Table Of Contents
What Is A Revenue Model?
A revenue model is a structure that defines a firm’s business operations; it outlines how the business generates revenue. It comprises a catalog of all products or services, the pricing structure, and distribution channels. It is different from the business model of a company.
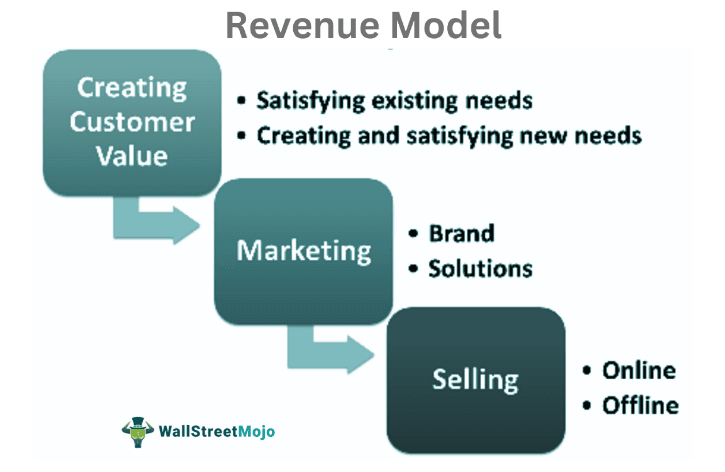
The revenue structure determines how the product or service offered by the company works at each level. The revenue structure aggregates every step; creating value, delivering, getting customers to pay, and generating profit.
Key Takeaways
- A revenue model defines how a business generates revenue. It outlines business operations and activities that lead to income generation.
- There are five revenue models primarily: recurring, sales, affiliate marketing, and advertising.
- Predominantly, revenue structures focus on profit maximization. To formulate a revenue structure, firms forecast future growth and project an annual figure that the particular model can achieve.
Revenue Model Explained
A revenue model is a structure that defines a firm’s business operations; it outlines how the business generates revenue. It comprises a catalog of all products or services, the pricing structure, and the distribution channel.
Before venturing into the structure, let us first define revenue. Revenue refers to a firm’s total earnings from primary business operations. Primarily, a business generates revenue from selling goods or rendering services. It is shown as a top-line item in the income statement and is often referred to as gross sales.

Revenue is an unfiltered quantity—the gross amount earned by an organization or a government without accounting for deductions. In other words, it is the inward cash flow generated from business activities. Moreover, it reflects the financial standing of a business—gross sales represent a positive cash flow.
Usually, revenue structures focus predominantly on profit maximization. Also, over time firms evolve, and the revenue structure needs to change with prevailing market conditions. To formulate a revenue structure, firms forecast future growth and project an annual figure that the particular model can achieve.
Some small firms follow revenue structure templates. But it is better to draft a customized model that suits the firm by removing unnecessary elements from templates. Similarly, new startups attempt idealistic models, but more often than not, they backfire. The revenue structure is a fundamental business concept; firms can replicate tried and trusted structures that have been successful in real-world scenarios.
Revenue vs Income Explained in Video
Types
There are five types of revenue models.
#1 - Recurring Revenue Structure
It is a subscription-based model where a certain content, channel, service, or facility is offered. In this structure, the business primarily earns from the periodic subscription fee paid by customers.
The business offers multiple scheduling options to customers. For example, customers can pay a fee every month, every quarter, or once a year. This model is followed by Netflix, streaming platforms, newspapers, TV channels, and podcasts.
It is called the subscription revenue structure because customers keep renewing the subscription till they opt out. In this model, the customers do not own the service but are subscribed to it.
#2 - Affiliate Revenue Structure
When a business generates most of its income via commissions, it follows an affiliate revenue structure. The firm employees connect with multiple channels of promotion—network marketing.
Such businesses drive sales and receive a commission from the manufacturer or service provider. These firms are categorized under affiliate marketing.
#3 - Sales Revenue structure
Most businesses use the sales revenue structure. The business generates revenue by selling products or services to customers. Customers either pay the manufacturer or a retailer. The model has many subtypes depending on the distribution channel.
Though multiple distribution channels can be involved, the whole model is based on selling products and earning revenue. B2B and B2C are the most popular distribution channels.
Business to Consumer (B2C) is a business model where businesses sell their products and services to end-users or customers. Similarly, a business-to-business model (B2B) is one business selling to another business.
#4 - SaaS Revenue structure
SaaS stands for software as a service. The firm provides a software application over the internet in the SaaS revenue structure. Customers install the software and pay the SaaS company via online transactions. The service could be a CRM, cloud space, HR portal, chat service, or a platform that connects people. Zoom, Slack, Zoho, etc., are popular examples of SaaS companies.
#5 - Advertising Revenue Structure
These firms offer publicity, promotional campaigns, content marketing, and advertisement services. These agencies operate via digital platforms or print media. In this revenue structure, the firm does not manufacture. Instead, it advertises other businesses. In return, clients (other businesses) pay a fee for the advertisement.
Examples
Let us look at some revenue model examples to understand the structure better.
Example #1
James was always intrigued by the fashion industry. He studied fashion design and opened a store. James is a manufacturer; he does not procure finished goods. His store stood out due to the USP. James allowed customization. Customers could come up with unconventional designs and measurements for outfits.
The store is open on weekdays and is closed on weekends. In the first six months, the business registered a revenue of $900,000.
Here, James followed a sales revenue model. James is a manufacturer, and customers pay him directly; the firm generates revenue by selling finished goods. Since it is a single store, James does not need any distribution channel.
Example #2
Let us assume that James tries to promote his business beyond the brick-and-mortar store. Initially, James opted for influencer marketing.
James hires Nathan—a social media influencer with over a million followers. Nathan promotes the clothing brand and schedules multiple posts and reels. James pays Nathan a predetermined fee for every position.
Here, Nathan’s business follows the affiliate revenue structure. Nathan does not manufacture anything but possesses an extensive network. Therefore, Nathan promotes the clothing store through his network and receives a fee.
Revenue Model vs Business Model
Let us look at revenue model vs business model comparisons to distinguish between the two.
- A revenue model allocates the value it creates. In contrast, a business model defines how the business generates value.
- A revenue structure explains how a business earns money. In comparison, a business model elaborates on business operations, management activities, and strategies.
- Revenue structures focus on future outcomes and foreseeable growth. On the other hand, business models narrow down on credit, funding, and investments.
- There is an apparent overlap between the two. The revenue structure is a small part of the business model. The business model renders a larger picture of the entire business. The revenue structure, therefore, is more streamlined.
