Table Of Contents
What Is Real Interest Rate Formula?
The Real Interest Rate formula refers to the mathematical equation or expression that helps calculates the interest rate after excluding the impact of inflation. It provides a means to measure inflation-adjusted return on investments in financial security or a loan or deposits.
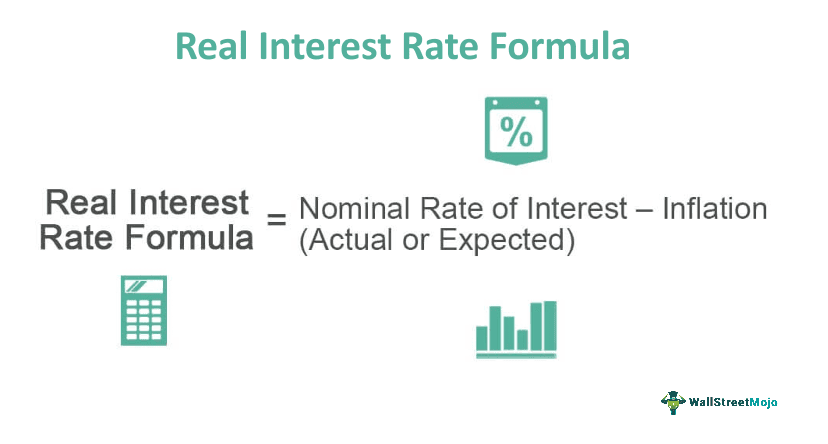
The real interest rate formula is, basically, the difference between the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate. The computation helps lenders learn about the real returns they are supposed to receive on the lent amount. When adjusted for inflation, the figure clear and hence, firms can evaluate the real values.
Key Takeaways
- The real interest rate formula estimates the interest rate after removing the inflation's effects. In addition, it enables a medium to determine the inflation-adjusted return on investments in financial security, a loan, or deposits.
- The difference between a nominal interest rate and an inflation rate is a real interest rate.
- The real interest rate must adjust the market's observed interest rate to eliminate the current or expected inflation impact.
- Moreover, it shows the purchasing power value of the interest paid on a loan or an investment.
- The interest rate represents the lender's and the borrower's preferred time.
- Since the inflation rate is not constant, the prospective real interest rate depends on the future inflation prediction expected over the investment or loan maturity.
Real Interest Rate Formula Explained
Real interest rate formula works on Fisher equation that clearly states that it is nominal rate of interest less the inflation, be it actual one or expected. This rate of real interest further determines the likelihood of people to prefer current goods over future items. In such instances, borrowers are ready to pay even higher rate of interest for the lent funds, given their willingness to the funds at that point in time.
The formula is given below:
The real interest rate is the nominal interest rate adjusted to inflation. The latter is the one that lenders reveal to borrowers. If they are willing to pay it, they can borrow the amount. It is important for lenders to adjust the real interest rate, making the nominal interest rate payable so that they do not have to suffer even if the inflation occurs.
In short, lenders or investors try to play safe by adjusting the real rate of interest and introducing nominal ones as the real rates to public. This is how the values become clear using the real rate of interest formula.
How To Calculate?
For calculating the real interest rate using the formula, there are a series of steps that one has to follow. Listed below are those steps:
- Have the nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate considered before adjusting it to inflation. This is one of the most components of the calculation.
- The second one is the inflation rate, which can be the actual rate of interest or an expected rate of interest.
- The difference between the two is that it is the nominal rate of interest and an inflation rate is the real rate of interest.
Examples
Let us consider the following instances to understand how this real interest rate formula works:
Example #1
The nominal rate of interest that has been prevailing for a long time has been around 9%, and the rate of inflation has come out as 3%. You are required to calculate the real rate of interest.
Solution:
Use below given data for calculation of real interest rate.
- Nominal rate of Interest: 9%
- Inflation Rate: 3%
Calculation of real interest rate can be done as follows:

We are given both figures to calculate the real rate of interest.
Real Interest Rate = 9% - 3%
Real Interest Rate will be -

