Table Of Contents
What Is A Retainer Fee?
A retainer fee is an advance payment or down payment made either monthly or quarterly or semi-annually, or annually for procuring future services or confirming future benefits from an individual or, in some cases, from any corporate entity who is a consultant, freelancer, lawyer, or any other professional or expert in the relevant field.
If a consultant retainer fee is agreed upon, it is usually deposited in an account other than the receiver’s to ensure that the funds are not used for other purposes before the agreed work is executed. This fee is paid to a professional in return for their reputation and expertise. Therefore, the fees for the actual work done might be additional.
Key Takeaways
- A retainer fee refers to an advance or down payment frequently made monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually for acquiring future services
- or confirming future perquisites from an individual such as a consultant, freelancer, lawyer, or any other professional or expert in the relevant field.
- The retainer fee is crucial to both the client and the consultant. It ensures that the firm works for the client. In turn, the client may manage spending for the work.
- As one pays the retainer fee, the lawyer may safeguard the client from sudden circumstances during or before the business transactions.
- If the lawyer wins the case, he may charge his fees and adjust the amount receivable against the retainer amount.
How Does a Retainer Fee Work?
A retainer fee is a fixed price paid upfront to a person for receiving a specified service. The payer of the retainer fee is called the service receiver or the client. An individual receiving the payment is called a retainer, service provider, expert, or consultant.
Retainership providers or service providers may be individuals (in most cases) or corporate entities with a group of experts. A retainership provider or service provider is generally an expert in the relevant field, a lawyer, freelancer, or consultant.
Generally, a contract is made by the payer with the service provider. The agreement is normally made for a year and then renewed based on last year's services. So, this fee is like a fixed cash inflow for the service provider with a commitment to future services. It ensures the specified services' commitment to the fee's payer.
Paying a retainer fee makes the client serious about the consultant’s services. In addition, it enables a harmonious relationship between the client and the consultant, indicating that the client trusts the consultant.
The retainer fee is vital to both the client and the consultant since this ensures that the firm is working for the client and the client, in turn, can manage how much to spend for the work. In addition, keeping the fee in separate accounts ensures that funds are not used for personal purposes, and funds represent the pendency of services to be performed by the consultant. Also, retainer fees confirm the receipt of consideration against the services performed.
Agreement
The individual or organization looking for an external source for professional advice or service look to hire someone full time or on a consultant retainer fee basis. Let us discuss the process of the agreement in detail.
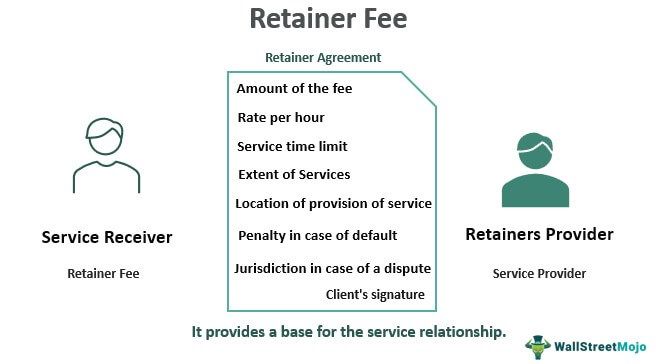
- Retainer fees provide the base for the service relationship.
- Firstly, an agreement between the service provider and the client is made. The contract specifies all the terms such as the amount of the fee, the rate per hour, service time limit, the extent of services, location of provision of service, a penalty in case of default, jurisdiction in case of dispute, etc. covering all the possibilities of a business transaction.
- The client must sign the representation agreement, and a reference is made to the attorney to make the agreement legally binding for both parties. Then, the client deposits the specified fee in a special account maintained by the service provider. A special account ensures that the service provider does not spend money for personal purposes before providing the service.
- When the service provider works on the assignment, he records the number of hours spent on the project. Such a record helps in invoicing at the end of the month. Then a settlement amount is derived by comparing the retainer fee and the invoice amount. The difference, if any, is either adjusted or cash-settled.
- This fee is normally paid to the attorney holders, lawyers, tax consultants, industry experts, quality check experts, etc.
Examples
Once both parties agree and the frequency of paying the fee is on paper, the agreement is made with the specifics including daily hours, remuneration, and quarterly or monthly retainer fee. Let us understand the concept better with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
Suppose a tax consultant is hired for an assignment. The typical workflow goes as under: -

Usually, the invoicing rate per hour includes charging for making phone calls, preparing or keeping records, etc. As you can see in the above example, the client gets $500.
Example #2
An agreement can be made between the client and a lawyer, wherein the lawyer gets a nominal account at the beginning and his complete fee only if he wins the case. Such an agreement is called a contingency fee agreement. Further, the client may enter into a retainership agreement with the lawyer to engage himself in the future whenever any legal issues are faced. Such retainership agreements are made for restaurants, hospitals, and tech-oriented companies.
Importance
To understand the importance of retainer fees, let us take an example wherein the client appoints a lawyer to handle the lawsuits of his business.
Once the retainer fee is paid, the lawyer can protect the client from unforeseen circumstances during or before the business transactions. If the lawyer wins the case, he can charge his fees and adjust the receivables against the retainer amount.
In case of any unexpected event, the lawyer can receive compensation for the work performed. Choosing the right lawyer is also essential since lawyers may settle the case without court procedures.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Shelling out a certain amount towards a monthly retainer fee can be a tedious task. However, there are advantages and disadvantages of hiring a professional on a retianer basis. Let us discuss them through the points below.
Advantages
- As the name suggests, you retain the best experts with you.
- Services can be promptly assured.
- The service provider gets a fixed income on time.
- Retainer fee ensures good relationships between the payer and service provider.
- The payer can consult the service provider as many times as he wants.
- There is no outer bound for the times the services are available.
- Payer gets a structured solution for his unstructured problems in the relevant field.
- Payer gets expert advice since the consultant is an expert in the relevant field.
- The payer does not need to consult the different issues relating to the service to varying consultants as he retains the expert.
- A fixed contract ensures commitment and is legally binding on the expert.
Disadvantages
- As a professional working on a retainer basis, it might feel like too much work for little money. This usually happens for professionals in the field of law, human resources, etc. where the work is not linear in nature. The quantum of work can keep fluctuating but for the same level of remuneration.
- For someone who pays a consultant retainer fee, might not use the services of their consultant for a period. Nevertheless, they might have to shell out the decided amount. For example, for a lawyer on a retainer basis, the courts are closed yearly during festival season. Therefore, no work can be executed but the monthly retainer fee is still liable.
