Table Of Contents
What Are Revenue Bonds?
Revenue bonds are bonds issued by municipal corporations where the revenue from income-producing projects such as toll bridge, highway, sewer facilities, airport construction, roads, local stadium are used in repaying the debt obligation (both interest and principal component).
These are often issued by the government agency and revenue is backed by income generated from the projects. There are issues with a face value of 1000 & 5000 with semi-annual payments. Some are issues in the form of zero-coupon bonds.
Rating agencies rate these bonds based on their abilities to pay back interest and principal. They also evaluate the cash-generating ability of the projects.
Mutual funds and municipal bonds investment trust are the most common way to invest in revenue and other forms of municipal bonds.
Just like normal bonds, revenue bonds are inversely related to interest rate, i.e., price falls are interest rate rises and vice versa.
These bonds may be issued in the form of a staggered maturity date and are known as serial bonds.
They differ from general obligation bonds which do not invest in income-generating projects but provide service to the entire community whereas projects funded by such bonds only charge those communities which pay for the service.
The lower the tax bracket, the more favorable corporate bonds investment as the tax charges increase. Municipal bonds appear more attractive.
How Do Revenue Bonds Work?
The industrial revenue bonds are issued by the local or state government as well as some government agencies to raise fund for certain particular revenue generating projects or operations. It is backed or supported by the cash flow that come from those operations.
The revenue can be in the form of toll, fees service charges, etc. The projects which they finance are expected to generate funds that will be enough to finance or cover the debt obligation of the bonds. The projects can be in the form of public utility, housing projects, roads, airports, etc.
Thus, these bonds are secured by the revenue generated which are paid to the bondholders. The investors, however, should assess the risk of the bonds by evaluating the viability, demand and future potential of the projects, the creditworthiness and financial strength of the issuer.
It is to be noted that the interest income form the bonds are generally exempt from the federal tax and if the bondholder resides on the same area of the municipality, then they may get a tax exemption from the local tax authority.
