Table of Contents
Real Estate Limited Partnerships (RELP) Meaning
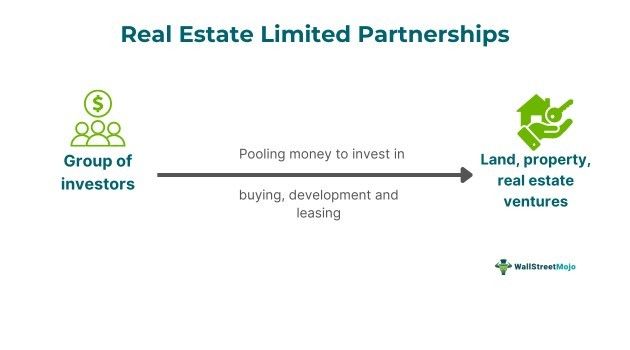
A real estate limited partnership (RELP) is a partnership that invests in land, property and different types of real estate projects and land development investments. It is formed by a group of investors pooling their funds to raise high capital to invest in buying property, developing and leasing it.
A RELP is structured in a way that one partner is responsible for taking care of the investment and is liable for every operation as a general partner. In contrast, the other partners mostly fulfill the role of contributing with their money and have limited liability and authority. It operates like a legal entity and so can own properties, enter contracts, sue and be sued.
Key Takeaways
- Real Estate Limited Partnerships represent a group of investors pooling money to invest in real estate ventures primarily.
- RELPs offer high returns and diversification in investment portfolios and are structured to offer large tax benefits to investors.
- Many people criticize it over lack of control, liquidity issues and not being a publicly traded company like real estate investment trusts (REIT).
- The RELPs typically have a period of 10 to 15 years and require a reasonably high amount of capital investment. In the end, the partnerships are liquidated and distributed among the partners.
Real Estate Limited Partnerships Explained
A real estate limited partnership (RELP) operates as a legal entity to form a pool of money through a group of investors serving as partners in the RELP structure. In this setup, there are two types of partners or investors. The general and limited partners, the former, are mostly one or, in rare cases, more than two who are liable and responsible for most of the partnership and investment decisions such as choice of real estate avenues, strategies, capital allocation, and overall management. The latter has less or no liability and only contributes with the money they bring in to raise the capital. RELPs offer investors a chance to invest in the real estate market, tax benefits, and management control.
Compared to stocks, bonds and equity, RELPs have less or no liquidity and are difficult to sell. They mostly invest in commercial properties such as office buildings, apartments, shopping complexes and market centers. Still, they are always open to investing in residential properties such as single-family residences, beach houses, vacation homes and condominiums. RELPs are good investments, especially for investors more interested in the real estate market than other financial markets. Still, the risks such as volatility, illiquidity and external factors exist there as well.
In this setup of general partners and limited partners, the general partners are mostly professional real estate managers with years of experience and expertise in the real estate market. The minimum investment in RELPs varies but is typically a large amount of money. The managers are responsible for finding properties, negotiating, managing and maintaining post-purchase. It ideally has a period of ten to fifteen years, at the end of which the partnership is liquidated and distributed among the partners.
Examples
Here are two examples of real estate limited partnerships, The first is hypothetical, whereas the second example is from World News -
Example #1
Suppose John and his other two friends form a RELP; John is the general partner and hence looks after the whole management of the partnership, strategies, investments and operations, while the other two partners serve as limited partners. Their only contribution is to bring in and pool funds to invest in real estate. This whole setup operates like a legal entity but like a private firm and, hence, is not a publicly traded company.
Since it operates like a corporation, it can buy, rent, lease, and develop properties under one single name, enter into contracts, sue or be sued by someone. It is a simple hypothetical example of real estate limited partnerships, but in the real world, many considerations must be taken into account.
Example #2
Suppose John and his other two friends form a RELP; John is the general partner and hence looks after the whole management of the partnership, strategies, investments and operations, while the other two partners serve as limited partners. Their only contribution is to bring in and pool funds to invest in real estate. This whole setup operates like a legal entity but like a private firm and, hence, is not a publicly traded company.
Since it operates like a corporation, it can buy, rent, lease, and develop properties under one single name, enter into contracts, sue or be sued by someone. It is a simple hypothetical example of real estate limited partnerships, but in the real world, many considerations must be taken into account.
Taxation
The tax implications of RELPs work as follows -
- Real estate limited partnerships are pass-through entities from the tax authorities' perspective. It avoids double taxation.
- In a pass-through entity, the partnership itself has no liability to pay income taxes. On the contrary, the profit and losses are passed through to the individual partners.
- Each investor in the partnership reports their share of the partnership income on their tax return filing.
- Some RELPs qualify for special tax incentives for renewable energy projects and affordable housing. The partners should consult tax professionals to help them understand every minute detail and complexity.
- RELP taxations are based on the treatment of distributions, which means the partnership distributes to their investing partners periodically, typically on a quarterly or yearly basis.
- Again, these distributions are part income and part capital return, but income is taxable, whereas the capital returns are not. It reduces the partner's tax basis in their investment, leading to higher capital gains.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages of real estate limited partnerships are -
- With RELPs, there exists a potential for high returns as they invest in both residential and commercial properties and generate substantial income with time.
- RELPs are well diversified within investment portfolios and operate with reduced risk exposure along with other asset classes.
- The RELPs are so structured that they provide major tax advantages and additional benefits. For instance, the profits are passed directly to partners.
- The disadvantages of real estate limited partnerships are -
- Since RELPs are not publicly traded firms, investors cannot easily sell stakes, and hence, this raises liquidity issues.
- There is a certain degree of risk attached to it with activities like property devaluation, economic downturns, and poor management.
- Limited partners are only tasked with bringing in the funds to invest but have limited control over the management of the partnership. In RELPs, one general partner is liable for the major control and authority.
Real Estate Limited Partnership vs REIT
The main differences between a real estate limited partnership and a REIT are -
- In RELPs, the structure is designed with one general partner managing the partnership and limited partners offering capital. In comparison, REITs are public traded companies that use investors' funds to invest across different real estate ventures.
- RELPs are more flexible regarding involvement, control, management and investment strategies. In contrast, REITs offer diversification and liquidity, allowing investors to trade shares in stock exchanges.
- RELPs provide better potential tax benefits but REITs are only subject to specific tax regulations as the tax implication differs between them.
