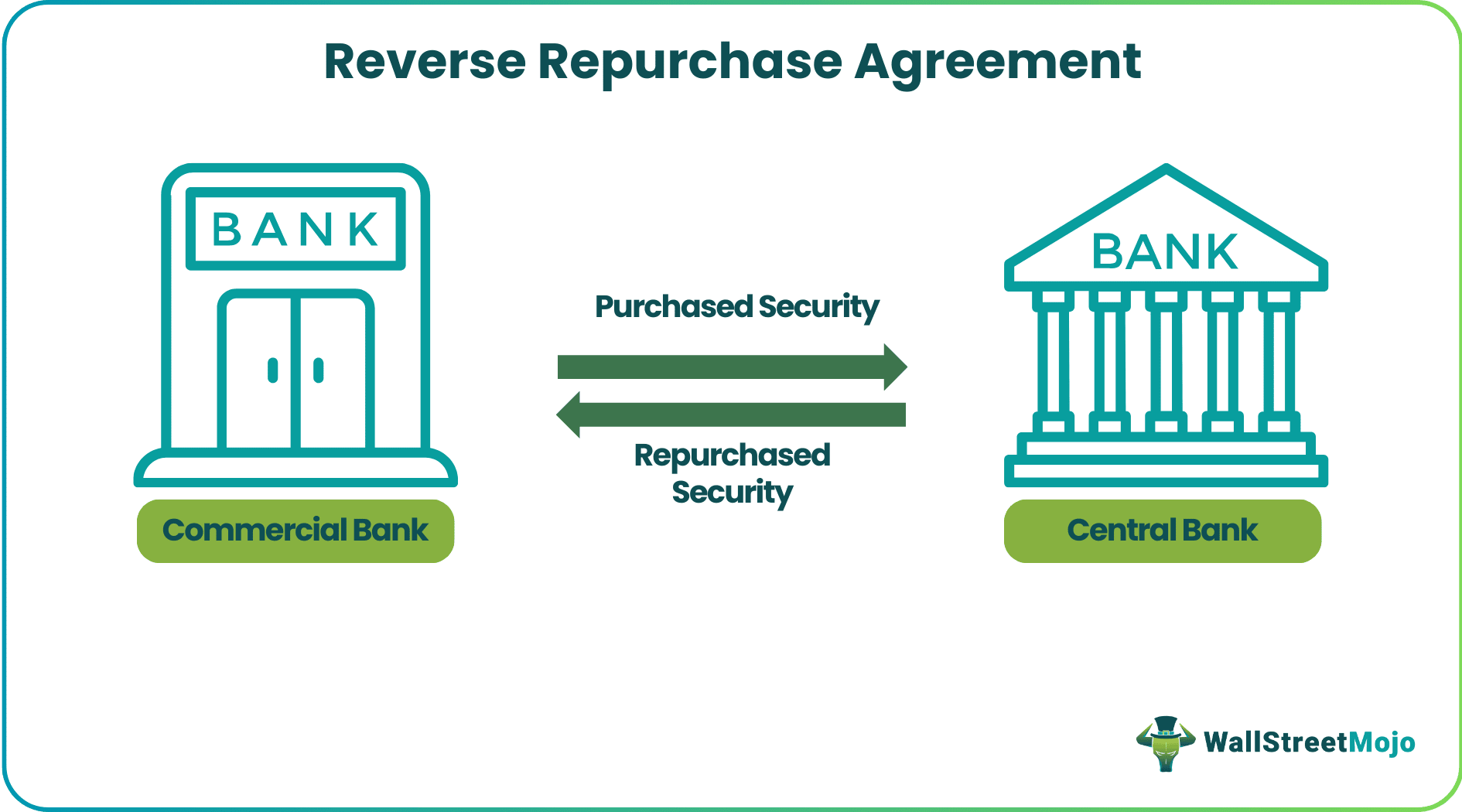
In a reverse repurchase agreement facility, there are generally two parties involved. One leg of the execution primarily comprises a commercial bank purchasing security from a central bank. The other leg of the executed transaction comprises the sale of exact security or assets purchased earlier from the commercial bank again to the central bank.
It is generally targeted to control the supply of money in the economy as a whole. They are also considered safer because it primarily involves treasury securities.
These transactions, which generally involve buying and selling securities, can also be seen from the viewpoint of a collateral-based loan. This agreement is, moreover, an overnight loan with the terms and conditions extending to a period to a maximum of fourteen days. The Federal Reserve implements reverse repurchase agreements with agreements lasting up to 65 business days.
