Table Of Contents
Payroll Definition
Payroll is an entity's financial list of the total number of employees working with it during the period and the amount paid to them in the form of the net pay comprising the salary, wages, bonuses, commissions, deductions, various perquisites, and similar other benefits, for a particular period of the time.
Payroll accounting software can be referred to for the amount paid by the companies to its employees in the form of net pay after deducting all the statutory dues and other things as required. It offers various benefits and has certain disadvantages, too. The payroll process should be adopted by the companies keeping in mind the nature and size of the business.
Payroll Explained
The payroll process is the process by which the company the company pays the total amount of compensation pays the total amount of compensation to its employees during a given period. This process includes all the work, starting with tracking the work done by the employees till the time when the amount is disbursed in the employees’ accounts. Along with this, the accounting of payrolls, taxes paid, and other extra pay will also be included. It is one of the major expenses of the company, and the same is allowed for deduction from gross income to derive the company's taxable income. Generally, the work is done by any company's human resource development department.
Process
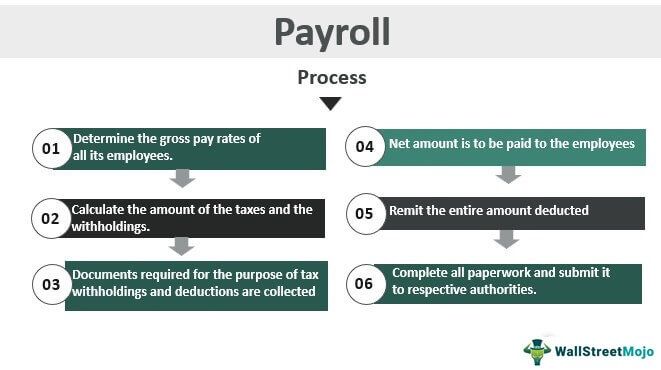
Let us understand the process of payroll accounting through the step-by-step process explained below.
- Firstly one should determine the gross pay rates of all of its employees.
- After that, all documents required for tax with-holdings and the deductions should be collected from the employees.
- Then calculate the amount of the taxes and the with-holdings.
- After step 3, the net amount is paid to the employees, along with providing the employees with a pay stub.
- Remit the entire amount deducted from the employees' gross pay to respective authorities or the benefits providers.
- Lastly, completing all the paperwork and submitting the same to respective authorities.
A payroll software or even a physical copy of such data is composed of the following components:

- Gross Pay: is the total amount paid to an employee before certain reimbursements and deductions. Sometimes, gross Pay may include bonuses, commissions, and other payments.
- Deductions: Payroll deductions can be broadly classified into pre-tax deductions and post-tax. Pre-tax deductions are not subject to tax, but post-tax deductions are not.
- Fringe Benefits: Fringe Benefits are additional benefits supplementing an employee's salary. Examples: a company's car, subsidized meals, health insurance, education assistance, retirement plans, etc.
- Tax: Employers withhold employees' share of various types of taxes concerning their federal or state law, along with paying their portion of taxes.
- Net Pay: The total amount ultimately paid to the employee after adjusting deductions, benefits, and taxes.
Different Ways to Run Payroll
The different ways by which one can conduct payroll accounting are:
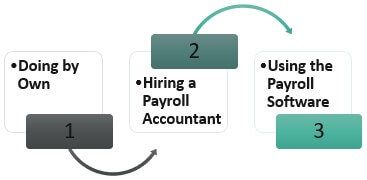
#1 - Doing by Own
One can run the payroll process by himself and without the help of any person or any software. This way is time-consuming because one has to learn every aspect by himself.
#2 - Hiring a Payroll Accountant
Under this entire work of the payroll is outsourced to the accountant. These accountants will take care of the entire process, and thus it will save time. But this option can be availed by the person with enough money because it might be the most expensive option out of the available ones.
#3 - Using the Payroll Software
Nowadays, various types of software are available in the market, and most of them are inexpensive. With the help of this software, one can automate many payroll processing programs, and the same can also be customized as per the requirement. For using and purchasing this, a one-time charge must be paid along with the maintenance charges as required. But the same will save time as one must spend less time completing the process.
Deductions
Payroll deductions are the amounts withheld from an employee's gross earnings to cover various taxes, benefits, and other obligations. Let us understand the different forms that are taken into account by payroll software or even physical maintenance of such records through the explanation below.
- Includes federal, state, and local income taxes, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes, which are mandatory contributions by the employee.
- Deductions for health insurance premiums, retirement contributions (such as 401(k) or pension plans), and other voluntary benefits chosen by the employee.
- Deductions for repayment of loans, such as student loans or advances taken from the employer.
- Covers premiums for various insurance policies, such as life insurance or disability insurance.
- Deductions to satisfy court-ordered obligations, like child support or alimony payments.
- Employees may opt for additional voluntary deductions, such as contributions to charitable organizations or stock purchase plans.
Tax
Both employers and employees must understand the intricacies of payroll accounting and taxation to ensure the right amounts are withheld and disbursed. Let us understand the most common taxes applied to payroll through the discussion below.
- Income Taxes: Employees are subject to federal, state, and local income taxes, with the withholding amount based on their declared withholding allowances and income level.
- Social Security Tax: Employees contribute a percentage of their income, up to a set limit, to fund Social Security benefits.
- Medicare Tax: Similar to Social Security, employees contribute a percentage of their income to fund Medicare, with no income limit.
- State and Local Taxes: Depending on the employee's residence, additional state and local income taxes may apply.
- Pre-Tax Deductions: Some deductions, like contributions to retirement plans and certain benefits, may be made before income taxes, reducing taxable income.
- Post-Tax Deductions: Other deductions, like union dues or certain voluntary benefits, are made after income taxes.
Advantages
The following are the different advantages:
- Simple Computation: Error-less and simple computations are made through the payroll system compared to manual calculations, saving time and money.
- Documentation: It helps create reports and financial documents easily, which are ultimately helpful in making certain comparisons (year to year, industry to industry, etc.) with no stress of maintaining payroll registers.
- Safe Backup: Maintaining registers manually is not an easy task. It helps secure the backup of all payroll software data online and presents it as and when required.
- Cost Cutting: This system aids in cost-cutting. Maintaining its registers requires hiring a person to keep the records. This system is easy to use and can be done in-house.
Disadvantages
The following are the different disadvantages:
- Manual Payroll System: It has a high chance of errors. Wrong calculation of taxes and other important fields can sometimes lead to penalties. It is undoubtedly a time-consuming process since every field is to be filled, and every calculation is to be done by hand.
- Online Errors: Errors done manually can be traced easily, but errors, if done online, can be tough to trace.
- Privacy Concern: Since payroll accounting is usually outsourced or utilized through online services, sensitive information about employees no longer remains under privacy.
- Backup: Proper backup must be available in case of an accident resulting in computers or systems being damaged.
Difference between Salary & Payroll
There are many differences between Salary and Payroll accounting, important ones of which are:
- Salary refers to the fixed amount earned by an employee during his employment. In contrast, payroll is a proper function used by my employers to process and record salaries or wages paid to employees.
- Salary is a condition of employment, whereas payroll is a process.
