Table Of Contents
LOOKUPVALUE in Power BI
Having said about the importance of the VLOOKUP function, we can use the same function in Power BI is the common question from all the Power BI beginners, but unfortunately, we don’t have VLOOKUP Power BI; instead, we have a similar kind of function, i.e., LOOKUPVALUE function in Power BI. In this article, we will guide you through this function. If I have to tell you the importance of VLOOKUP in excel for all the excel users in simple words, “it is just an integral part.” Yes, VLOOKUP is an integral part of all the excel users and household functions in the Excel world.
What Does LOOKUPVALUE Function Do in Power BI?
The LOOKUPVALUE function is similar to the VLOOKUP function in MS Excel, which looks for the required column from one table to the other based on the search value. Since we know enough about VLOOKUP, we will not theoretically go deep into this function. So, let us look at the scenario now.
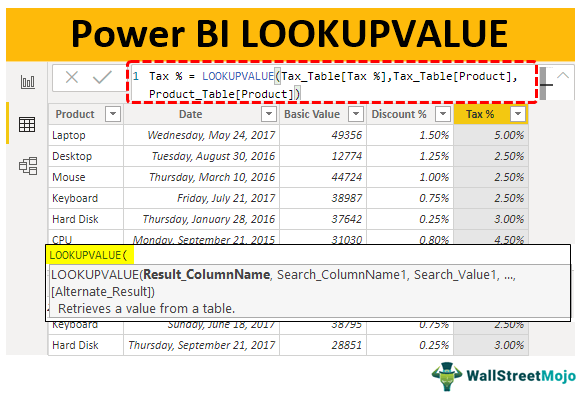
We have three tables with us. Below are the screenshots of the same.

We have three tables named “Product_Table, Tax-Table, and Discount_Table,” respectively.
In Product_Table, we do not have “Tax %” and “Discount %” information, which is there in the other two tables. So, in all the three tables, the common column is “Product.” So, using this, we need to fetch the data to “Product_Table.”
Before we apply the LOOKUPVALUE function, let us look at the syntax of this function.

Result Column Name: This is nothing but from the other tables from which column we need the result. So, for example, from “Tax_Table,” we need results from the “Tax %” column, and from “Discount_Table,” we need results from the “Discount %” column..
Search Column Name: This is nothing but in the targeted table (Tax_Table or Discount_Table) based on which column we are looking for the Result Column. So our Search Value: This is the column name in the present table (Product_Table), which is the same as the column in the Search Column Name of other tables.
So, eventually, Search Column Name and Search Value both columns should be the same. The "Search Column Name" is from the result table, and the "Search Value" column will be from the present table where we apply the LOOKUPVALUE function.

Example of LOOKUPVALUE DAX Function in Power BI
Above is the data we use to apply the LOOKUPVALUE DAX function in Power BI. You can download the workbook from the link below and can use it to practice with us.
- Upload all three tables to the Power BI file to start the demonstration.

- For "Product_Table," we need to fetch the values from the other two tables, so first, we will fetch "Discount %" from "Discount_Table." Then, right-click on the "Product_Table" and choose "New column."

- Give the "New column" name as "Discount %."

- Open the LOOKUPVALUE function now.

- The first argument is the "Result Column Name" since we are looking for the discount percentage from "Discount_Table," choose the "Discount %" column name from "Discount_Table."

- The next argument is "Search Column Name 1," so this will be the "Product" column name from "Discount_Table."
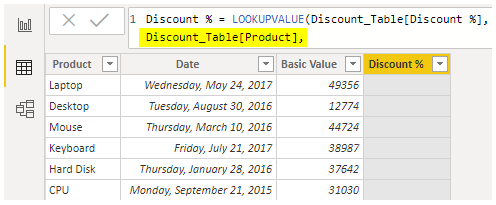
- The next argument is "Search Value," so this will be a "Product" column name from "Product_Table."

- We are done. Close the bracket and press the "Enter" key to get the result.
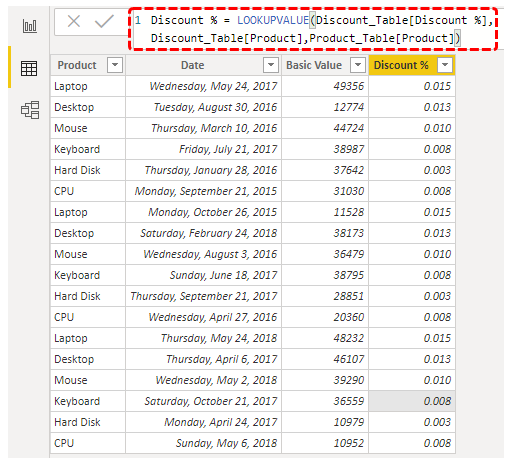
There you go, we have got the result from "Discount %" from "Discount_Table." But, when we look at the result column, it is not in a percentage format. So, we need to change the number format to the percentage format. - Go to the "Modeling" tab, choose the "Format" as "Percentage," and keep the decimal place as 2.

- It will apply the format to the selected column as below.
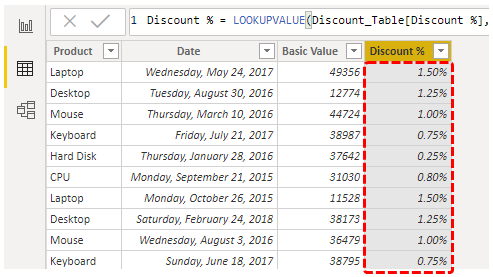
- Similarly, we need to insert one more column to fetch "Tax %" from "Tax_Table." As usual, right-click and choose "New column," give the name to the new column as "Tax %." Then, open the LOOKUPVALUE function again.

- This time "Result Column Name" will be from "Tax_Table," i.e., "Tax %."

- The "Search Column Name" will be the "Product" column name from "Tax_Table."

- The next argument is "Search Value," so this will be the "Product" column name from "Product_Table."

- Close the bracket and press the "Enter" key to get the "Tax %" values.

Like this, using the Power BI LOOKUPVALUE function, we can fetch data from one table to another.
Note: We can also download the Power BI LOOKUPVALUE file from the link below and view the final output.
Things to Remember
- The LOOKUPVALUE is incorporated into Power BI as a lookup value function.
- If the lookup value is not found, then it will return blank as a result.
- Result Column and Search Value columns are the same in both tables.
- Unlike the VLOOKUP function, we need to give any column name and range lookup parameters.