Table Of Contents
What Is Public Investment?
Public Investment is the expenditure made by the government to fund or create projects and assets that contribute to economic development. Also known as public capital expenditures, these initiatives carried out by federal or local governments focus on the well-being of citizens and the development of properties meant for public use.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
Government expenditures could be used for various reasons, such as stimulating economic growth, providing employment opportunities, and improving infrastructure facilities. The primary aim is to improve the well-being of society and enhance the quality of life of the people living there. These are also keys to inducing development.
Key Takeaways
- Public investments are government expenditures to fund projects that focus on social welfare. Federal or state governments can make them through publicly owned companies.
- These investments exist in three different forms: physical or tangible, human or intangible, and current investments.
- It is important because investments improve economic activities and increase employability and GDP. Additionally, they help facilitate private and foreign investments, thereby boosting the well-being of society's individuals.
- It differs from private investment, which only has its focus on making profits.
Public Investment Explained
Public investments are investments made by the government (federal or local) through corporations and industries. Such investments provide goods, services, and infrastructure for effective welfare outcomes. They are implemented in the national interest to ensure the upliftment of the people living in a country. The investment is measured quantitatively on a yearly basis. It is estimated as a percentage of a region's total national income for a given period.
The utilization of such investments always seemed justified, given their economic and political purposes. In both World Wars I and II, the participants used public investment to expand their military setups, which served the political requirements of the nations involved. Similarly, these investments were justified by economists like John Maynard Keynes, who argued that such spending helps during economic downturns by enhancing the consumption needs of the public, thereby increasing the demand for products and services, which, in turn, boosts employment.
The investments could vary and could be physical or tangible, human or intangible, and current investments. Proper public investment management becomes a necessity, given its role in ensuring the growth and development of different regions and cities, depending on the type of investment they require. For example, a country with a poor literacy rate would progress through intangible investment. At the same time, a nation with a not-so-good trade infrastructure would benefit from a physical or tangible form of investment.
Types
Public investments exist in different forms, which are included and broadly classified into three categories – physical, human or social, and current investments.
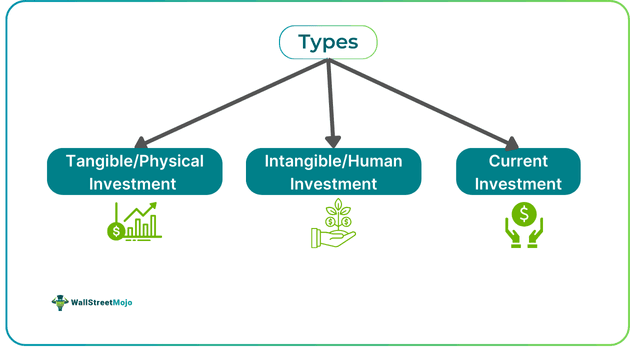
#1 - Physical/Tangible Investment
Investments in infrastructure involve spending on the development of systems or units that enable the effective functioning of a society. Such facilities include roads, transport systems, etc. They facilitate the country's delivery of goods and services.
#2 - Human/Intangible Investment
Investing in amenities that make a society progressive always adds to owning assets. These investments facilitate the well-being of a nation or a society by forcing authorities to spend on improving education, healthcare, public housing, and other systems that directly offer their services to the public. They contribute to the betterment of people and the overall society comprising the country.
#3 - Current Investment
These are investments that support the improvement in economic activities. This includes agricultural developments, trade facilitation, industrial developments, etc. In short, these include spending on economic services that would help the country develop and progress financially.
Examples
Let us look at some of the instances below to understand the public investment meaning better:
Example #1
Suppose XYZ is a country with many villages that are yet to be connected by railway lines. Though roads connect the villages, the country must have railway tracks set up to open factories and transport raw materials for speedy transportation. Given the scope of better agricultural outcomes, the country plans to lay railway lines to connect all villages in the town and across the nation, thereby facilitating better transfer of material from one place to another. To serve this purpose, it makes the public invest in agriculture with the aim of benefiting the public.
Example #2
An October 2020 article depicted how public investment could help in the economic recovery after COVID-19. The International Monetary Fund's Fiscal Monitor highlighted how the investment activities undertaken by the government could revive the economies around the world. It stated that the increase in such investment could create millions of jobs and support employability in the long term. It was estimated that a 1% increase could result in a two-fold increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP). However, it also pointed out that such spending can also lead to increased losses.
Importance
Given below are some of the reasons why investments by the government for the public are important:
- They support the delivery of public services. They are important for a country's wider economic growth, attracting private investments due to reduced costs and great infrastructural facilities.
- It improves the gross fixed capital formation in a country.
- It improves the infrastructural facilities in a country, which facilitates educational and healthcare advancements.
- It provides a stepping stone to building human skills. Human resources, both skilled and unskilled, bring in employability. It raises productivity through human capital advancements and the advantages provided by good infrastructural facilities.
- It boosts aggregate demand and can stimulate economic activity and open job opportunities.
- Employability improves a country's gross domestic product (GDP), helping it achieve economic growth and development. This could improve the quality of life experienced by the majority of the country's population.
- It could put the country on an international map and attract foreign investments and international trade opportunities, helping it build a name for itself in the international market.
- Apart from the above, a state that concentrates on the welfare aspects of society is prone to fewer conflicts and political tension. This, thus, paves the way for political, social, and economic stability.
Public Investment vs Private Investment
Both public and private investments contribute to improving a nation's global status. Though their purposes are similar, there are certain differences between them, which one can quickly examine.
Given below are some of the differences between both concepts:
- Public investments are investments made by the government through public companies for the benefit of society. On the other hand, private investments are investments made by private parties.
- Government investments are welfare-focused, but they can also be profitable. Investments made by private people are profit-oriented.
- Government investments advance society as a whole. Private investments, on the other hand, do not concentrate much on social goods and typically commercialize all services and goods to earn money.
- Government investments are often made within the country's boundaries, while private investments are not confined to only one nation.
