Table Of Contents
Formula to Calculate Opportunity Cost
Opportunity Cost is the cost of the next best alternative, forgiven. When a business must decide among alternate options, they will choose the one that provides them the greatest return. Frankly speaking, there is no such specifically agreed or defined on a mathematical formula for the calculation of opportunity cost, but there are certain ways to think about those opportunity costs in a mathematical way, and the below formula is one of them.
However, this value may or may not always be measured in terms of money. Value can also be measured by other techniques, for example, satisfaction or time.
Opportunity Cost = Return of Next Best Alternative not chosen - Return of the option chosen

One relative formula for the calculation of opportunity cost could be -

If we think about the cost of opportunity like this, then the equation is very easy to understand, and it's straightforward.
Examples
Example #1 - Reliance JIO
Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd (known as Jio), a mobile network operator in India that is owned by Reliance Industries, which is headquartered in Mumbai.
The service that was launched for all users on 5th September 2016 with a ‘Welcome Offer,’ was originally introduced in beta version for the employees of Reliance only on December 27, 2015, to mark the eighty-third birth anniversary of Dhirubhai Ambani, who was the founder of Reliance Industries.
The introductory offer lured many Indian customers, and it was able to manage to get 72 million prime customers within the first three months of its launch, but later, the company decided to extend its freebies for another three months when it had another option of actually charging the customer and earn revenue and hence it chose to forgive it’s another best alternate for not choosing to bill their customers for the services.
Reliance Jio Infocomm actually missed out on an $800 million (which is Rs 5,400 crore) revenue opportunity as mentioned above by offering an additional three months freebies, i.e., free services to its 72 million Prime customers who were actually ready to pay them from 1st of April.
Example #2 - Paytm Investment Opp
Paytm is an Indian e-commerce digital wallet and payment system company, based out of NOIDA S.E.Z in India. Paytm is available ten Indian languages, and it offers online use-cases like utility bill payments, travel, movies, mobile recharges, and events bookings as well as in-store payments at the grocery stores, vegetables and fruits shops, restaurants, pharmacies, parking, tolls, and education institutions with the QR code of Paytm Paytm, which is presently also loss-making company and which has yet to prove its mettle when it comes to the business model and providing the long-term sustainable product.
Berkshire a globally renowned firm that has a market capitalization of around $500 Billion. Based on its past record, it is also known for one of the most astute and sharpest investors in the world. Berkshire decided to pick up a 3 to 4% stake in payments major with Rs 2,500 crore (around $356 million) that was made.
The question now arises as to why and what led Berkshire to invest in Paytm, whose losses stood at Rs 900 crore, whereas it's coming to its revenue it was around Rs 829 crore, and in the year prior, its loss figure had touched Rs 1,497 crore? What is its expectation with that investment?
Berkshire was aware of the financial opportunity which was available in the Indian market that it had to offer. It would not like to miss it. So here, the opportunity cost for Berkshire will be Rs 2500 crore as easily it could have chosen any other listed company with a profit-making company.
Interpretation
- Opportunity cost is the value of something when a certain course of action is chosen. The benefit or value that was given up can refer to decisions in your personal life, in an organization, in the country or the economy, or in the environment, or on the governmental level.
- These kinds of decisions will typically involve constraints like time, social norms, resources, rules, and physical realities.
- An investor goes completely to cash when he decides that the market is overvalued. This will dramatically reduce their risk at the cost of opportunity of the potential returns that are being invested.
- Another example where student considers the cost of 4-year university education by calculating total hostel, tuition, and other expenses for the period. They could also include the cost of the opportunity of missing 4-years of salary in their calculations.
- A headphone manufacturer facing healthy competition from low-cost products with similar designs of their own. They can decide to increase the quality of their build (for e.g., Apple) to make the competition look and feel comparatively cheap. The opportunity cost of the new design of the product will be the increased cost and its inability to compete on price.
- Opportunity costs are truly everywhere, and they occur with every decision we make, whether it's big or small.
Opportunity Cost Formula - Explained in Video
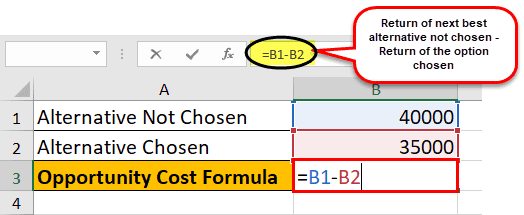
Opportunity Cost Calculation in Excel
Let us now do the same Opportunity Cost example in Excel. This is very simple. You need to provide the two inputs of return of the next best alternative not chosen and return of the option chosen. You can easily calculate the ratio in the template provided.

The opportunity cost will be -