Table Of Contents
Promissory Note Meaning
A promissory note is defined as a debt instrument in which the issuer of the note promises to pay a specified amount to a party on a particular date. Simply speaking, a promissory note is written by a borrower as evidence of the promise to repay the due amount to the lender.
The debtor issues the note in favor of the creditor. It bears all essential information, including the debt amount, maturity or due date, interest rate, debtor's signature, issuance place and date.
Key Takeaways
- A promissory note signifies a borrower/issuer’s written unconditional promise to pay the due amount on a specific date or as on-demand by the lender.
- It is a means of availing funds by individuals or business organizations. While for investors or lenders, it is a form of debt instrument that typically provides a periodic interest income.
- The note is duly signed by the issuer. However, its acceptance by the payee is not required as it already serves the on-record purpose by being a written payment promise from the debtor’s side.
- The other relevant clauses of this debt instrument include name, address and contact details of the parties involved, principal amount, issuance date and place, interest rate, due date, etc.
How does Promissory Note Work?
A promissory note works as an evidence of a borrower’s payment obligation. The note usually appears whenever a creditor provides a loan to the debtor, with the latter assuring repayment in writing. This written promise that also contains the due amount is a legally enforceable document.
The debt instrument is common among other lenders other than banks. In fact, they serve as financial aid to borrowers who cannot acquire loans from banks. Companies that require short-term loan and are unwilling to raise money through equity can utilize this facility. It usually allows the creditor to receive a periodic interest income.
The format of a promissory note holds the principal amount, issuance date and place, interest rate, due date, parties’ contact details, etc. One can make the payment in instalments or as a lump sum, thus ensuring flexibility. Although it usually does not specify the recourse if the borrower defaults, the lender can undertake usual processes such as written reminders or filing a lawsuit against the debtor.
During the period of the Renaissance in Europe, the notes were used widely. For years, they had been used as an alternative currency when paper notes hadn’t taken over. Changing with times, today in the US, they are most commonly used in real estate, student and personal loans.
Features of Promissory Notes
Other than those mentioned above, a promissory note comes with many features listed below –
- Types – there are different types of promissory notes available in the financial market with varying features suited to different situations. For example, if it is of the convertible kind, the lender will have the freedom to convert the instrument into equity. This comes in handy if the lender finds abundant opportunities in staying invested in the borrowing company.
- Tradable/Negotiable – certain type of notes can be transferred to a third party for settling dues by the issuer. The issuers' consent is crucial in such cases as they’d need to prepare a new note.
- Collateral – since the note is usually a part of loan agreements, it could come as unsecured or secured. An unsecured kind will not be backed with the debtor’s asset and vice-versa.
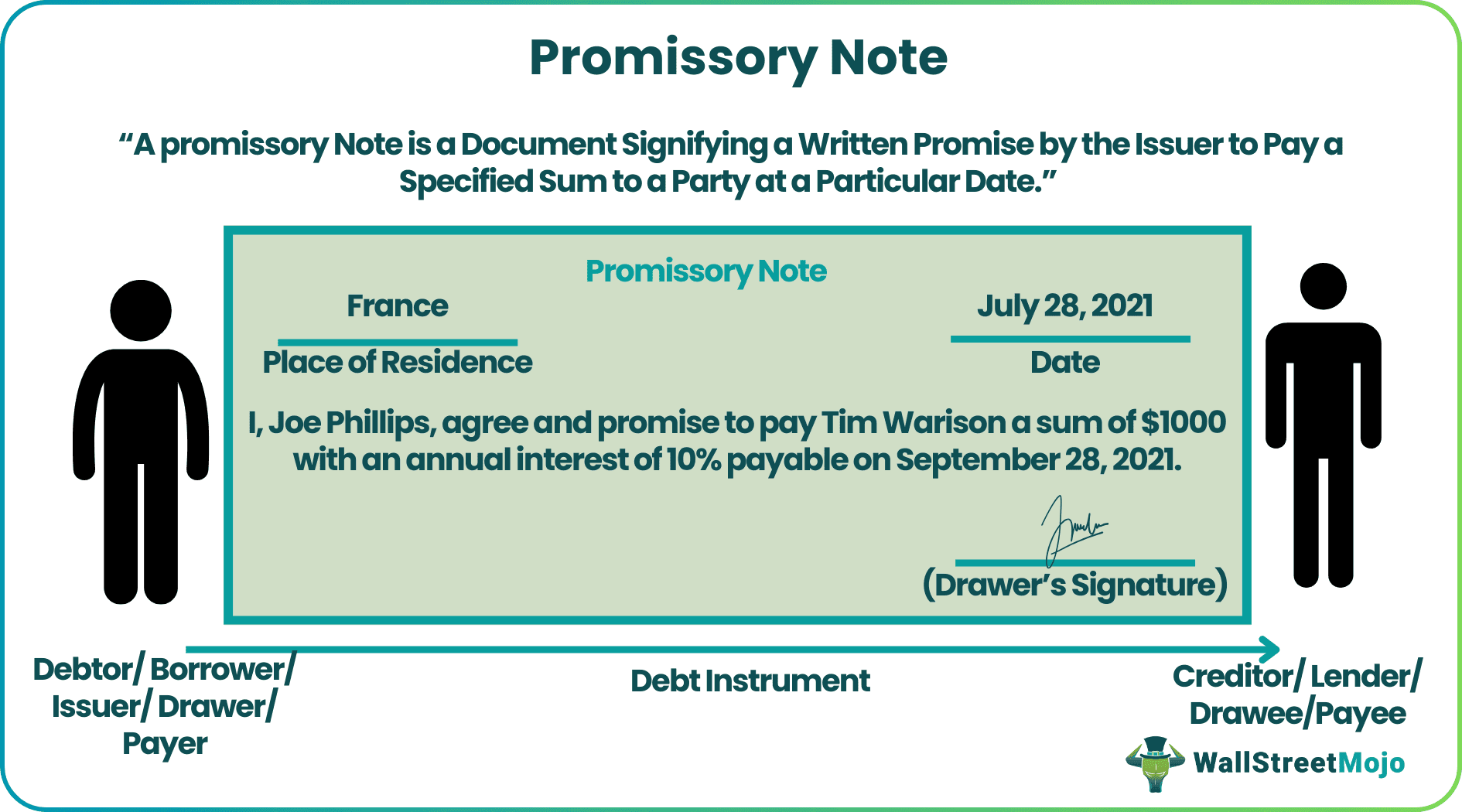
Promissory Note Format
The format of a promissory note usually holds the following entries -
- Drawer/Issuer: An individual, corporate entity or investment company that takes money from the lender and commits to repay in an unconditional written promise.
- Drawee/Payee: Drawee is the person in whose favor the debt instrument is prepared. However, the drawee isn't liable to receive the payment if he/she transfers the note to a third party or payee.
- Payee: A person who holds the promissory note on the due date and is scheduled to receive the outstanding amount.