The industrial revenue bonds make up the vast majority of municipal bonds. Investors willing to buy these bonds must know the varieties available, as well as how the project will produce the promised return on a consistent basis. It is advisable to take the help of financial advisors before investing in any such bond because they have the proper knowledge, skill and understanding to make informed decisions.
Characteristics
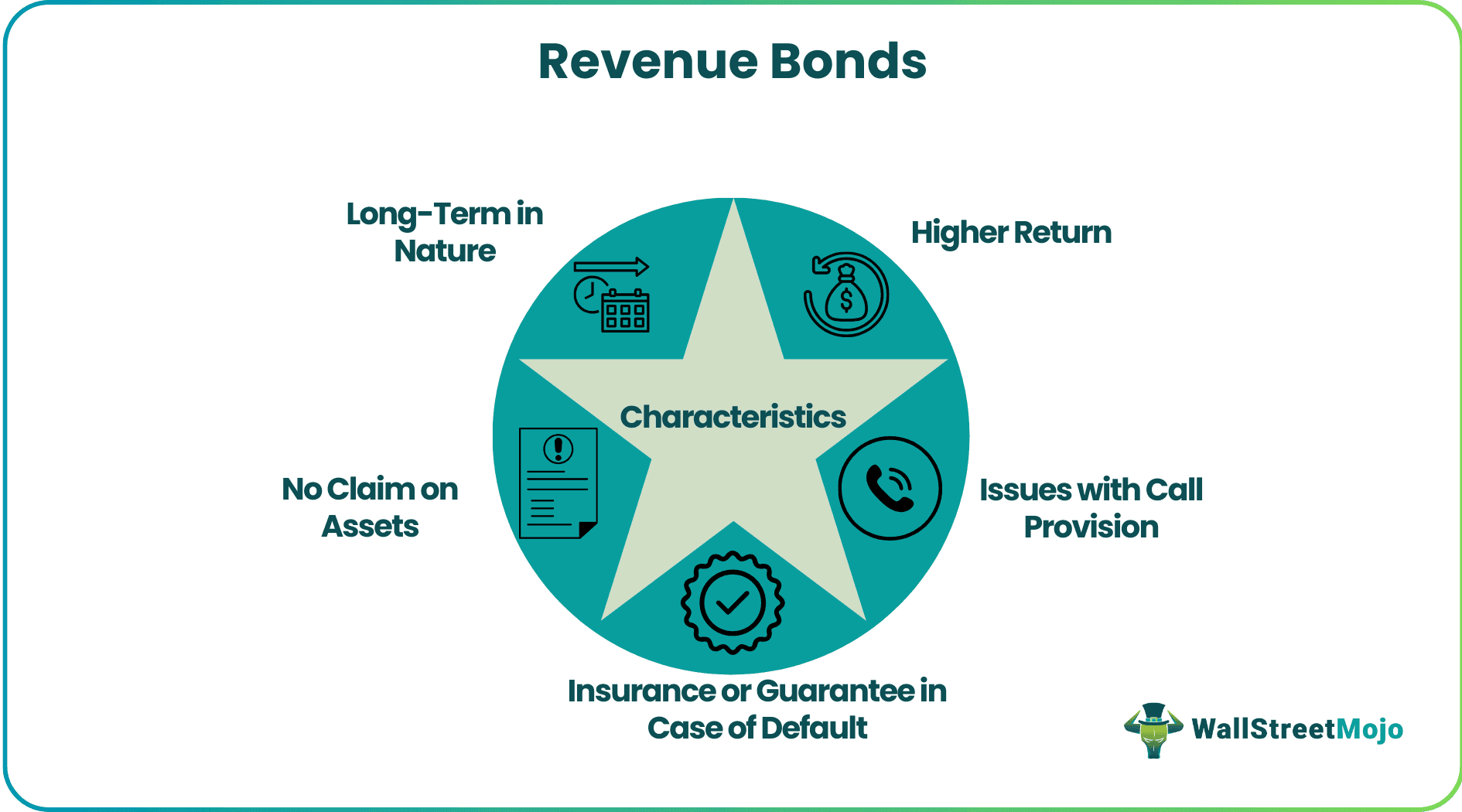
#1 - Longer-Term in Nature
These municipal revenue bonds are used to fund long term projects, so the maturity date often ranges from 20 to 30 years. Interest and principal payments are both made after meeting the operating expenses of the projects. If the project does not generate enough funds, payment can be deferred to a later date.
#2 - Higher Return
They provide a higher return than the general obligation bonds since they are secured by the revenue generated from the project, there is a greater risk of non-payment of the promised return, so the investor is compensated with a higher return as compared to general obligation bonds to attract them.
#3 - No Claim on Assets
Bondholders do not have any claim on the assets of the projects. If the projects do not turn out to be successful, bondholders cannot repossess the toll roads or equipment.
#4 - Issues with Call Provision
These bonds are issued with a catastrophe call provision, which allows the issuer to call back the bonds if the revenue-producing facility is destroyed.
#5 - Insurance or Guarantee in Case of Default
Such mortgage revenue bonds are exposed to credit, interest, call, and market risks similar to other classes of debt. To avoid defaulting on its obligation, the issuer often provides insurance on their bonds. In some cases, federal agencies also provide a guarantee.
Revenue vs Income Explained in Video
Types
- Industrial bonds finance public projects like parks, the stadium they will generate usage feed when booked for concerts, sports events, meetings.
- Airport bonds to fund construction of airports, landing fees, fuel fees, lease payments to secure the bonds.
- Public utility bonds which fund through the sale of electricity.
- Hospital bonds that fund hospital construction, renovation, equipment purchase.
- Highway bonds used to build revenue-producing facilities such as bridges and toll roads.
- Transportation bonds are issued to finance local public transportations such as buses, subway systems.
- Special tax bonds-generate funds by levying a tax on a particular activity or asset, for e.g., the special tax may be levied on the sale of alcohol or tobacco.
