Table Of Contents
Remuneration Meaning
Remuneration refers to overall monetary and non-monetary compensation that employees or independent contractors receive for providing services to an organization or company. The employment contract breaks it down into the base salary, bonuses, incentives, overtime payments, commissions, vacations, etc.
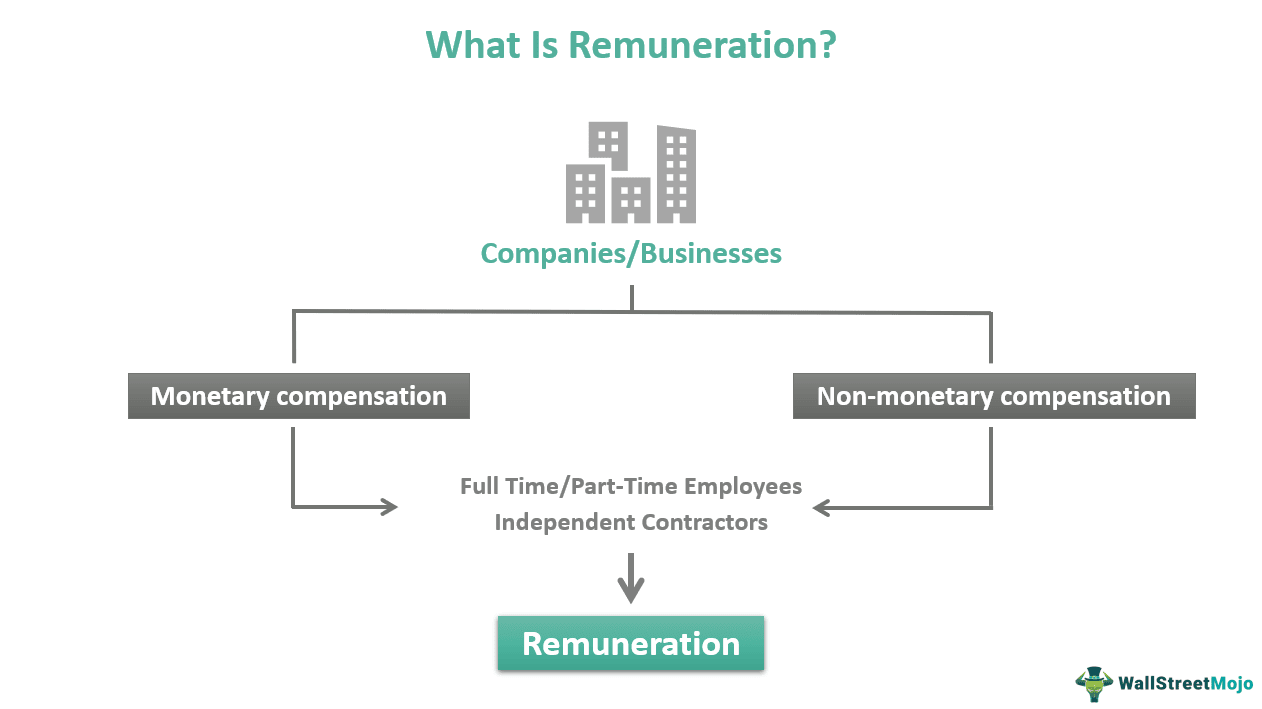
The payment can be direct, i.e., fixed or indirect, i.e., variable, depending on the nature of the job, worker abilities, and corporate structure. Companies provide this as a means of motivating employees and increasing productivity. Recompense differs from salary in that the latter is a subset of it and is a fixed and regular payment for services.
Key Takeaways
- The remuneration definition describes the total monetary and non-monetary compensation that workers or independent contractors receive for performing services for an organization or firm.
- The recompense components include base salary, bonuses and incentives, overtime payments, commissions, paid time off, retirement contributions, vacations, and other benefits.
- It can be direct (fixed) or indirect (variable) based on the nature of the job, employee capabilities, and business structure.
- It differs from salary in the latter is a subset of the former and is offered as a fixed and consistent payment for services.
- Recompense received is a precondition of work and is an effective means of motivating employees and increasing productivity.
