Table Of Contents
What Is The Production Cost Formula?
The production cost formula is composed of costs that the business or a company incurs in making finished goods or delivering specific services and includes typically direct labor, general overhead expenses, direct material expenses, or expenses on raw materials and supplies.
The production costs should be directly aligned with the business's revenue generation. The manufacturing business typically has raw materials costs and labor costs. In contrast, the specific service industry is composed of technical labor developing a specific service and material costs incurred in delivering such services to the clients. The production cost formula is generally used in managerial accounting to segregate costs into direct and indirect costs.
Production Cost Formula Explained
The production cost formula is a financial metric that is used for calculating the total cost incurred for production of any product or service within an organization. It includes all types of costs including the direct and indirect costs. Let us study the formula as given below.
The production cost formula can be expressed as follows: -
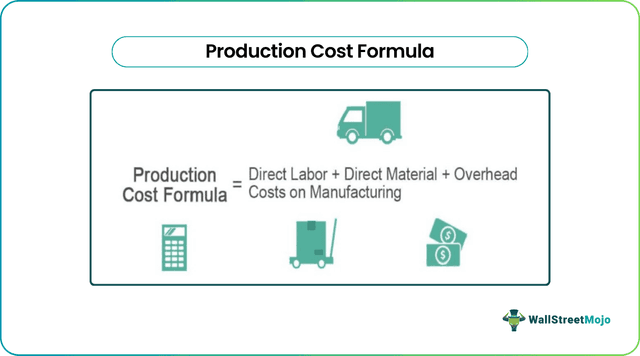
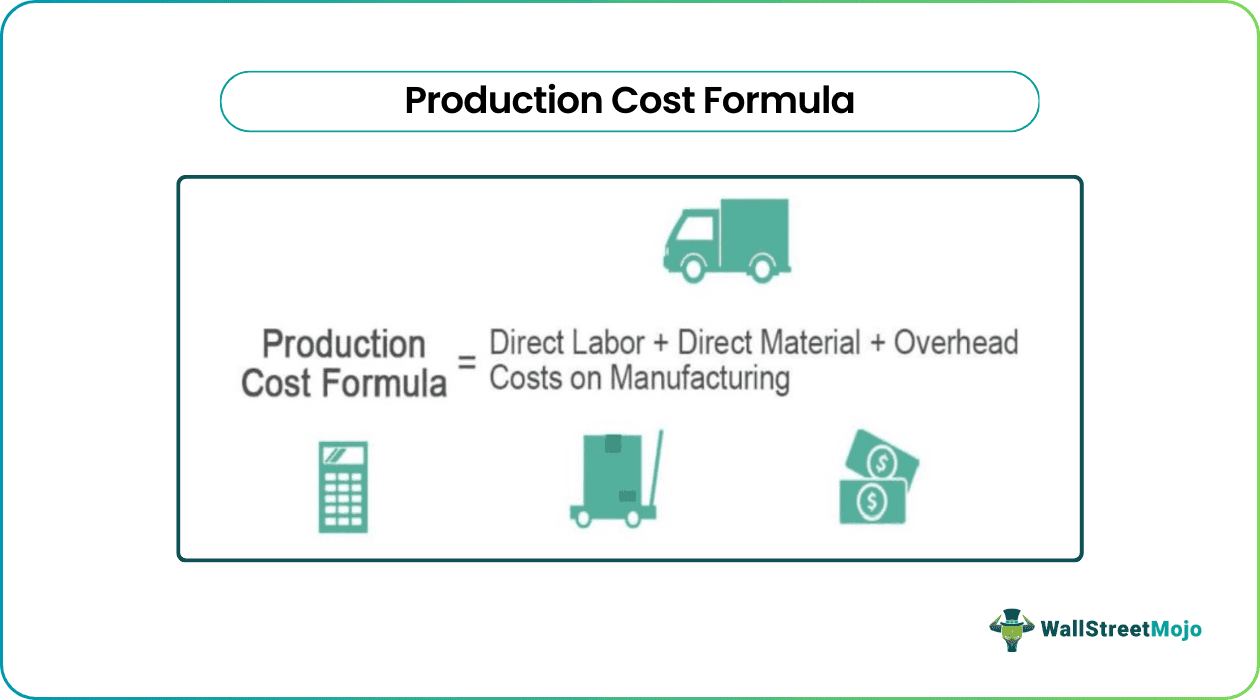
Production Cost Formula = Direct Labor + Direct Material + Overhead Costs on Manufacturing
Here,
Overhead costs on manufacturing= Indirect labor cost + Indirect Material cost + Other variable overhead costs.
In the above formula for production cost, the direct cost is the cost that can be associated directly with the production of goods and services. These include the direct material and labor, which are the raw materials, components and supplies, salary and wages of laborers and employees.
Then comes the overhead cost of manufacturing that has all the indirect costs. The indirect labor cost are those wages and salaries of labors who are not directly involved in the manufacturing but help in the process, like supervisors, staff responsible for quality check, etc. The cost of indirect materials includes tools, lubricants, cleaning supplies, etc.
The other variable overhead in the formula for production cost has any other costs that contribute to the production process, like rent for the premises, maintenance costs for the building, plants, and equipment, depreciation on the machinery, etc.
Once the data for all the above are accumulated, they are put into the total production cost formula to calculate the total cost of production. It should be noted that even though the formula appears to be very simple, the actual implementation is quite complex due to various cost categories involved in a manufacturing process.
How To Calculate?
The calculation of Production Cost Equation can be done by using the following steps:
- Firstly in the total production cost formula, determine the costs of direct material. Direct materials are usually composed of costs related to the procurement of raw materials and utilizing them to produce finished goods.
- Next, determine the costs of direct labor. The direct labor cost is usually composed of costs on labor costs and costs of the workforce that are in line with the production process. Such costs generally consist of wages, salaries, and the benefits the business compensates to the labor for delivering finished goods or services.
- Next, Determine the costs of manufacturing. Such costs typically comprise costs that cannot be attributed to the production process but indirectly impact the production. Such costs can be bifurcated into indirect labor costs, indirect material costs, and variable costs on overhead.
- Next, add the resulting value in steps 1, step 2, and step 3 to arrive at the cost of production.
Examples (With Excel Template)
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples of per unit production cost formula to understand it better.
Example #1
Let us take the example of a manufacturing business that incurs $25,000 indirect labor. It incurs $30,000 in manufacturing overheads and $50,000 in direct material costs. Help the business to determine the overall cost of production.
Use the given data for the calculation of production cost.

