Table Of Contents
Profit and Loss Accounting Meaning
Profit and loss (P&L) accounting is the process of creating a profit and loss statement to help companies have a clear view of the revenues and expenses over a period. The segregated view of the financial inflows and outflows enables organizations to track their financial performance and implement ways to keep up the same or improve it.
Table of contents
A profit and loss statement is one of the most important financial documents as it assesses whether a company has made profits or incurred losses in a fiscal quarter/year. The report, in turn, lets investors and other stakeholders decide whether to invest and involve in the organizations' initiatives and operations.
Table of contents
- Profit and loss accounting is when companies prepare the profit and loss statements to figure out their financial performance for a fiscal quarter or year.
- These statements let creditors and investors make well-informed decisions on whether to involve with or invest in a company.
- Revenue, cost, accrual and prepaid, EBITDA, and net profit are some of the components that help format a standard P&L statement.
- To ensure accurate P&L accounting, the professionals prepare separate ledgers first and then create a trial balance and profit and loss statements.
Profit and Loss Accounting Explained
Profit and loss accounting generates a profit and loss statement, also referred to as an income statement, that becomes a ready reference for creditors and investors. These stakeholders refer to the document to track the financial performance of the organizations and make well-informed, smart investment and business decisions. Going through the P&L accounting records thoroughly enables them to determine the level of risk involved in collaborating with these ventures.
There are two methods by which the accounting professionals prepare the P&L statement. The first step is the single-step method in which professionals calculate the business' total revenue, subtracting the expenses for that period from it to derive the amount remaining with the company.
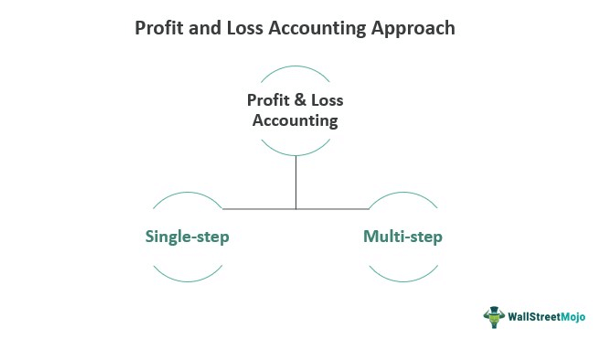
A second method is a multi-step approach. The total revenue is calculated in this process, and operating expenses are subtracted from it first. It helps obtain the operating income, which further adds to the remaining non-operating figures, including revenues, expenses, investment gains, or losses. The figures obtained show the pre-tax income for the period. Then, the applicable income taxes are deducted, and the net income is found.
Preparing P&L Statement
Preparing a statement of profit and loss accounting involves generating other sets of statements first. These financial statements help accounting professionals assemble the required data before creating the final income statement. The first step to preparing the profit and loss statement is to create ledger accounts. Here, the professionals prepare a statement for each ledger to figure out the closing balance.
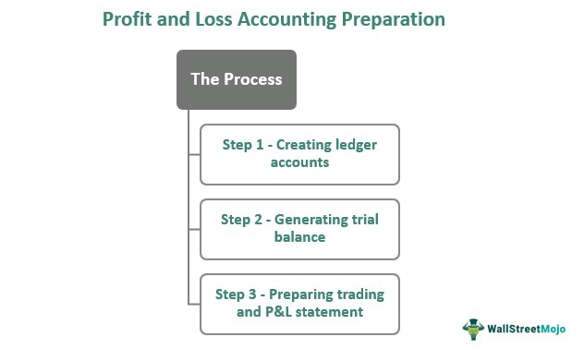
Next is creating a trial balance, which summarizes the data obtained from the ledger accounts and their respective closing balance. Finally, the trading and profit and loss statement are prepared. The accounting professionals record the ledger accounts, along with the type of sales, purchase, direct and indirect expense, and income in this statement.
Components
Five components offer a standard profit and loss accounting statement format to the organizations. These include:
Revenue
It is the amount that marks a business or organization's income generated over a period by selling the goods and services to customers. For example, in the P&L accounting, revenue figures might enter in different forms, including recurring revenue (monthly fee), non-recurring revenue (repair or one-time additional charge), and non-trade revenue (income not directly linked to the main business), etc.
