Table Of Contents
Formula to Calculate Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Purchasing power parity refers to the exchange rate of two different currencies in equilibrium. The PPP formula is calculated by multiplying the cost of a particular product or service with the first currency by the price of the same goods or services in U.S. dollars.

The “purchasing power parity” is a term used to explain the economic theory that states the exchange rate of two currencies will be in equilibrium or at par with the ratio of their respective purchasing powers. The formula for purchasing power parity of country 1 w.r.t. country 2 can be derived by dividing the cost of a particular good basket (e.g., good X) in country 1 in currency 1 by the cost of the same good in country 2 in currency 2.
Purchasing Power Parity = Cost of good X in currency 1 / Cost of good X in currency 2
A popular practice is to calculate the purchasing power parity of a country w.r.t. the U.S. We can also modify the formula by dividing the cost of good X in currency 1 by the cost of the same good in the U.S. dollars.
Purchasing Power Parity = Cost of good X in currency 1 / Cost of good X in U.S. dollar
Key Takeaways
- Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a concept that describes the equilibrium exchange rate between two countries. In other words, it is the exchange rate at which the purchasing power of each currency is the same.
- The PPP formula can be calculated by multiplying the cost of a product or service in one currency by the price of the same product or service in US dollars.
- Understanding the PPP formula is crucial for comparing national incomes and living standards across countries. By adjusting for differences in purchasing power, PPP allows for a more accurate comparison of economic well-being.
Calculation of Purchasing Power Parity (Step-by-Step)
You can derive the PPP formula using the following four steps:
- Firstly, try to identify a good basket or commodity which is easily available in both the countries under consideration.
- Next, determine the cost of the good basket in the first country in its currency. The price will be reflective of the cost of living in the country.
- Next, analyze the cost of the good basket in the other country in its currency.
- Finally, we can compute the PPP formula of country 1 w.r.t country 2 by dividing the cost of the good basket in country 1 in currency 1 by the cost of the same good in country 2 in currency 2, as shown below.
Purchasing Power Parity = Cost of good X in currency 1 / Cost of good X in currency
Examples
Example #1
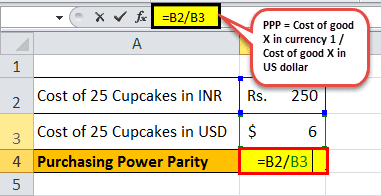
Let us take the example of purchasing power parity between India and the U.S. Suppose an American visits a particular market in India. The visitor bought 25 cupcakes for ₹250 and noticed that cupcakes are quite cheaper in India. The visitor claimed that, on average, 25 such cupcakes cost $6. Calculate the purchasing power parity between the two countries based on the given information.
Given the cost of 25 cupcakes in INR = ₹250
Cost of 25 cupcakes in USD = $6, we can calculate the purchasing power parity of India w.r.t U.S.:

Purchasing power parity = Cost of 25 cupcakes in INR / Cost of 25 cupcakes in USD
= ₹250 / $6
Calculation of purchasing power parity of India w.r.t U.S. will be:
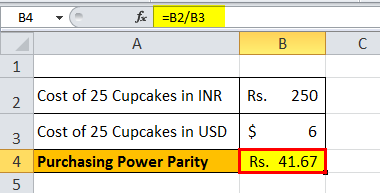
Purchasing Power Parity of India w.r.t U.S. = ₹41.67 per dollar.
Therefore, the purchasing power parity ratio of the exchange for cupcakes is USD1 = INR 41.67.
Example #2
Take another example to compute purchasing power parity between China and the U.S. In January 2018, a McDonald’s Big Mac cost $5.28 in the U.S., while the same Big Mac could be bought for $3.17 in China during the same period. Calculate the purchasing power parity between the two countries based on the given information.
- Given, Cost of Big Mac in CNY = 3.17 * CNY6.76 = CNY21.43
- Cost of Big Mac in USD = $5.28
The below table shows data for the calculation of purchasing power parity between China and the U.S.:
| Particulars | Value |
|---|---|
| Cost of Big Mac in China in USD | 3.17 |
| Cost of Big Mac in the US in USD | 5.28 |
| Exchange Rate (CNY/USD) | 6.76 |
| Cost of Big Mac in China in CNY | 21.43 |
The calculation of the cost of Big Mac in CNY will be:

Cost of Big Mac in CNY = 3.17 * CNY 6.76 = CNY 21.43
Therefore, the purchasing power parity of China w.r.t U.S. can be calculated as:

Purchasing Power Parity = Cost of Big Mac in CNY / Cost of Big Mac in USD
= CNY 21.43 / $5.28
Calculation of purchasing power parity of China w.r.t US will be:

Purchasing Power Parity = CNY4.06 per dollar
Therefore, the purchasing power parity ratio of the exchange for Big Mac is USD1 = CNY4.06.
Relevance and Uses
It is very important to understand the concept of the PPP formula because it is required to compare the national incomes and the standard of living of various nations. Hence, the metric of purchasing power parity between two countries represents the total number of goods and services that a single unit of one country's currency will purchase in another country, considering the price levels in both countries. Therefore, when the theory of purchasing power parity holds good, this metric should be equal to unity.
Another major application of the purchasing power parity is calculation of the gross domestic product as it helps offset the impact of inflation and other similar factors. The metric mitigates the problem of the large difference in inflation rates across countries and aids in the measurement of the relative outputs of various economies and their living standards. The variables based on purchasing power parity show the real picture, thus allowing comparison. The purchasing power parity method plays a significant role and is preferred in the analyses carried out by researchers, policymakers, and other private institutions. The variables based on purchasing power parity do not show major fluctuations in the short run. However, in the long run, the metric exhibits some variation, which indicates the direction of movement of the exchange rate.