Table of Contents
What Are Private Debt Fund?
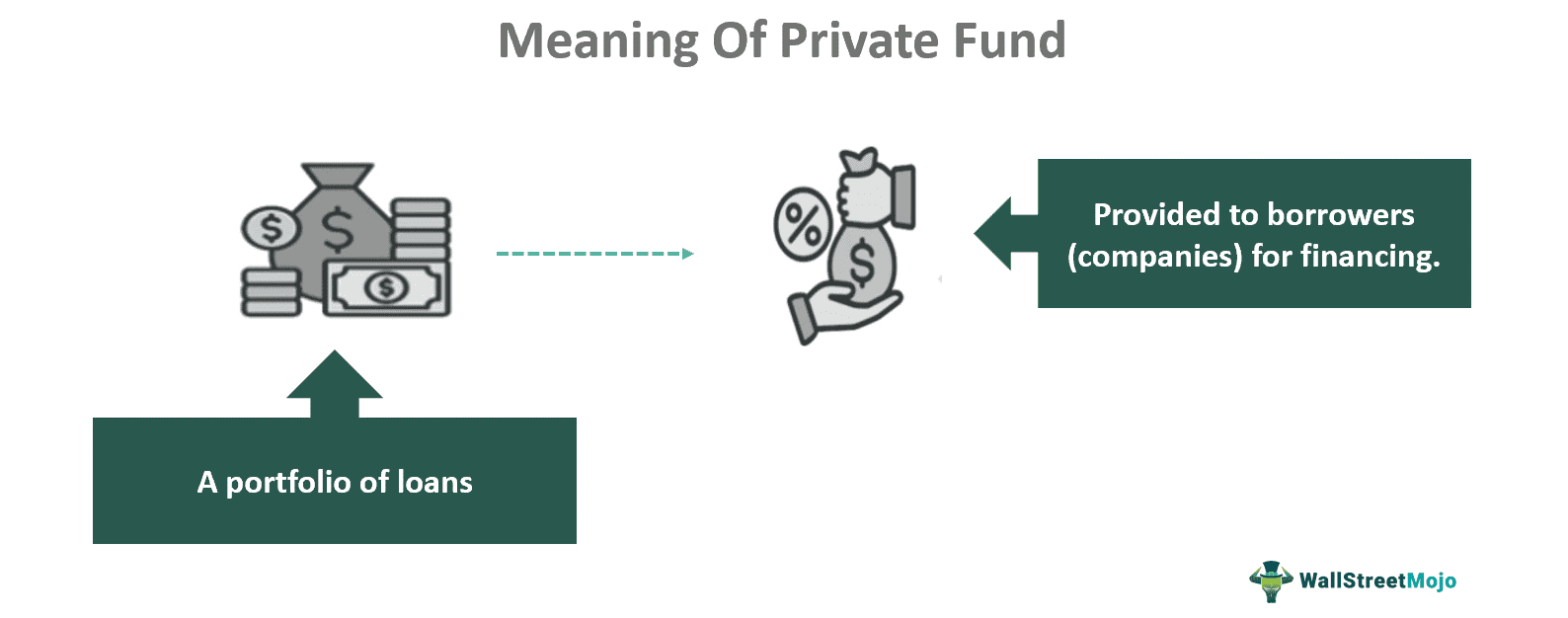
A private debt fund is a type of debt fund where different portfolio loans reside. It is used as a part of debt financing for companies in the absence of bank loans. Its main purpose is to accumulate loans from individual investors and place them in a fund.
The origin of these debt funds started after the Global Recession crisis that occurred in 2008. At that time, the credit facility faced various banking regulations. Hence, traditional lenders cut their financing, which later brought space for these debt funds to exist. It provided an opportunity for alternative sources of lending to investors.
Key Takeaways
- A private debt fund is a fund house providing financing to borrowers through debt securities. It includes a portfolio of loans invested by investors and then lent to firms.
- It came into existence after the global financial crisis of 2008. At that moment, it provided a source of financing amid strict banking regulations.
- The popular types of investment securities include direct lending, venture debt funds, and special situation financing.
- A few examples include Oaktree Capital Management, GSO Capital Partners, Goldman Sachs Merchant Banking Division, and others.
How Does Private Debt Fund Work?
A private debt fund is a lending facility provided by investors to the required companies. It acts as a bridge between them to raise money from investors and utilize the same to finance companies. Hence, such funds do not reside in the equity markets. Instead, they invest in private debt and earn from it. For instance, four investors may put their funds here, and later, the fund will direct them to the needed borrower.