Cost
Cost or expense is the total expenditure an entity makes for profits at the end of production and sale of goods and services in a fiscal year. The cost incurred can be the cost of revenue, which indicate direct expenses related to boosting the revenue. Other expenses include office expenses, depreciation, selling & administration expenses, etc.
Accrual and Prepaids
Most countries follow accrual accounting which only summarizes the revenue generated and the cost incurred in the current period. The P&L accounts or statements reflect these pieces of information. In this case, while finalizing the books of account, if it is found that a few invoices have not been received, accounting professionals must accrue those expenses. Such expenses are recorded in the liability column of the balance sheet.
On the contrary, the future expenses already paid are recorded as a current asset on the balance sheet.
EBITDA
It stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. As the name implies, it marks the earnings of any business before applicable deductions. The operational cost is subtracted from the total revenues, and the amount obtained becomes the EBITDA. It indicates if an individual or firm is making profits from the daily operations it conducts. It also marks an entity's capacity to repay its financial obligations.
Net Profit
Net profit is the amount obtained after all deductions, including taxes, depreciation, amortization, etc., are made from the revenue.
Examples
Let us consider the following profit and loss accounting examples to understand its function:
Example 1 – For Individuals and Sole Proprietors
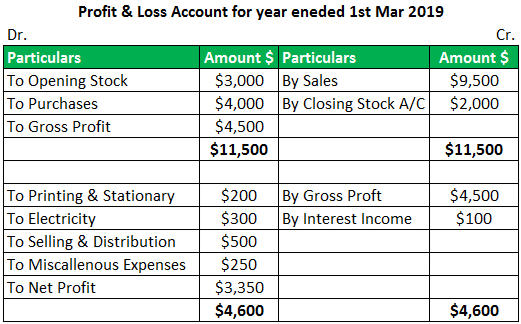
Example 2 – For Listed companies
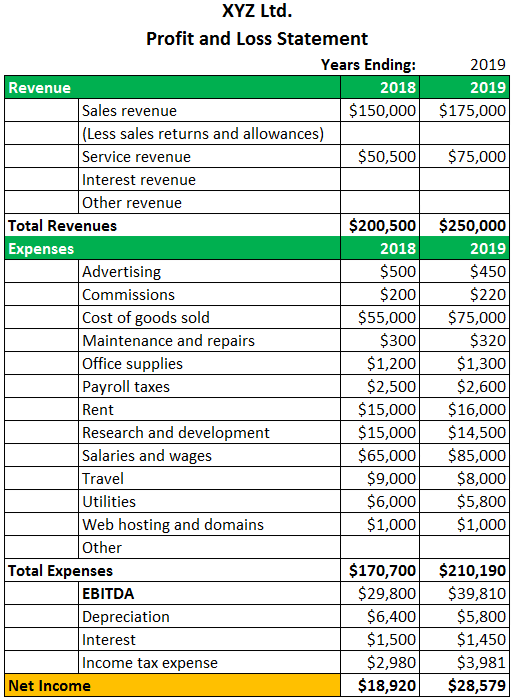
Pros & Cons
Profit and loss accounting advantages are many, but the process is not devoid of limitations. So, let us have a quick look at the pros and cons of P&L accounting:
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Comparing financial statements becomes easy | Time consuming |
| Summarizing and data retrieval is smoother and faster | The accrual method of accounting is used, which burdens profits with non-cash expense settlements. |
| Helps track performance month-wise or year-wise as recorded | |
| Makes performance analysis easier |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
P&L accounting involves the creation of reliable profit and loss statements to assess the financial performance of an individual or business. These statements provide a clear picture of the company's profits and losses incurred during a specific period. Based on the same, the creditors and investors decide whether to collaborate with the business or look for other entities in the market for fruitful investments.
Profit and loss figures are calculated by deducting the total expenses from the revenue generated from different sources in a fiscal quarter or year.
The P&L statements include income, expenditures, and profits made within a specific period. On the other hand, a balance sheet separates the assets and liabilities up to a particular date. While the former assesses the financial performance of the companies or individuals, the latter reflects how strong a company is in terms of the finances and resources it possesses. In addition, a balance sheet is normally presented on the last day of the fiscal year, whereas the P&L statement may be presented at the end of a quarter or year.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to what is Profit and Loss Accounting and its definition. Here we explain how to prepare it, its format, components along with examples. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles -

