Table Of Contents
What is Quantitative Analysis?
Quantitative analysis (QA) is a mathematical approach that collects data, studies, measures, and analyzes it. It uses various techniques like statistical research, financial modeling, and other scientific methods. The main objective of QA is to use simplified, refined data to make better decisions and forecast trends.
Quantitative analysis of data is a very important statistical tool with countless applications. For example, governments employ quantitative analysis to measure the economic parameters and is used by businesses to evaluate their financial performance. Investors also adopt it to select investments.
Key Takeaways
- Quantitative analysis is a statistical tool that collects and studies vast amounts of relevant data. Insights gained from the data can help understand the behavior and trends.
- It is a diversely adopted approach as it has many benefits and can help achieve corporate, public, or individual objectives.
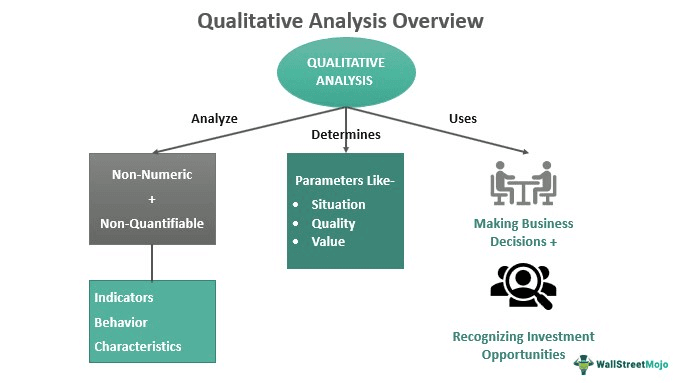
- Like QA, qualitative analysis is another important tool that uses intangible information in decision-making. One can incorporate quantitative and qualitative analysis for best results.
- Major types of quantitative analysis include descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental analysis.
Quantitative Analysis Explained
Quantitative analysis of data is a concept that has always been used. For example, since people moved on from the barter system and started using commodity money, they have estimated and evaluated their profits and losses in value.
However, the QA techniques now in use are very complex. There are tons of data available, each important in its way. For instance, suppose there's an e-retailer. There are many factors the retailer has to consider, such as the number of people visiting the website, the number of people who make purchases, the average bill amount, etc. These are the basic factors any retailer will consider.
But in the digital era, the e-retailer will also have to evaluate the performance of online advertisements and social media marketing and even account for why visitors are not making purchases or why a certain marketing campaign is ineffective. Nevertheless, fortunately for the retailer, there is data.
Complexity of Quantitative analysis
The complexity of the QA can be attributed to technology and digitization. As a result, there are many metrics to track, many variables to measure, and many parameters to evaluate. Especially in big establishments like governmental organizations, there are numerous factors to consider.
For example, governments measure different parameters related to national income, expenditure, public health, international and domestic trade, education, employment, etc. They also analyze past trends, understand present conditions, and predict changes in the future.
Methods
There are mainly four methods or types of quantitative analysis – descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental analysis.
- Descriptive analysis – This type of analysis is mostly observational, i.e., the analyst observes the area of study, collects data, and develops insights. There is not much technical aspect here, except in the compilation and differentiation of data. It helps measure a variable, and to an extent, it is possible to establish relationships between two variables. Descriptive analysis is used in case studies or mostly for understanding the present situation of the analysts' field of study. For example, how do teenagers react to a strict reduction in screen time at home? Or what are the unemployment patterns in a country? These questions need to be answered.
- Correlational analysis – In this method, analysts establish the correlation between multiple variables. It quantifies how a change in one variable can alter the other dependent variables. The correlational analysis is a type of descriptive analysis, as its scope only extends to studying the relationship. Such a type of analysis can be used in understanding the improvement in living standards when per capita income increases by a certain amount or the increase in sales of a particular product when a new version of its complementary product is introduced. The correlational analysis doesn't require complex tools. Small amounts of data can be analyzed with simple excel tools.
- Quasi-experimental analysis – Also known as causal-comparative analysis, it evaluates data and establishes the cause-effect relationship between multiple variables. Therefore, it is more complex than descriptive and correlational analyzes. In addition, such a study would require the participation of different study groups. It studies why two variables show a certain relationship. For example, how do gender and culturally diverse decision-making groups come up with better decisions? Or, why does the Russia-Ukraine war change the consumption patterns of people globally? These questions need to be studied.
- Experimental analysis – In this type of analysis, the analyst or experimenter first develops a hypothesis. Then, study groups are formed with diverse participants. The method is very complex and time-consuming. It uses scientific approaches to test the hypothesis by employing vast amounts of data and other inputs. Examples of this analysis include proving a hypothesis that encouraging creativity in the workspace can increase employees' productivity.
Example
Let's look at an example of how quantitative analysis helps to navigate uncertain markets for investments. Geopolitical risks are one of the major issues concerning those investing in foreign markets. The risk only becomes intense after the COVID-19 pandemic and worldwide surging inflation.
A recent online survey by Bloomberg shows that around 70% of investors spend too much time analyzing and optimizing risk exposure. This is where the QA tools step in, like the 'Factor Evaluation Model' created by Bloomberg Intelligence. It considers factors like value, volatility, dividend yield, etc.
In this model, investors can research and find the country-wise geopolitical trends in the past and how they affected the markets. For example, investors can check the effects of the 2020 presidential election, Greece's financial crisis, the 2011 Japan earthquake, etc. Such a tool will help investors consider different perspectives, understand the markets, and invest wisely. It also gives them better returns and assists in diversifying their portfolio by reducing risk.
Applications
QA has many real-world applications precisely because of its benefits. It can provide many insights and advantages to the entity or individual undertaking it. Check out a few applications of QA in business and finance.
Quantitative Analysis in Business
Quantitative analysis research in business is a very important tool at the companies' disposal because everything depends on data in this digital era. Today, data makes or breaks a business. But most importantly, it provides them a competitive edge if used correctly.
Businesses use QA techniques to understand consumption patterns, forecast demand, optimize supply and demand levels, organize production activities, and plan the budget. It can also tell them about customers' likes and dislikes and the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
Quantitative Analysis in Finance
The financial quantitative analysis finds applications in economies, businesses, and investments. For example, governments usually have to consider many financial aspects of an economy, like GDP, fiscal deficit, per capita income, etc. Similarly, QA in companies evaluate their financial performance, measures the value of assets, and is also necessary for financing the firm's operations. Finally, investors too analyze the performance of companies over the years, track the performance of stocks, and consider ratios like EPS, P/E, etc., before investing.
Quantitative Analysis vs. Qualitative Analysis
Like QA, qualitative analysis helps analysts study data, make better decisions, and predict outcomes. However, there are certain basic differences between the two:
| Quantitative Analysis | Qualitative Analysis |
|---|---|
| It deals with numbers and tangible sets of data. | It studies non-quantifiable and intangible information. |
| QA involves gathering data and working on it. | This type of analysis involves talking to people and understanding them. |
| Data science, machine learning, and other computer programs can help QA. | Here, machines are not of much use, as the information cannot be easily quantified. |
| Useful tools include correlational analysis, experiments, etc. | The tools used are surveys, open-ended questions, concepts, theories, publications, etc. |
| Objective in nature. | Subjective in nature. |
| Examples: Consumption patterns and economic parameters. | Examples: Why do high-paid professionals leave their corporate jobs? |
Despite these differences, both these methods are extremely significant in understanding any specific issue. Not only that, both these analyzes have different applications and are equally important in the bigger picture.
