Table Of Contents
What is Process Costing?
Process costing is a method wherein the products go through two or more processes. The costs are assigned/charged to individual processes or operations, averaged over the number of units produced during the said period. It is used commonly in manufacturing units like paper, steel, soaps, medicines, vegetable oils, paints, rubber, chemical, etc. use this method widely.
A product may be manufactured through one process or more than one process. If two or more processes are involved in manufacturing one finished product, the question arises, "which process has consumed the expense?" The answer lies within process costing. It helps identify the specific cost assigned to each process. It enables the management to further decision making.
Key Takeaways
- Process pricing is an approach that involves putting the items through two or more processes. A cost average across the number of units produced over the specified period is applied to particular processes or operations.
- Process costing is of three types. These include the average weighted method of process costing, standard costs, and First-In-First-Out methods.
- The process starts with the recording of inventory, followed by conversion of work in process inventory, calculation of inventory costs, calculation of the per-unit cost of inventory, and ends at the allocation of costs.
- Process costing is appropriate for industries where the output is continuous and uniform. Additionally, the entire production process is standardized.
Types

#1 - Weighted Average Method of Process Costing
Here the actual cost is divided by the weighted average of products produced. This calculation is simple as compared to any other method. A weighted average of units means the summation of the product of the rate and quantity of each item.
#2 - Standard Cost
Here the actual cost of units is not considered; instead, it follows a standard costing method. Standard cost assumes the cost of certain materials as per management estimate. Any difference in standard & actual costs is recorded separately under the variance account
#3 - First-In-First-Out
This method assigns the expense of first inputs to the processes in the order of production. However, it does not precisely identify which a lot of raw material is taken for production and its procurement rate.
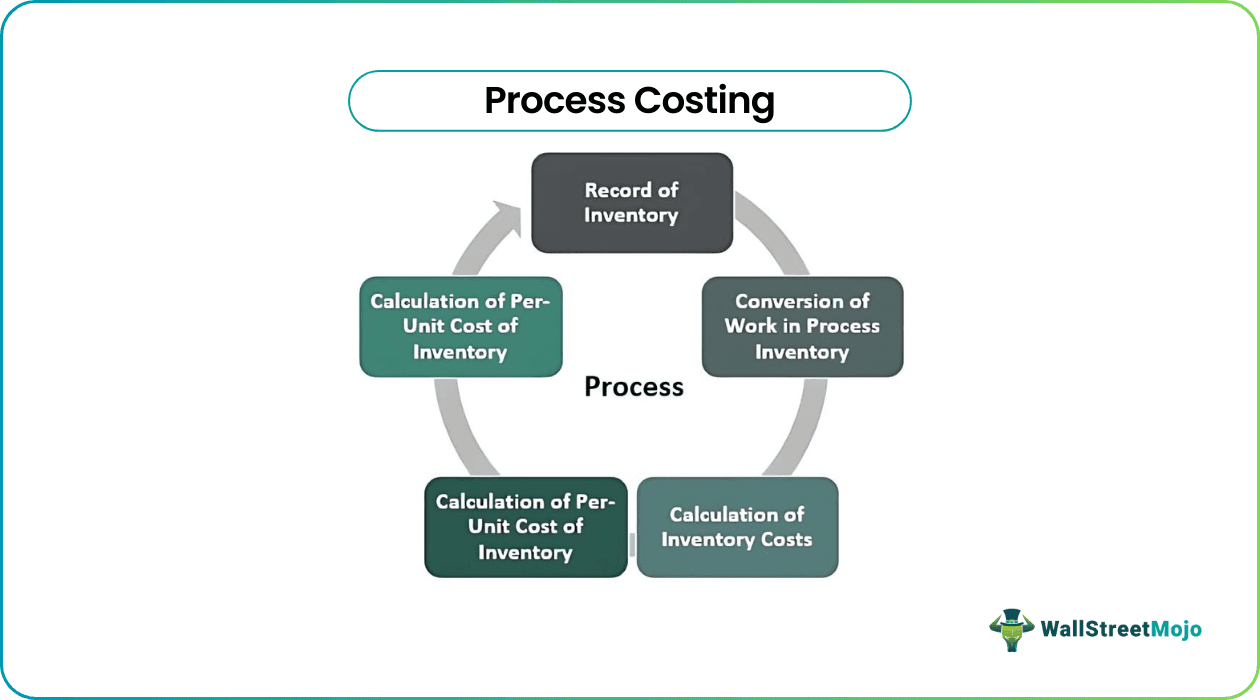
Steps of Process Costing
Step#1 - Record of Inventory
This step involves the identification of inventory at the end of each process. The organization can identify such inventory by physically counting the units or through software inbuilt into the manufacturing process. In addition, the costs of inventory under each process are also identified at this change.
Step #2 - Conversion of Work in Process Inventory
Apply the percentage of completion to the units which are under any process & not yet completed the production. Say 80,000 units of soaps are under process & these are 60% completed. Then the equivalent completed units are 80,000*60% i.e. 48,000 units.
Step #3 - Calculation of Inventory Costs
Here, the organisation calculates the direct cost and indirect costs in the production phase. These costs are accumulated from the first process to the last process. The said is then bifurcated into an inventory of complete products & inventory of products that are under process.
Step #4 - Calculation of Per-Unit Cost of Inventory
We calculate this by dividing the total cost by equivalent completed units in the production phase. The cost per unit calculated here reflects the cost of only completed units. The basis of equivalent units can be the weighted average, standard cost, or first-in-first-out inventory method.
Step #5 - Allocation of Costs
The per-unit costs are then split according to the number of units completed & units that are under process.
Examples of Process Costing
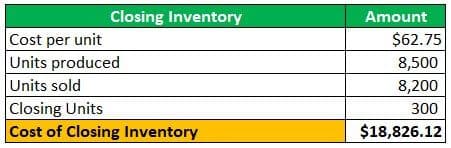
The entity has provided the following information & wants to calculate the cost involved in each manufacturing step. Also, it intends to calculate the value of closing inventory.

Solution:



When Is Process Costing System Suitable?
Process costing is suitable for industries where the product is continuous and the end products are identical. Also, the entire process of production is standardized. In such industries, the production cycle is standardized & even the quantum of the normal loss of inputs & outputs is quantified earlier. In case of abnormal expense, it is a charge to the profit & loss account directly and not to any individual process.
Industries such as cement, soaps, steel, paper, chemicals, medicines, vegetable oils, rubber, etc., use this method to assign the costs.
Features
- Each plant is divided into several processes/centers. Each such division is a stage of production or process. Thus, we first clearly identify the cost centers.
- Direct & indirect costs are assigned and accumulated to each process in the factory.
- The output of one process may become input for another process.
- The finished products are identical & cannot be easily distinguished unless batch coding is done.
- The production process is continuous for all days in the year except for regular breakdown hours required to maintain the machinery.
- The total cost of production is divided among each process on a suitable basis.
- The company is required to keep records for each production process, such as units or costs introduced in each process and passed on to the next stage of production.
- The production may result in joint products or by-products.
Conclusion
Process cost allows an organisation to assigns the cost to different steps in the production phase. It helps management in decision making. The organisation can use this method to identify the relevant costs (i.e., direct and indirect costs) for each process, and no abnormal expenses are charged to any process.