There are different private loans available for residing under this fund. Investors then hire lending teams and managers who will allocate the funds in a better marketplace. Here, every individual loan may have a different investment size. For instance, the portfolio of loans residing may be worth millions or trillions of dollars. As a result, these debt funds do intensive market research before financing any firm.
In the past decades, investors have reduced their interest in debt instruments. As an alternative, they have switched to firms involved in private debt fund administration. It has provided investors with more yield than bond-like returns.
Investment Strategies
The private debt fund structure includes various subcategories of financing. Let us look at each level in detail:
#1 - Direct Lending
As the name suggests, this lending provides funds directly to the companies. It includes senior or subordinated debt, which has multiple uses. For instance, these funds may be used for expansion, acquisition, project management, and others. Here, the administration makes money from management fees charged to outside investors.
#2 - Venture Debt Financing
The next type includes venture debt financing, in which the company is already backed by venture capital. Here, such companies have already experienced two or more rounds of financing. Later on, venture debt can help them scale new milestones and projects. The main benefit received by entrepreneurs here is the non-dilution of ownership. They can access capital and still avoid losing their stake.
#3 - Special Situations
In general, special situation funds exist when a company is in financial distress. They focus on companies whose value is greatly impacted by certain market events. Thus, this fund proves beneficial when a firm is on the verge of bankruptcy. As a result, the private debt fund structure may include debt as well as equity financing.
Examples
Let us look at some examples of these debt funds to understand how they work in the real world as well:
Example #1
Suppose John owns a company that has recently acquired two rounds of funding from venture capitalists. They made massive sales in the first few years and also received appreciation from customers. But, later on, they started facing a defect in their products. As a result, they had to recall the products and re-manufacture them. In this process, they saw a huge gap in their account balance and came on the verge of bankruptcy. At such a moment, a debt fund came to the rescue.
John was able to receive a loan from Maple Source Ltd. This capital was further used to develop better and innovative products free from radicals. Also, quite a good amount was utilized for marketing purposes as well. In no time, John recovered the firm's position and repaid the debt, also.
Example #2
According to a recent news update as of May 2024, the private debt fund firms may expect the assets under management (AUM) to reach $2.7 trillion by 2028. Also, experts see debt fundraising to witness an annual growth trend of 6.9 percent by 2028. Among the major investment strategies, direct lending may take the largest stake of $900 billion. However, in the good case scenario, it could reach $1 trillion as well. The current economic environment supports private debt, with elevated central bank policy rates and low default rates. The floating-rate feature of private debt helps weather rate-hiking storms and diversifies portfolio risks.
Benefits
There are several benefits of these funds to investors and firms. Let us understand them in brief:
- Entrepreneurs do not have a risk of losing their stake in the company with this financing. They can access capital at an effective lending rate.
- The returns obtained on this fund are comparatively higher than those from other debt instruments.
- Such funds also work on a global level. They are observing government regulations and bodies. As a result, it is a secure and safe way to borrow money from them.
- The norms and terms under these debt funds are much more flexible. In the client negotiation, chances of curating better and feasible solutions are possible.
- Any private debt player, like venture debt funds, would always wish the business to prosper. As a result, they act as fuel to boost the firm's growth.
- Plus, lenders help tackle industry challenges as well. They advise on some issues and tend to develop better, long-term relations with borrowers.
Private Debt Fund vs Private Equity vs Private Credit
Following are the points that describe the difference between these debt funds, private equity, and private credit. Let us look at them:
| Parameters | Private Debt Fund | Private Equity | Private Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It refers to the portfolio of loans residing in a fund house. | Private equity is an alternative investment made in companies but not listed on stock exchanges. | Private equity is an alternative investment made in companies that are not listed on stock exchanges. |
| Returns | There are fixed returns usually more than traditional debt instruments. | Here, returns are higher than the other two. | It has a fixed return rate for investors. |
| Types | Direct lending, venture debt, and special situation lending. | Leveraged buyout (LBO), venture capital, growth equity, mezzanine capital, and others. | It includes senior debt, mezzanine debt, distressed debt, real estate debt, and more. |
| Form of lending | Here, it is mostly debt instruments, except for special situations (including both equity and debt). | It includes an equity mode of investment. | It also includes debt securities like loans, bonds, and more. |
