Table Of Contents
What Is Quantitative Trading?
Quantitative trading is a computer software-based trading strategy that uses mathematical models and calculations to assess patterns and trends in the movement and behavior of stock prices to pick undervalued stocks at the right time and execute a profitable trade.
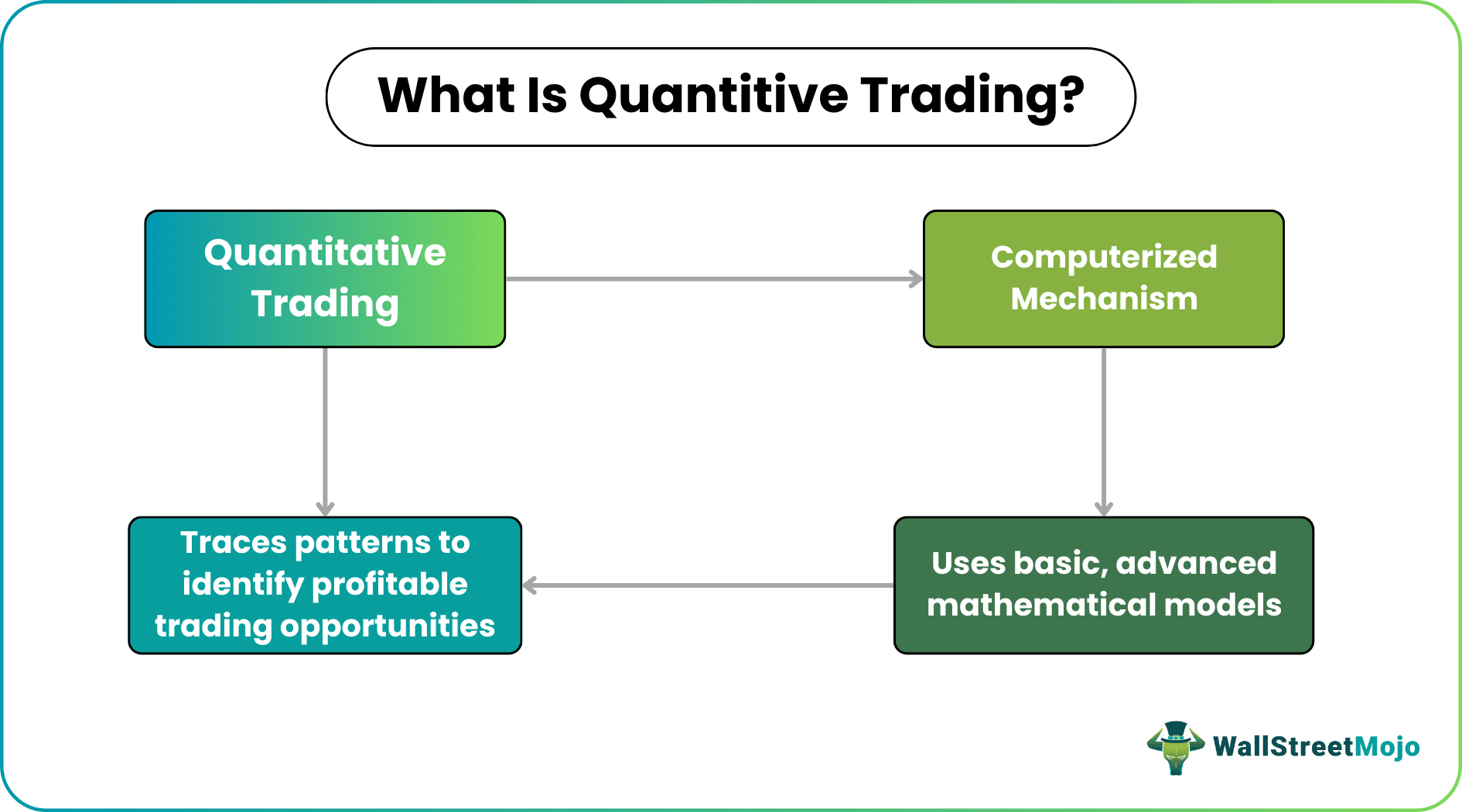
A quantitative trading firm helps pick under-priced stocks and find assets above their actual worth, eliminating human intervention from investment decision-making. This computer program-based model picks up a trend that the human mind may fail to grasp, thereby helping traders identify hidden trading opportunities. Retail investors widely use quantitative trading strategies.
Table of contents
- What is Quantitative Trading?
- Quantitative trading is a computer-based software strategy that utilizes mathematical models and calculations to evaluate patterns and trends in the stock price movement and behavior to select undervalued stocks at the right time and execute a profitable trade.