- Sewerage projects where cash is generated from usage fees, assessment fees, connection feed is used for paying municipal revenue bonds.
Example
Peter invests in fixed income securities. He identifies that a local municipality is raising $10 million to finance the construction of the new bridge by issuing revenue bonds. After carefully evaluating the creditworthiness of the projects, he is quite confident that the project will be successful in generating sufficient revenue to repay the proceeds, so he decides to buy it.
Advantages
Every financial instrument has its own advantages and disadvantages, so does this financial instrument. Given below are some of the advantages of this kind of bond.
One of the advantages of investing in revenue bonds is that interest income is usually exempt from federal, state, or local taxes. So, it is quite beneficial for investors with a high-income tax bracket. Due to this advantage, it is popular in high tax rate states. Consider an investor with a total portfolio of $500000. He considering alternative ways of investment out of which he chooses two option below:
- Option 1 To purchase corporate bonds which provide a total annual yield of 7%, i.e., $35000
- Option 2 To purchase tax-free municipal bonds @yield of 5%, i.e., $25000 interest income per year.
If he chooses option 1, he is still liable to pay income tax of say 30%(applicable in that state), i.e., $10500, which reduces his interest income to $24500. However, in the latter case, he does not have to owe anything to tax authorities and can keep the full amount.
#1 - Municipal Bonds can be Considered Less Volatile
Short-duration bonds are less volatile, and their value does not frequently fluctuate as compared to bonds with longer duration. However, there is a trade-off between risk and reward where returns tend to lower for shorter maturity bonds.
#2 - Bondholders are Quite Emotionally Attached
When a bondholder buys a municipal bond which is used by the government or local authorities to finance hospital, school, or gymnasium in the locality, this helps to improve the lifestyle of an average person, so the bondholder does hold it until maturity
Disadvantages
Some disadvantages of this type of bond are as follows:
#1 - Higher Default Risks
Since mortgage revenue bonds or any similar ones are not backed by full faith and credit of the municipality, they are subject to higher default risks as compared to general obligation bonds
#2 - Inflation Puts Downward Pressure on the Return
The inflation rate dramatically impacts the returns generated from these bonds. However, variable-rate revenue bonds do offer some protection against inflation.
#3 - Tax Exemption Advantage can be Revoked
Pending tax legislation does impact the value of revenue bonds if the state or federal tax rate is reduced. In other words, these bonds provide maximum benefit to the high tax environment where a high tax bracket individual gets tax exemption advantage. As an exemption, these tax exemption advantages provided to revenue bonds can be revoked by an IRS.
Revenue Bonds Vs General Obligation Bonds
Both the above are two types of bonds issued by the local and the state governments, with some distinct differences. Let us try to find the differences between them.
- In case of revenue bonds, the repayments are generally made from the operating revenues only but for a general obligation bond, the repayment of principal and interest is made from all the revenues, including the taxes at the time of default,
- For general revenue bonds, the repayment is dependent on operating revenue, or revenue generated form a particular project or any business associate with the bond.and thus it is sometimes risky to get the repayments on time but the repayment is guaranteed in a general obligation bond because it is made from the general funds of the government.
- The former is considered risker than the latter because the latter is backed by government agencies who give the issuers the authority or permission to increase the tax rates and raise money to pay off the debt. But the former is dependent on the revenue generating from the projects or operations.
- The general revenue bonds have no voter approval system since they are backed by projects or enterprises, but the general obligation bonds require voter approval for issuance through ballot initiative or referendum.
- Both use the proceeds raised in different ways. The former uses the money raised to finance projects that generate revenue and profits for the economy whereas the latter use the proceed raised from the bond to finance public infrastructure projects like schools, bridges, highways that will benefit the public.
- The general obligation bonds interest rates will be lower as compared to revenue bonds because the former has government support and is considered safer than the latter.
It should be noted that both the funds vary in different ways like security, voter approvals, method or repayment, method of raising money and areas where the funds are used. But it is always a good practice to carefully evaluate the credit rating and risk of the issuer before deciding to invest in such bonds.