Understanding Remuneration
The remuneration package consists of financial and non-financial perks that a full-time or independent worker gets for their work. It is the precondition of employment and acts as a motivation for employees who desire fair compensation. Thus, companies develop a remuneration policy to reward and motivate their staff to be better and more productive. Also, it let employees know what they can expect from their efforts at work. While some people seek higher monetary compensation, others value non-monetary perks such as paid sick leaves, holidays, use of business assets, etc.
Recompense can either be direct (fixed) or indirect (variable). Direct compensation includes any cash payments made to employees, such as wages, salary, bonuses, incentives, commissions, etc. Indirect compensation includes rewards like overtime pay, contributions to retirement plans, travel packages, flexible work hours, food, lodging, and business transportation, among other things.
When the demand for skilled workers is more than the supply, the recompense automatically increases to a great extent. That is why some companies propose lavish packages with better compensation and more benefits – a tactic called golden hello - to recruit desirable candidates.
The remuneration for employment may include base salary, bonuses, allowances, expense accounts, and other financial benefits. Some companies offer deserving candidates stock options as part of the recompense if their business model allows.
The National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI) establishes some guidelines for determining what qualifies as recompense and what does not in the context of workers' compensation insurance. According to the Internal Revenue Service, wages, allowances, and other perks provided as recompense are taxable.
Remuneration Factors
The remuneration policy for a worker depends on the value they add to the organization. In short, employee productivity is an essential consideration before finalizing the recompense. Besides, several other factors determine its components, including:
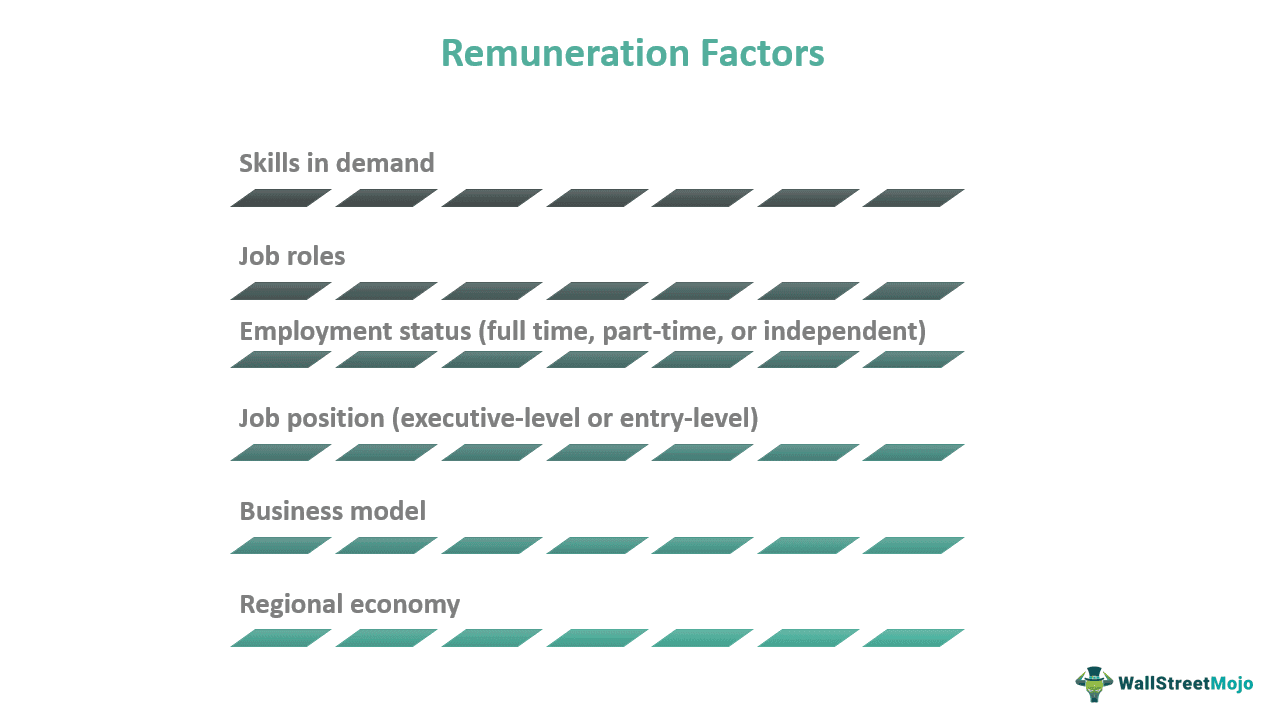
- Skills in demand
- Job roles
- Employment status (full time, part-time, or independent)
- Job position (executive-level or entry-level)
- Business model
- Regional economy
Types of Remuneration
As previously stated, there are two types of remuneration - direct (fixed) and indirect (variable):
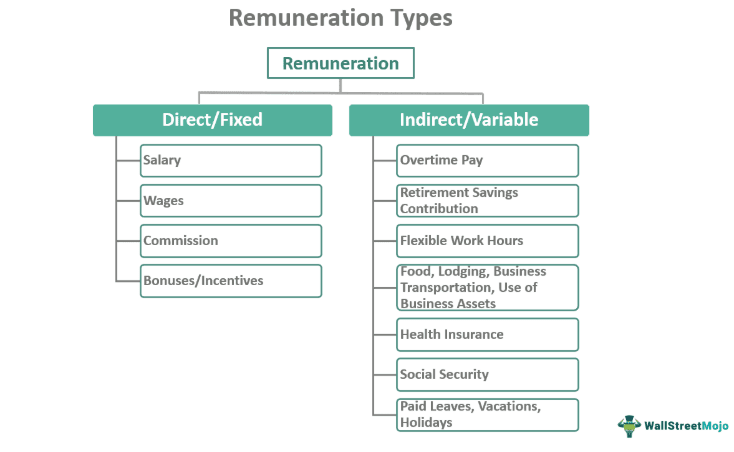
Direct Remuneration
#1 - Salary
Most workers do not even think beyond salary when it comes to the recompense offered to them. For them, recompense means salary, and hence salary is the most common form of direct compensation. Companies consider the value an employee can bring to the role before deciding the salary.