The prime users of such an agreement are generally monetary authorities, financial institutions, mutual fund companies, sovereign funds, commercial banks, pension funds, insurance companies, etc. The reverse repo rate is primarily used by monetary bodies to obtain money from the banking system and to squeeze or prohibit increased liquidity in the market to keep a check on the supply of money in the economy.
This short term lending is provided to investors who may be highly cash sufficed but are prone to take risks. This may be utilized to procure short positions in the market, which was previously covered by the other party. The securities are sold by the seller to the buyer with a commitment that, in a future date, the buyer will again sell the same securities to the seller. Reverse repurchase agreements, for the time being, reduces the number of reserve balances in the banking system.
Components
The different components of this kind of agreement can are explained in details below.
- A reverse repurchase agreement accounting or reverse repo accounting primarily consists of two parties and thus two legs of transaction. One part is the “Sale,” and the other part is “Buyback.” It involves collateral or security, which the seller in the “Sale” part procures from the buyer and again, which is returned back to the buyer during the “Buyback” part.
- Suppose the seller sells securities at $100 in the first leg taking collateral of $1000. In the second leg, the same seller will buy back the securities at $150 and return the security of $1000 to the other party involved. The difference i.e. $150 – $100 = $50 is called the haircut margin.
- The other party makes money in the form of interest on the transaction, which is the difference obtained in the way of selling the asset or security at a higher rate. The party, in this way, has also derived the temporary usage of security.
Examples
Let us understand the concept of reverse repurchase agreement accounting with the help of a suitable example.
The reverse repo rate is the rate of interest that is offered by the federal bank to other operating banks that deposit or invest their cash reserve or securities into the treasury of the federal bank. This is considered to be a much better and safer parking avenue than lending the same to companies or customers as in reverse repo, the securities or funds are safe with the federal bank.
To cite an example, every federal bank will have a fixed percentage of reverse repo rate, which it offers to the other parties involved in these agreements. Suppose we assume the reverse repo rate fixed by a federal bank in the US is 6%, which means if a commercial bank has an excess cash surplus of $500,000 available with it, the bank can invest the same in a reverse repo agreement with the federal bank.
Doing this, the particular commercial bank will earn an interest of $30,000, which is also called the haircut margin.
Benefits
Below are some benefits of the reverse repurchase agreement facility.
- It encourages other banks to store their excess cash with the federal bank during high levels of inflation in the economy so that the banks can earn more returns on their excess funds.
- It is a way of profit earning in the method of the margin earned due to selling of a particular security or cash reserve at a higher rate to the original seller. In cases of a bank, the profit earned is in the process of interest earned due to parking of excess cash with the federal or central bank.
- The reverse repo rate is an instrumental method of controlling the money supply available in the economy.
- A high rate helps in injecting liquidity into the economy.
- It stimulates commercial banks to invest or store excess funds with the federal bank to earn higher returns.
Risks
Let us understand the various risks involved in this type of transaction, as given below:
- Federal banks have to confront costs with reverse repo agreements, which are not similar to the costs facing other federal counterparties, so these cost differences must be accounted for somewhere.
- A reverse repo on a large scale can lead to major banking disintermediation.
- The reverse repurchase agreement with an entity’s counterparty typically has no proper establishment.
- The financial health of the two parties involved and the value of the collateral is not judicially measured or checked.
- The counterparty has a chance to default on its said obligation.
- The collateral given is prone to lose value due to volatility in the market and changes in the market scenario.
Reverse Repurchase Agreement Vs Repurchase Agreement
Both the above are two different forms of financial transactions that are frequently used in the money market. They help in managing liquidity for short term and control the rate of interest. However, let us find the differences between them.
- The former is the seller’s side of the agreement whereas the latter is the buyer’s side of the agreement.
- In case of the former, the seller sells the securities to the buyer at a lesser price to buy them later whereas for the latter, the buyer buys the securities at a low price to sell them later.
- In case of the former, the seller is the borrower who sells the securities as collateral to the buyer and for the latter buyer is the lender who buys the securities from the seller.
- Reverse repo is commonly used money market funds or institutional investors or central banks to invest their surplus funds. But repo is used commonly by banks of financial institutions to meet the needs for short term liquidity.
Both the above are very common methods for short term liquidity management but they are two different sides of the same transaction. They reflect the role of each party in the transaction.