Calculation of Production Cost can be done as follows:

- = $25,000 + $50,000 + $30,000
Production Cost will be -
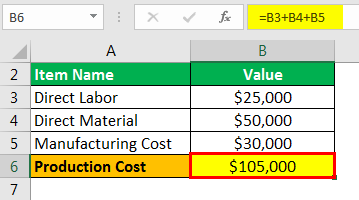
- Production Cost = $105,000
Therefore, the manufacturing business incurs a production cost of $105,000 when manufacturing finished goods.
Example #2
Let us take the example of a business that specializes in producing chairs. The raw material cost accounts for $75,000. The wages and salaries for the labor and workers account for $40,000. The company compensates benefits worth $3,000 to the labor for delivering exceptional service. The company additionally bears once in a while polishing costs on chairs of $30,000.
The business stores the finished chairs in a rented warehouse. They pay a rental amount of $20,000. They additionally pay $15,000 as the wage for security guards. Help the business of finished chairs to determine the cost of production.
Use the given data for the calculation of production cost.

Calculation of Direct Labor using below formula can be done as follows,

Direct labor = Wages of Production Workers + Benefits of the Production Workers
- = $40,000 + $3,000
- Direct Labor = $43,000
The direct material costs correspond to the cost of raw material procured by the business, which would be regarded as $75,000. The manufacturing costs would account for the sum of polishing, rental expenses, and wages for the security guards.
Calculation of Manufacturing Cost using below formula can be done as follows,

Manufacturing Cost = Polishing Cost + Rental Expense+ Wage for Security Personnel
- = $30,000 + $20,000 + $15,000
- Manufacturing Cost = $65,000
Calculation of Production Cost can be done as follows:

- = $43,000 + $75,000 + $65,000

- Production Cost = $183,000
Therefore, the manufacturing business incurs a production cost of $183,000 when manufacturing chairs.
Relevance And Uses
Now let us analyse the various uses of the concept in the corporate and financial market.
- The determination of the per unit production cost formula is necessary as well as critical for the business to ensure its profitability of the business and sustainability. It also helps in the comparative analysis of the costs. Once the manufactured items reach completion, the business records the item's value as an asset on the balance sheet until the product is sold to the customers.
- The production cost has to be initially capitalized and not expensed. Additionally, reporting the value of the end products could be termed as a sophisticated way to inform all the necessary stakeholders on the level of productivity that is being delivered.
- Production cost formula usually is composed of direct materials, direct labor costs, and variable manufacturing overheads. The management accountants often transform these costs per unit basis. By doing so, they easily compare the per unit with the selling price the management is considering for the business, thereby determining its sustainability.
- It helps in decision making as well as cost control. The management is able to set competitive prices for its products and services based on the production cost because they need the prices to be abe to generate enough revenue that will cover its cost as well as initiate higher sales. The cost control helps in minimising wastage and optimizing resource usage, which ultimately leads to an increase in profitability.
- Management can use the data related to production cost as a benchmark to compare themselves with other peer companies. This acts as a guide to evaluate their competitive position within the sector.