Thus, the salary becomes a fixed reward for employees, and they work hard to receive a raise either quarterly, annually, or even earlier in some cases. Salaries are represented in annual terms and are payable during paid time off, holidays, and vacations.
#2 - Wages
These are payments provided to employees on an hourly or daily basis. Wages are another type of direct compensation, and workers are eligible for overtime pay for working extra hours.
#3 - Commissions
This payment structure is quite common in sales and brokerage. Salespeople usually receive a portion of sales revenue as a commission for closing the deal. Similarly, brokers get a percentage of the purchase price as commission for assisting the owner with selling their property.
#4 -Bonuses & Incentives
Some businesses reward their employees based on their performance or project completion or holidays or on making a profit. Those who perform well receive hefty bonuses, and hence these are another form of direct compensation for individuals. For example, when sales and marketing executives achieve their targets, they get incentives. It can be paid either in cash or as gifts.
Indirect Remuneration
#1 - Overtime Payments
Employees or individuals working beyond their usual working hours receive monetary incentives.
#2 - Retirement Benefits
Employees receive a regular, fixed monthly income or salary, but most companies secure their future after retirement by offering monetary benefits. Thus, if individuals retire from their jobs, they get paid for their long-term services to their employers.
#3 - Flexible Work Hours
Providing flexible working hours to workers and employees might result in increased productivity. It, thus, adds more value to the company output. Most importantly, employees feel valued this way, which is more than any monetary reward they would ever receive.
#4 - Social Benefits
Health insurance coverage, restaurant checks, gym memberships, Social Security, Medicare, the use of company assets (such as mobile or car), housing, meals, store credits, etc., are some of the benefits that organizations offer to their employees.
Remuneration vs Salary
People sometimes interchange the phrases recompense and salary. There are a few differences between the two, though.
- While remuneration is the total compensation that an employee receives, salary is one of its components.
- Employees or workers receive recompense in exchange for their services, but salary indicates a level of professionalism.
- Recompense is a broader term that includes everything from basic salary to bonuses to other benefits, etc. On the other hand, salary is a subset of this.
- Recompense can be direct or indirect, while salary is a fixed and regular payment for services.
- The word remuneration finds its origin in the Latin term, ‘remuneration,' meaning ‘reward’ or ‘repayment.’ Salary is the term derived yet again from the Latin word ‘salarie,’ which means ‘salt money.’
