Table Of Contents
Rent Control Definition
Rent control is a legislative practice allowing governments to determine maximum limits and annual growth in rental rates in certain cities and states. Once enacted, the rule restricts landlords from charging or raising rent or lease rates past a certain percentage.
These laws are put in place to protect the rights of tenants and their unexpected eviction. It also aims at preventing dramatic rent increases, thus promoting affordable rental housing. Rent regulation will look different depending on the governing body enacting the laws and competition in the housing market.
Key Takeaways
- Rent control is a method of regulating rental prices in certain cities and states. It also protects tenants' rights, such as wrongful eviction.
- The first generation of rent regulations was essentially a cap on rental rates, preventing the landlord from raising rental rates. The term used today is more closely associated with rent stabilization (excluding NYC).
- These laws vary depending on the location of the rental house.
- The measure works well in areas where there is a lot of competition in the housing sector, and it helps to keep rental housing affordable.
How Does Rent Control Work?
It is common to find rent regulations in populated cities with high rent prices or minimal units available to rent. Earlier, when rent regulations were first introduced in the 1920s, they acted as price ceilings that did not allow the landlord to raise rent prices over a specific amount.
It went on for some time until the housing boom of the 1950s hit following World War II, and cities had no choice but to discontinue the practices that regulators put in place. This set of laws became known as the “first generation rent control.”
However, it is hard to find ideal first-generation rent regulations in the modern world (outside of NYC). Since the laws have been revised to suit the needs of society, they are now considered obsolete.
When rent regulations are in place, the landlord has to follow the municipality guidelines while charging or raising the rent.
Second-Generation Rent Control Laws
Rent regulations today look much different from when they were first introduced and can vary depending on the tenant's location. These are now decided by a board of members commonly referred to as “rent boards.” The rent board will draw up detailed guidelines that outline specific tenant and landlord laws. These laws will look different in each state or city.
These rent caps determine how many times a landlord can raise the rent and the percentage of rent increases that can be made. Along with these laws, the rent boards will usually include other regulations such as hindering the landlord’s ability to evict the tenant.
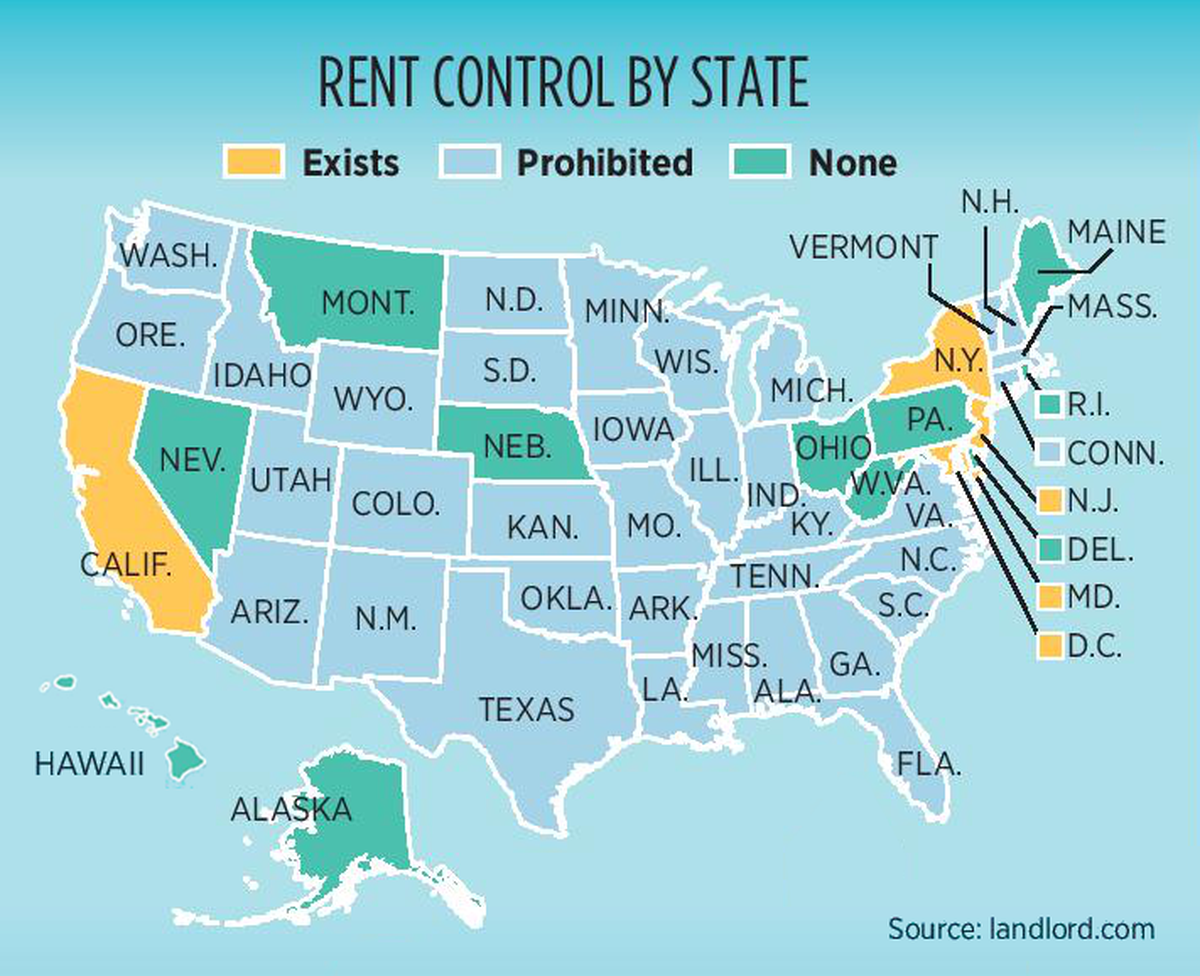
However, not every state in the US will regulate rent and put forth rent regulations. Only four states have active rent regulations, including:
- New Jersey
- New York
- California
- Maryland
These four US states and Washington D.C. have dedicated rent regulations to protect the rights of tenants. One can also find variations of rent regulations in various jurisdictions, such as Europe and Canada.
