Table of Contents
What Is Projected Financial Statement?
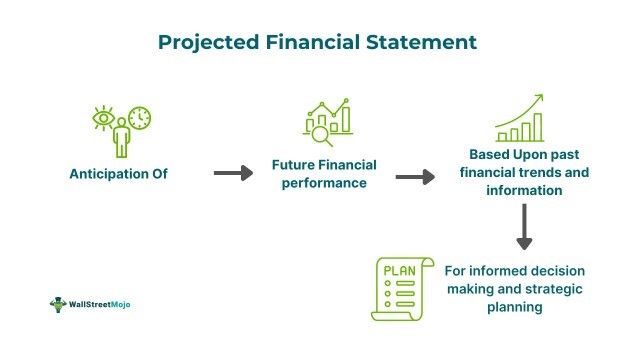
A projected financial statement refers to the potential revenues, expenses, cash inflows, and cash outflows that the company expects over a future period. Based on the current revenue trend and other real-time information, these estimations are represented as a summary of the income statement, statement of cash flow, and balance sheet.
Financial projections serve as critical insights for management to plan the company's growth and expansion strategies. They help firms raise funds by presenting their future plans and growth prospects to investors. Moreover, they facilitate banks' determination of the organization's ability to repay debts in the future before extending them loans.
Key Takeaways
- The projected financial statement is the expectation of financial performance, I.e., the anticipated cash flows, expenses, revenues, assets, and liabilities of a company in the future accounting period.
- Such financial projections are gauged by analyzing a firm's past or historical financial insights and planned future strategies and projects.
- It involves the creation of projected income statements, statements of cash flows, and balance sheets.
- It is critical information for investors, creditors, financial institutions, management, and other stakeholders to determine the potential growth, profitability, and return on investments that a company could offer in the future.
Projected Financial Statement Explained
The projected financial statement is an anticipated summary of a business entity's financial performance and position in the future, i.e., in the upcoming quarter, year, five years, or ten years. It involves projecting cash flows, expenses, and revenues as determined by the company's management for the next few months or years based on historical or past financial data.
Such insights are crucial for analyzing the future growth potential and expected outcome of the planned strategies to attract investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. Moreover, it comprises the preparation of three different types of financial statements:
- Projected Income Statement
- Projected Cash Flow Statement
- Projected Balance Sheet
A startup can use a projected financial statement template to begin creating financial projections for its potential investors and shareholders.
Let us now have a look at some necessary tips and tricks for financial projection:
- It is necessary to consider step costs for expense projection to create room for revenue surge and decline.
- The finance manager should ensure a simple financial projection that is easy to interpret and analyze for the stakeholders.
- Also, it is essential to undertake realistic assumptions for better anticipation of future possibilities.
- Again, the management should emphasize efficiently analyzing the historical information of the company's finances to make future projections.
- The company should consolidate the financial information from all the different departments while stating the projected statements to have a comprehensive overview of the potential business performance.
How To Prepare?
The finance manager can use the projected financial statement format to reflect future business revenues, expenses, cash flows, opportunities, and threats. Some of the necessary steps undertaken in such forward-oriented financial reporting are as follows:
- The foremost step is to identify the two kinds of projected financial statements—short-term and long-term. The short-term projections anticipate the company's financial performance in the near future, i.e., months to a year, while the long-term projection is made for 5 - 10 years.
- Next is estimating the expected sales over a future period. This involves forecasting potential sales based on the historical sales record.
- Now, analyze the company's one-time (property, licenses, and trademarks) and ongoing expenses (rent, salaries, and utilities) to determine revenue.
- Then, anticipate the future assets, liabilities, and stockholder's net worth over the period for balance sheet projections.
- Now, project the net income in the upcoming period based on trends of past income statements that would feature future performance trends.
- Lastly, prepare a summary of the projected financial statements highlighting the expected financial position, opportunities, assumptions, and recommendations.
Examples
The financial projection is critical information for the management and stakeholders of a company. Let us understand its significance through the following examples:
Example #1
Suppose a 2-year-old tech company, XYZ Pvt. Ltd., needs funding of $5 million. The company enters the Series A Funding round to approach the potential angel investors. The company's management prepared their financial projection with the help of projected financial statement samples and templates. The finance manager analyzed the past 2 year's financial statements of the company and its future projects and strategies to forecast the expected revenues, expenses, and cash flows in the next 5 years. The summary of the financial projection also stated the potential returns that the business could generate for its investors and shareholders.
Example #2
Air Canada disclosed its preliminary second-quarter financial results and updated its full-year financial guidance in 2024. The Q2 2024 financial insights include:
- Operating Revenues: $5.5 billion, a 6.5% rise in capacity compared to Q2 2023, which had revenues worth $5.4 billion.
- Operating Income: $466 million, representing an operating margin of 8.4%, which was less than $802 million operating income in Q2 2023.
- Adjusted EBITDA: Around $914 million, which was $1.2 billion less than that of Q2 2023.
Updated Financial and Capacity Guidance for 2024:
- ASM Capacity: The available seat miles capacity is expected to rise by 5.5-6.5%, which was earlier assumed to increase by 6-8%.
- Adjusted CASM: The adjusted cost per available seat mile could surge by 2.5-3.5%, again a little lower than the previous estimate of 2.5-4.5%.
- Adjusted EBITDA: The adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization are estimated at $3.1-3.4 billion, which was earlier assumed to be $3.7-4.2 billion.
Lower yields, market environment challenges, significant competition in the global markets, geopolitical factors, supply chain disruptions, and weaker-than-expected load factors are the major triggers for the decline in projected figures.
Importance
The startups often make a projected financial statement for a business plan, while the financial projections facilitate the following different purposes:
- Strategic Planning: Management can plan future and current strategies, including marketing campaigns, expansion, product launches, etc., centralizing the projected revenues and expenses.
- Fund Raising: When companies raise capital through series A, B, or C funding rounds, they must state their financial projections on their future projects, profitability, and expenses to facilitate investors' decision-making.
- Debt Repayment Ability: Banks also request such statements before sanctioning a loan to a company to determine its repayment capacity by gauging its future endeavors and strategies.
- Estimate Investment Returns: The investors perform projected financial statement analysis to review the potential shareholders' returns that the company would reap in the future.
- Shows Future Profitability: Such insights provide an overview of the anticipated profits that a business, based on its strategic plans, would generate in the near future.
- Budgeting: Further, a forward-looking approach to the company's financial performance can facilitate management's planning of the business's capital and operating budget.
- Resource Management: When the projected expenses and need for resources in the future are known, the management can better plan the investment and use of business resources today.
- Predict Future Cash Flows: The business can also determine future cash inflows and outflows, which would help maintain sufficient funds in the account in case of any potential deficit.