Real Interest Rate = 6%
Hence, the real rate of interest is 6%.
Example #2
The World Bank has been tasked with completing statistics of some of the countries. They are now left with two countries for which the deadline to complete the statistics is by next week. William has recently joined the team, which calculates interest rates. William is an economist and has done the master's in it. He was given a task to calculate the real rate of interest for the remaining two countries, X and Y. Below are the details collected by the ex-employee for these countries.
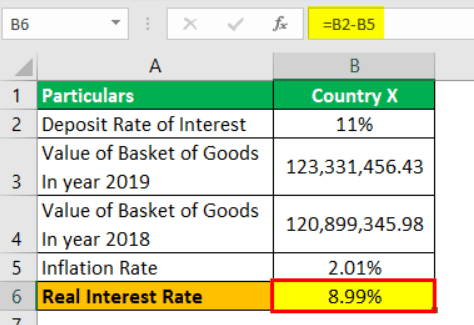
| Particulars | Country X | Country Y |
|---|---|---|
| Deposit Rate of Interest | 11% | 10.50% |
| Value of Basket of Goods in year 2019 | 123,331,456.43 | 141,678,331.23 |
| Value of Basket of Goods in year 2018 | 120,899,345.98 | 140,993,221.77 |
Based on the above available information, you are required to calculate the real rate of interest. If someone wants to invest their funds, where should one invest whether in Country X or Country Y?
Solution:
Here, we have to have a nominal rate of interest which is the deposit rate of interest, but we are not given the real rate of interest which we shall calculate for both countries.
Inflation Rate for Country X will be -
Inflation Rate = 123,331,456.43 / 120,899,345.98 - 1 = 2.01%.
Calculation of Real Interest Rate for Country X can be done as follows:

Real Interest Rate = 11% - 2.01%
Real Interest Rate for Country X will be -

Real Interest Rate = 8.99%
Inflation Rate for Country Y will be -
Inflation Rate = 141,678,331.23 / 140,993,221.77 - 1 = 0.49%
Calculation of Real Interest Rate for Country Y can be done as follows:

Real Interest Rate = 10.50% - 0.49%
Real Interest Rate for Country Y will be -

Real Interest Rate = 10.01%
Hence, in real terms, it is better to invest in country Y as the country provides a higher rate of interest.
Example #3
XYZ wants to invest in a fixed deposit, and he wants ABC bank. The bank pays a 7% rate of interest irrespective of the duration and amount. The fixed deposit amount is $100,000. He happily invests the amount for a period of 3 years. Later, on a news channel, he learns that the country is facing a high level of inflation, and currently its 8% and further it was expected that after 3 years it will be 8.50%.
Based on the above scenario, you are required to confirm whether XYZ will earn or lose money?
Solution:
Use below given data for calculation of real interest rate.
- Nominal Rate of Interest: 7.00%
- Inflation Rate: 8.50%
First, we shall calculate the real rate of interest. Since XYZ is investing for 3 years, and hence while calculating a real rate of interest, we shall use the expected inflation rate of interest which is 8.50% and not 8.00%.
Calculation of real interest rate can be done as follows:

Real Interest Rate = 7% - 8.50%
Real Interest Rate will be -

Real Interest Rate = -1.50%
Hence, the real rate of interest is -1.50%, which clearly indicates XYZ will lose money in real terms since inflation is greater than the rate of interest offered by the bank.
Relevance and Uses
The real interest rate formula, when applied, helps lenders and investors be aware of the returns on their investments post adjustment to inflation criteria. As a result, they remain prepare even for the worst scenarios that may occur in the future. In addition, there are individuals who, when the real interest rate is obtained, opt to enjoy the present use of the financial goods than waiting to have it in future. Let us have a look at some of the points that reflect the importance and relevance of this formula:
- The real rate of interest shall adjust the observed interest rate of the market so as to remove the effects of ongoing or expected inflation.
- The real rate of interest does reflect the purchasing power value of the interest which is paid on a loan or an investment and which shall represent the rate of interest that will be preferred time of the lender and the borrower.
- As the rate of inflation does not remain constant, the prospective real rate of interest will rely on the estimates of future inflation that will be expected over the time to maturity of an investment or a loan.