- Legal Names of Parties Involved - the legal and full names of the issuer and drawee, along with their addresses and contact details are included in the note. In other words, it specifies that the borrower has taken a debt from the lender who is due to receive the repayment.
- Loan Amount – this includes the principal amount of the debt provided by the lender to the borrower.
- Interest Rate – specifies the percentage at which the interest is payable by the debtor to the creditor on the principal amount.
- Repayment Sum – contains the total money due on the debtor after adding interest to the debt amount.
- Repayment Terms – specify whether the debtor will pay the sum all at once or in instalments. Also throws light on whether it is due on a specific date or is on-demand.
- Maturity Date – clarifies the date when payment is to be made by the debtor. In on-demand notes, the payment is made on demand.
- Debtor's Signature – includes the legal signature of the debtor and the date of signing the document in addition to the name and signature of the co-signer.
- Witnesses: signatures of individuals from both sides standing as witnesses to the deal.
- Date and Place of Issuance: the date and state (place) in which the note is issued.
- Notarization (if necessary): although not compulsory, the information of such a debt instrument can be verified by the state or local regulatory body.
- Other Details: include the collateral pledged (if any), name and signature of the witnesses, acceleration events, prepayment terms, joint and several liabilities, and transfer rights.
Promissory Note Examples
Real estate
In real estate, promissory notes are usually an implicit part of secured loan where borrowers promise to repay in a written agreement. As such, they contain repayment terms like maturity date, interest, principal amount, etc. In addition, the borrower pledges collateral that lenders can use to recover the loan if the debtor defaults. Therefore, the deed contains other legal clauses like collateral, foreclosure terms, etc.
Other Sectors
The other forms of promissory notes are unsecured, joint liability, corporate credit, vehicle, foreign, inland, commercial, personal loan, student loan, investment, interest-bearing and demand notes.
Real-life Example
In response to the Eurozone crisis, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) had announced a new borrowing initiative. The intention was to help meet any emergency financial requirements of member countries. In 2012, BRICS countries had declared their contributions towards the same.
The terms of the borrowing programme involved the member countries issuing promissory notes to the IMF. The debt instrument was a part of note purchase agreements which the bank could utilize for emergency payment needs. In addition, the arrangement gave the IMF the right to partially/fully encash the notes on the bank’s call.
Promissory Note Sample/Template
Given below is a template or sample of a standard promissory note. The format varies as per requirements.

How to avoid being defrauded?
A promissory note is a boon for credit buyers and borrowers, although it is sometimes misused as a means of fraudulent practices. At times, companies issue this instrument to raise funds from investors by offering excessive interests and top it off with minimal risk claims. Unfortunately, it often turns out to be a scam in due time.
When promissory notes are utilized as securities, i.e. for investment purposes, investors should exercise the following tips to prevent being defrauded -
- Verify that your security seller is duly registered with the regulatory authority.
- Check your investment instrument's registration with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or any other regulatory body; or the proof of exemption from such registration.
- Beware of the sugar-coated deals offered by borrowing companies like excessive and insured returns, zero or minimal risk, etc. since not all that glitters is not gold.
- Make sure to compare the securities' rate of return with that of other competent products available in the market.
