Table Of Contents
Explanation
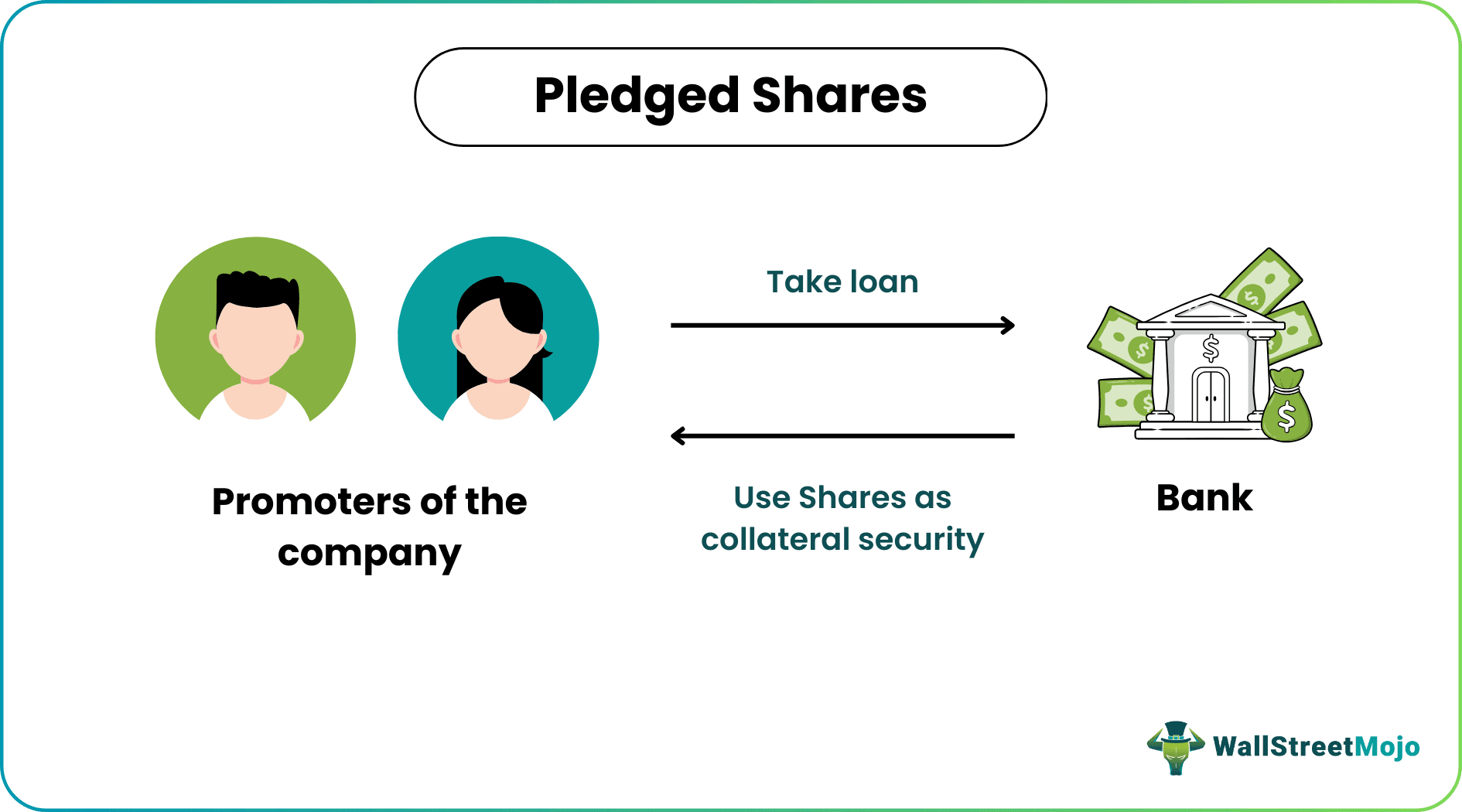
Promoters of the company pledge shares & uses shares as collateral security for getting a loan to meet the business requirement or personal fund requirements. For business, the loan can be taken to meet the working capital requirements, loans for acquiring new business, starting new projects, and acquiring assets. It is different for the hypothecation of assets. In pledging of shares, shares will be in the promoters' name, but they will be transferred to the bank as security of the loan. Till repayment of the loan, promoters can't transfer ownership of shares. It is only preferable when promoters are assured about future performance and inflow of business, and with that inflow, they can repay the loan.
Conclusion
Promoters can pledge their shares to get funds for business or personal requirements. The company considers this method a last resort for availing funds from lenders. The company doesn't prefer to give shares for security because that can affect the company's goodwill. The company keeps this as the last option for funding. First, they prefer-current and current assets to give as security for raising funds, and if all the assets are already given as security to a bank or financial institution, then they try to get the unsecured loan based on business and their goodwill.
But if the company is healthy, growing, and expecting good inflow in the foreseeable future and is in a condition of repaying the loan installments timely. It can raise funds by giving shares as collateral security against the loan amount.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Pledged shares offer a range of advantages, including the ability for shareholders and promoters to access capital without divesting their ownership interests. This grants them the liquidity needed for personal or business needs while retaining control over the company's operations. The practice also facilitates financing at lower interest rates than unsecured loans, leading to potential cost savings.
Pledging shares carries inherent risks. Chief among these is the exposure to price volatility. If the stock's value drops significantly, the pledged shares may no longer adequately cover the loan amount, possibly triggering margin calls or enforced selling. Furthermore, the loss of control over the pledged shares and the potential negative perception among investors could adversely affect the company's reputation and market value.
Yes, pledged shares are eligible for buyback, but the process can be complex. If a company wishes to buy back pledged shares, it must coordinate with the lender to ensure proper transfer of ownership. Additionally, the terms of the loan agreement and any legal restrictions must be considered before initiating a buyback of pledged shares.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Pledged Shares and their Meaning. Here we discuss how pledged shares work along with an example and detailed explanation. You can learn more about financing from the following articles –