Although the amount a landlord can increase rent is limited while the tenant is living in the unit, it will typically have the ability to raise the rent to relative market prices when the tenant moves out. This practice is designed to protect the tenant from the landlord attempting to raise rates on a tenant to get them to move out.
Lease vs Rent - Explained in Video
Rent Control Examples
Considering the growing demand for affordable housing in 2020, US states like California, New York, and Oregon have introduced the latest rent regulations as a potential solution. Here are a few examples of rent regulations currently in effect in cities throughout the US and abroad.
#1 - Rent Control in Los Angeles
Los Angeles undeniably fits the description of a populous city with limited units available to rent. The majority of people living in the Los Angeles area are renters as the city has one of the lowest homeownership rates in the US.
California became the second state in the US to implement a statewide rent control act in 2019. In Los Angeles, the following rules apply:
- Overall rent increases are limited to 8%
- Landlords can increase rent rates once a year (12 months)
- Additional roommates may add 10% to a tenant's rent
- Landlords must give a 30 days-notice when increasing rent
On top of these rules, if the landlord pays the tenant’s utilities, they may also raise the rent by 1% each year.
#2 - Rent Control in San Francisco
San Francisco is known for its sky-high housing prices. But with so much demand for rental units, this is one way to keep costs in check. In San Francisco, the following rent regulations apply:
- Rent increases are limited to a maximum of 7% per year
- Prices can be raised every 12 months
- There is no charge for additional roommates
San Francisco also does not have rules for when tenants pay utility bills.
#3 - Rent Control in New York City
New York City has been at the center of rent regulations ever since they were first introduced to the city. The rent control situation in NYC is slightly different than in other cities. They have two types of regulation with different meanings, including:
Rent Control
This term has a different meaning in the NYC area. Units considered “rent control” requires it to have a tenant living there since July 1, 1971. However, the tenant can pass its apartment to a family member so long as they have lived in it for a minimum of two years. The regulations include:
- Increases are limited to 7.5% every two years
- Rent cannot exceed a maximum rate set on a per-unit basis
Rent Stabilization
Once a tenant from a rent controlled apartment moves out, the unit will then be considered “rent stabilized.” The NYC regulation does not necessarily provide an exact amount that limits the amount that a landlord can raise the rent by.
However, specific rules apply to protect tenants, such as written notice when raising rates over 5%.
#4 - Rent Control in Ontario
- In Ontario, the rent regulations are regulated by the Landlord and Tenant Board. They set the maximum amount of landlords can increase rent each year. For example, in 2020, the board limited the maximum rent increase to 2.2%.
- They will also only have the ability to increase rent every 12 months and provide written notice at least 90 days in advance.
Rent Control Pros and Cons
Pros
- Keeps a check on rental prices, keeping the cost of housing affordable in big cities
- Allows low- and moderate-income families and elderly to afford rental housing
- Limits the landlord’s ability to “squeeze out” tenants by raising rent substantially
- Allows different classes of workers to live in big cities
Cons
- Constricts the landlord’s ability to raise rent and generate more income
- Can lead to fewer units available to rent
- Forces landlords to use rent controlled apartments for commercial purposes
- Disincentivizes builders and property owners to construct or maintain rental units
Rent Control vs. Rent Stabilized
The two terms rent control and rent stabilized are often used interchangeably. They do, however, have some main differences that one should be aware of.
- With the first generation of rent regulations being considered the ideal “rent control,” the landlord cannot raise rent past a certain amount that acts as a ceiling. Most rent-controlled units are families that have lived in the units before 1971. Many states prevent these types of laws or do not use them in their cities.
- On the other hand, with rent stabilization, the landlord can increase rent by a certain percentage determined by a rent board. In most cases, the landlord can only implement the rent increase after a certain amount of time has passed since the last increase.