- The objective of quantitative trading is to choose under-priced stocks and search for assets above their actual worth, discarding human intervention from human decision-making.
- The components of this trading technique are strategy identification, strategy backtesting, execution systems, and risk management.
- Most quantitative models are profitable only for a specific market type or condition for which the model is made. As market conditions evolve, one must redevelop them.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
How Does Quantitative Trading Work?
The quantitative trading strategy is usually based on inputs, like price and volume at which they are traded. However, share price fluctuations often do not have a fixed pattern and they exhibit cyclical patterns, This is where these quantitative techniques help cash in on those trends.
The trading models use price and volume as their core inputs for mathematical model building. It has technology as its cornerstone, which enables a faster and more profitable trade execution.
These are based on algorithmic and complex statistical models and are fast-paced with short-term trading goals. Quantitative traders are well-versed in numerical tools like moving averages. They capitalize on technology and mathematical and statistical models for sharp trading strategies. Finally, they take a trading strategy and build a mathematical model based on historical data. Once the model is created, it is then tested and evaluated.
The results derived post-implementation of these techniques are used for real capital and market trading. The operation of these models is analogous to climate forecasting, where probabilistic techniques are utilized based on historical data to predict the weather. Also, traders use the same method to market data to make investing decisions.
Examples Of Quantitative Trading
Bob trades an XYZ fund. He uses an algorithmic system to select and pick stocks. The system scans more than 50 variables in five categories, i.e., momentum, value, earnings, and volume, to pick and choose stocks.
It puts a value on each variable Based on the results, Bob decides to choose the highest ratings.
Components
It broadly consists of four major components: -
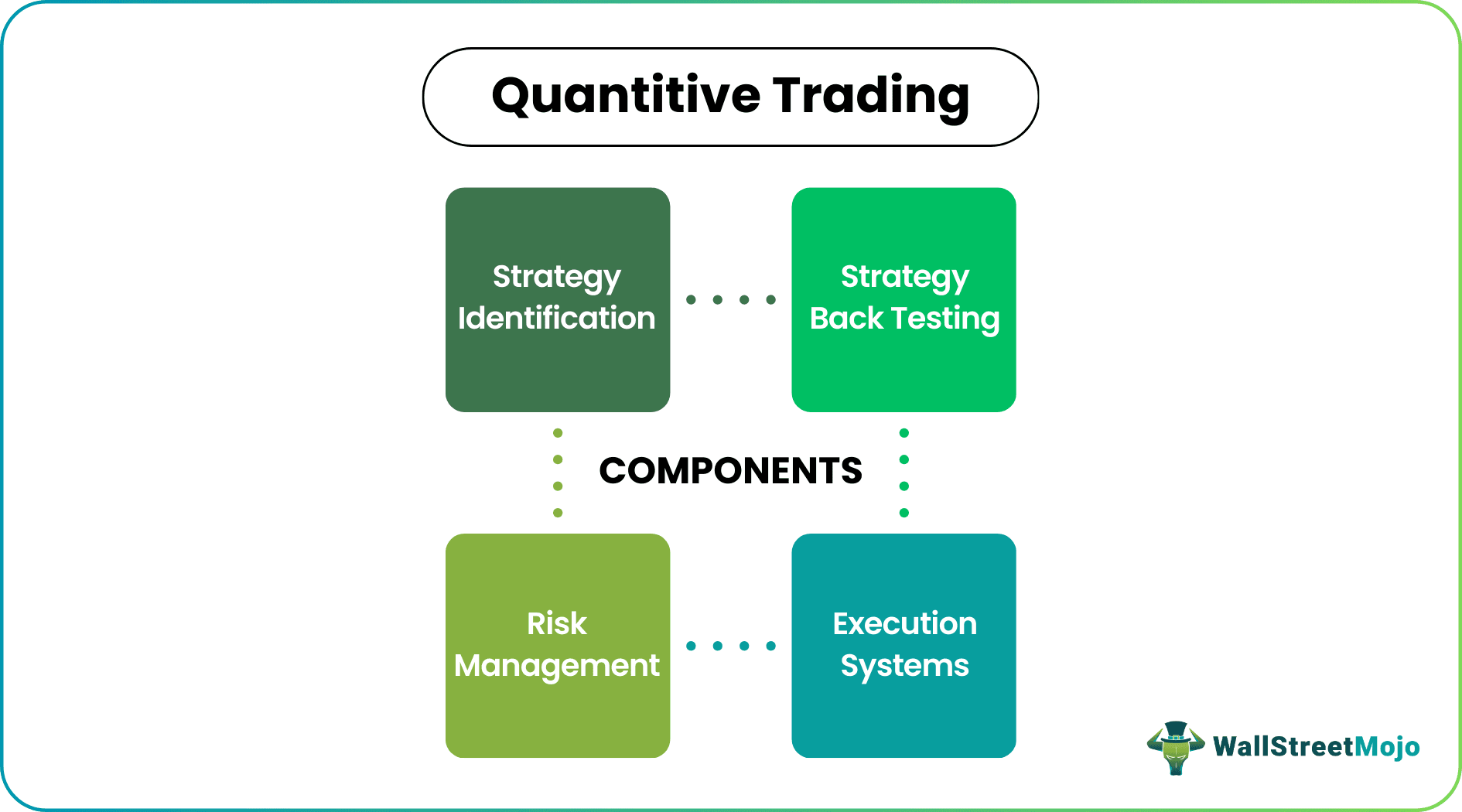
#1 - Strategy Identification
It starts with finding a strategy, exploring a market opportunity, and narrowing down the trading frequency. Any quantitative trading plan commences with an extensive period of research. The process includes: -
- Devising a strategy and assessing whether it is suitable with the current set of designs.
