Table Of Contents
What Is Public-Private Partnership?
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is a long-term agreement between a government agency and a private entity to offer a public service or asset. It helps generate increased efficiency in delivering public services like energy, transportation, education, and healthcare. Also, the public-private partnership examples like Natcom (Haiti) assist discern the definition and significance of PPP rules and types.
PPPs can also permit improved risk and authority distribution between private and public organizations. Moreover, a detailed analysis of long-term expansion goals and splitting risks is crucial to attaining a flourishing PPP.
Key Takeaways
- The public-private partnership definition denotes a medium or long-term contractual relationship between the public and private sector to offer quality public utilities.
- Its benefits include enhanced financing for infrastructure, increased private sector efficacy, motivated public sector refinement, and decreased risk for the public sector.
- There are seven distinct PPP models depicting the lowest to the highest degree of private sector participation.
- The real-life PPP examples include solid waste management by the West Bank and Gaza, Arlanda Express (Sweden), the West gate tunnel project (Australia), and Natcom (Haiti).
Public-Private Partnership Explained
The public-private partnership can be an instrument to provide better quality infrastructure facilities to more individuals. Moreover, it acknowledges the perception of shared perks between private and public divisions corresponding to each other in discharging particular tasks.
Governments experiencing poor infrastructure or failure collaborate with the privately held company to usher revenue streams and promote advanced and good results. Moreover, the World Bank Group assists confirm well-planned and financially sustainable PPPs, benefitting from a steady regulatory framework and efficient management.
Public private partnership rules authorize the governance to gain from the competence of the private enterprise and avoid any financial risk. Rather, it can emphasize regulations, plans, and organization by assigning regular activities. As a result, its global utilization to construct, plan, and bring architecture has notably augmented in recent decades.
Please note that the private sector duties might involve project planning, funding, functioning, building, preservation, and operation. So, this paradigm has certainly proven successful in establishing civic and industrial infrastructure.
Models Of Public-Private Partnership
In other words, here are six types of public-private partnership portraying least to most degree of private sector involvement:
1. Utility Restructuring Corporatization
Please note that these arrangements focus on public utility betterment. Moreover, they do not imply selling government shares, and the private sector is solely accountable for coherence in commercial activities.
2. Civil Works and Service Contracts
Utilities often originate goods and services via private-sector third parties. To clarify, this incorporates buying stationery and spare parts or obtaining public works like deploying cables or pipes. Also, utilities can outsource a certain service, including client service.
3. Management And Operating Contracts
These are normally short-term contracts (2-5 years) wherein the contractor governs various activities. Furthermore, they are conventionally found in the water and (somewhat) energy sector. Also, the contractor is usually compensated with fixed charges to cover the costs and employees.
4. Leases And Affermage Contracts
Mainly, these are public-private department arrangements where the private entity does not fund the investment but handles and sustains the utility. Moreover, the medium-length deals (8-15 years long) pass the collection risk to a contractor in lease.
5. Concessions, BOT and DBO
The results-focused build-operate-transfer (BOT) and Design-Build-Operate (DBO) projects commonly implicate significant layout and development and long-term assignments for greenfield (new build) or projects with necessary renovation and expansion (brownfield). Moreover, concessions cover the whole infrastructure system comprising the concessionaire’s acquisition of current assets and the production and management of new assets.
6. Joint Ventures or Partial Divestiture
Please note that the extent of share ownership varies as per the regime’s decision to maintain the utility’s management control or get the scheme off the annual report. Especially if the jointly owned company retains assets, the public sector may (at least primarily) regulate the organization for diplomatic reasons.
7. Privatization Or Full Divestiture
Privatization indicates the transferal of complete or nearly complete government interests in the sector or utility asset to the private sector. As compared to concession, it is mostly regarded as a more ultimate type of private sector participation in the utility.
Examples
Without further ado, let’s go through the public-private partnership examples.
Example#1
Check out some real-life examples of Public-Private Partnerships, namely,
- Solid waste management (West Bank and Gaza)
- National telecom Societe Anonyme (Natcom) – Haiti
- Public street lighting – India
- West gate tunnel project – Australia
- Boston logan international airport terminal A – US
- Arlanda Express – Sweden
Example#2
Switzerland recently launched a new public-private partnership titled the Sustainable Development Goals Impact Finance Initiative. Moreover, it is aimed to raise a maximum of $1.09 billion (1 billion Swiss Francs) for environmental and social schemes in developing nations.
The initiative is among the many “blended finance” reserves to be launched in new months to assist investment amplification in poorer nations.
Moreover, the prime target of the current COP26 climate convention will hopefully lure private investors to schemes in developing markets advancing the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Advantages Of Public-Private Partnership
That is to say, the following are the merits of different types of public-private partnership:
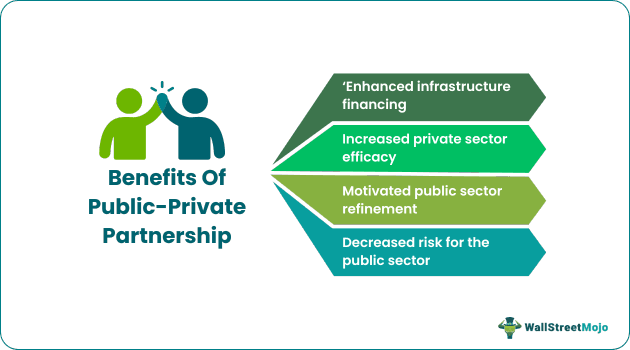
- PPPs permit the project cost expansion for the public over a prolonged period, aligned with the anticipated merits.
- It certainly allows for increased private sector efficacy through better work organization and arrangement, maximization of lifecycle expenditures, and risk management.
- PPP motivates public sector improvement with more accountability and transparency, better management, and acquisition skills.
- Above all, project risks are partially shared between private and public entities, reducing a single party's burden.
- It refines the service level uniquely for projects necessitating road user costs (like tolls).
