Table Of Contents
Portfolio Management Meaning
Portfolio management involves overseeing a set of investments, including securities, bonds, exchange-traded funds, mutual funds, cryptocurrencies, etc., on a personal or professional level. Its purpose is to help investors achieve their long-term financial goals and manage their liquidity needs and risk tolerance.
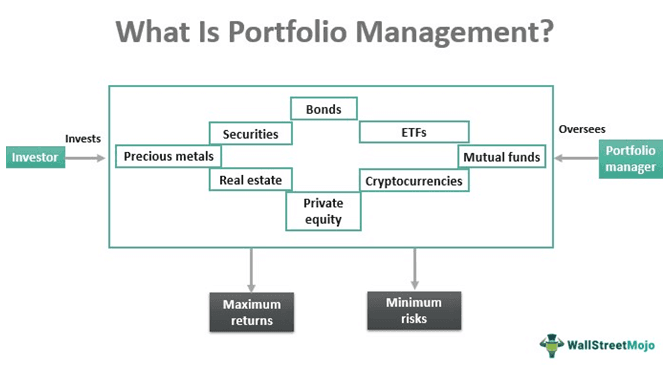
The approach intends to maximize investors’ earnings based on their income, savings, budget, and timeline while minimizing the market risk. This strategy emphasizes choosing the optimum investment policy or a collection of investments called a portfolio. It comprises various processes, including asset allocation, rebalancing, diversification, and tax reduction. Portfolio managers are those who monitor and manage investments on behalf of their clients.
Table of contents
- Portfolio Management Meaning
- Portfolio management refers to building and supervising a group of investments, such as securities, bonds, exchange-traded funds, mutual funds, cryptocurrencies, etc., either personally or professionally.
- It is a three-step process that includes planning, implementation, and feedback, with asset allocation, diversification, rebalancing, and tax reduction being the four most common tactics.
- The four different styles of investment portfolio management include active, passive, discretionary, and non-discretionary.
- Portfolio managers help investors accomplish their long-term financial goals, maximize returns based on their income, budget, and timeline, and minimize risk tolerance by monitoring and managing investments on their behalf.
Understanding Portfolio Management
Portfolio management protects the assets of investors against market risks while also allowing them to profit handsomely. It usually entails setting financial goals, picking the correct investments, allocating assets, assessing risks, and diversifying resources to avoid losses. Investors can make significant profits by aligning their income and financial objectives with their risk tolerance. They can develop a strategy to invest in assets, such as stocks, bonds[, ETFs, mutual funds, private equity, digital currencies, real estate, and precious metals.
Individuals and businesses build and manage their income and assets through the portfolio management process, which involves considering various short- and long-term financial plans. They can do so by themselves or by contacting a portfolio manager for better understanding and outlook. The latter recommends the best and most tailored investment policies. Portfolio management services also guide investors about unforeseen risks, market stability, opportunity, and the right time to invest. In both circumstances, the method could lead to higher profits and lower risks in a set period.
Objectives Of Portfolio Management
The strategy focuses on picking the optimal pool of investments based on the investor's income, aim, time horizon, and risk tolerance. Let us look at some of the portfolio management objectives:

- Capital appreciation
- Improving portfolio flexibility and proficiency
- Maximizing return on investment
- Optimal resource allocation
- Protecting earnings from market hazards
- Risk management
- Securing future
- financial planning
Types Of Portfolio Management
The portfolio management process comes in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics:

#1 - Active
Here, portfolio managers actively sell and purchase stocks, bonds, and other assets using quantitative or qualitative methods to maximize profits for their clients. They strategize to outperform the stock market index by buying undervalued securities and selling them at higher prices.
#2 - Passive
In this type, portfolio management services build and manage a fixed portfolio of index funds, such as ETFs corresponding to current market conditions. Even though these funds offer lower returns, they are more consistent and profitable over time.
#3 - Discretionary
Investors appoint portfolio managers to make financial decisions on their behalf based on their goals and risk appetite to maximize earnings. It may also include paperwork and filing in addition to investment management.
#4 - Non-Discretionary
In this case, portfolio managers can only advise on the best investment plans, while the decision-making authority rests solely with investors.
Process Of Portfolio Management
The following are some of the steps involved in managing an investment portfolio:
#1 - Planning
Understanding the investor's needs is the initial step in the process, which entails several stages, such as:
- Identifying portfolio management objectives and limitations. The goals may include capital appreciation, consistent returns, and risks, whereas restrictions are liquidity, timeframe, and tax
- Calculating the prospective risks, and profits of different asset classes in the capital market.
- Strategizing asset allocation based on market behavior and investor goals
#2 - Execution
After having developed an effective investment plan, the portfolio manager proceeds with the following steps:
- Identifying, analyzing, and selecting assets depending on their popularity, liquidity, profitability, etc.
- Investing in the chosen portfolio of securities or other alternative investments to generate returns
- Mixing up the portfolio based on investment limits and risk tolerance to minimize risks and losses
#3 - Feedback
Once investments have been made in a group of assets, it is crucial to keep track of their performances at regular intervals:
- Monitoring and evaluating the portfolio performance (risk and return) over a period to improve efficiency
- Revising and rebalancing the portfolio as per market conditions to maximize returns
Portfolio Management Strategies
Various strategies can be employed to accomplish the goal of investment portfolio management, i.e., to outperform the market, generate returns, and lower risks. Although predicting the future of financial markets is almost impossible, there are a few proven ways to improve profitability:

#1 - Asset Allocation
This strategy involves investing in different types of assets (volatile and non-volatile) based on the investor’s investment goals and risk tolerance. Eventually, it can result in significant returns with little risk.
#2 - Diversification
Investors or portfolio managers must diversify the investment portfolio to spread the risk and generate profits. Financial markets are volatile and subject to risks. Hence, having a diverse portfolio of assets with little or no correlation means profit made by one can easily offset the loss incurred by another.
#3 - Rebalancing
Market volatility may cause an investment plan to diverge from its target allocation. Therefore, rebalancing the portfolio based on market conditions might result in higher returns with little risk. The common ways to do this include buying and selling assets as required or increasing portfolio investment.
#4 - Tax Reduction
It is nothing more than figuring out a strategy to avoid paying excessive taxes on investment returns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Portfolio management helps investors match their financial goals with their risk tolerance while making considerable profits. They can develop an investment strategy for various assets, including equities, bonds, ETFs, mutual funds, private equity, digital currencies, real estate, and precious metals. Setting financial goals, choosing the correct investments, allocating assets, identifying risks, and diversifying resources to avoid losses are all part of it.
Portfolio managers or portfolio management services monitor and manage investments on behalf of investors. They, thus, assist their clients in achieving their long-term financial goals, maximizing returns depending on their income, budget, and time horizon, and reducing risk tolerance. Besides, they offer advice on unforeseen risks, market stability, opportunities, and the optimum time for investment.
Portfolio management could result in higher returns on investment with fewer risks by considering multiple short- and long-term financing options over a set period. Investing in a variety of assets ensures the growth and stability of managed investments. Other benefits include capital appreciation, effective resource allocation, and a financially secure future.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to portfolio management and its meaning. Here we discuss how portfolio management works along with its process, strategies, types, and objectives. You can learn more from the following articles -