- Gathering any data required to test the strategy.
- Upgrading the strategy to get greater returns and reduce the risk.
This helps retail investors determine their capital requirements and how transaction costs affect their decisions.
#2 - Strategy Backtesting
The backtesting technique is profitable when used on historical and out-of-sample data and works in the actual market. However, backtesting is not conclusive evidence of how successful the plan will be. It is subject to numerous biases that it may remove as far as possible. The other backtesting factors include the availability of historical records, transaction costs involved, and deciding a suitable backtesting method. Once the strategy is determined, one must gather historical records to perform testing. There are many data sources available for the same. Their costs may vary based on the quality of the data.
#3 - Execution Systems
An execution system is an approach to executing a set of trades per trading strategy. The trade execution may be semi-manual or automated. The major concern when devising an execution system is the interface with the brokerage and the minimization of transaction costs. So, the ideal path will be to automate the execution mechanism of one trade. Also, it allows you to focus on research and run strategies of higher frequency.
#4 - Risk Management
The final issue in quantitative trading is risk management. It includes biases like technology and brokerage risk, which is the broker's bankruptcy. In brief, it provides everything possible that may hinder trading.
How To Become A Quantitative Trader?
A potential quant trader must possess the appropriate skills and tools before getting into quantitative trading jobs. Therefore, strong finance, mathematics, and computer programming background are prerequisites for an aspirant quantitative trader.
Advantages
The advantages of using these techniques are as follows:
- This trading type aims to calculate the probability of a gainful trade.
- It enables effective monitoring, analysis, and trading judgments on a given set of stocks.
- Quantitative methods enhance effective trading decisions by using computer algorithms to analyze and make profitable trading decisions.
- It weeds out the emotion of fear and greed and promotes rational decisions, not leaving things to surmise or chance.
Disadvantages
The strategy has its set of flaws, which include the following:
- The financial markets are volatile, requiring the algorithmic models to evolve consistently.
- Most quantitative models are profitable only for a particular market type or condition for which the model applies. Thus, the analysts need to redevelop them as the market conditions evolve.
Quantitative Trading vs Algorithmic Trading
Though both quantitative trading and algorithmic trading are computerized trading techniques, their approach to analyzing patterns and trends differ widely. Let us have a look at the differences between the two terms:
| Category | Quantitative Trading | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Models used | Mathematical and statistical models | Algorithms |
| Objective | Predicts market trends and patterns | Places trades based on predefined rules |
| Focus | More technical and complex datasets | Historical stock data |
| Execution | Trading executed manually after analysis | Trading executed automatically |
For professional-grade stock and crypto charts, we recommend TradingView – one of the most trusted platforms among traders.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
One who aspires to be a quant must have a minimum background in finance, computer programming, and mathematics. In addition, one must also have exceptional skills in quantitative analysis. The pay and benefits that come with becoming a quant trader seem to be quite profitable. Still, those who wish to enter this fiercely competitive industry must possess various abilities. Due to fatigue, many quantitative traders diversify their portfolios or move on to different markets after a few years. As a result, they often have a mediocre success rate.
Usually, quantitative traders have a moderate success rate. Many even diversify or opt for the other streams after a run down.
Master’s degrees in quantitative financial modeling, financial engineering, an MBA, or a bachelor’s degree in Math are all helpful for quantitative trading.
Quants use machine learning, neural networks, statistical tools like the Sharpe ratio, etc., and technical tools/indicators like moving averages, trend lines, and oscillators.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to what is Quantitative Trading. We explain how the strategy works along with an example, components, advantages, and disadvantages. You can learn more about trading from the following articles: –