Table Of Contents
NPV Function in Excel
NPV in Excel is also known as the net present value formula in Excel, which is used to calculate the difference between the current cash inflow and cash outflow for an investment. It is a built-in function in Excel. It is a financial formula that inputs the rate value for inflow and outflow.
The NPV (Net Present Value) function on Excel calculates the net present value for periodic cash flows based on a supplied discount rate and a series of payments. The NPV in Excel is generally leveraged under financial calculation.
In financial projects, the NPV in Excel is useful in finding the value of an investment or analyzing the feasibility of a project. Therefore, it is recommended that financial analysts should use the XNPV function over the regular NPV (Net Present Value) in the Excel function.
NPV Formula in Excel

The NPV in excel accepts the following arguments:
- Rate (argument required): It is the discount rate over the length of the period.
- Value1, Value2: Value1 is required. They are numeric values that represent a series of payments and income where:
- Outgoing payments are mentioned as negative numbers.
- Incoming payments are mentioned as positive numbers.
NPV in Excel Explained in Video
NPV Equation
The calculation of NPV (Net Present Value) of an Investment in the Excel’s NPV function is based upon the following equation:
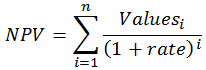
How to use the NPV Function in Excel? (with Examples)
Let’s take a few NPV excel calculation examples before using the NPV function in the Excel workbook:
Example #1
Suppose we are working on the following data set on cash inflows and outflows:
The below spreadsheet shows a simple example of the NPV function in excel.
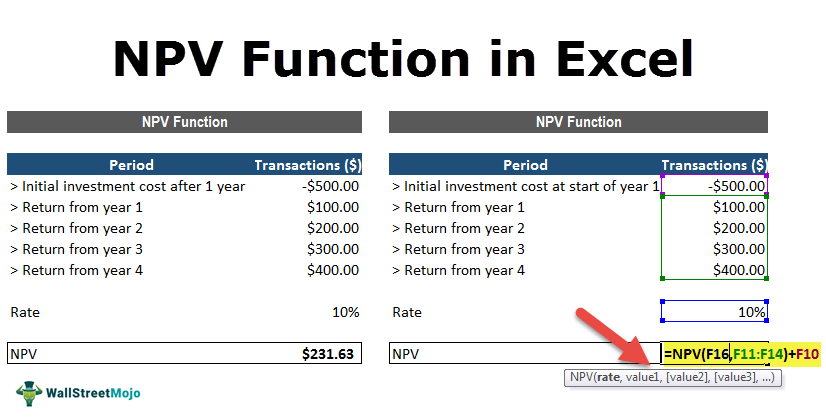
The rate arguments that are supplied to the function are stored in cell C11, and the value arguments have been stored in cells C5-C9 of the spreadsheet. The NPV in Excel is entered in the cell C13.
This function gives the result of $231.63.
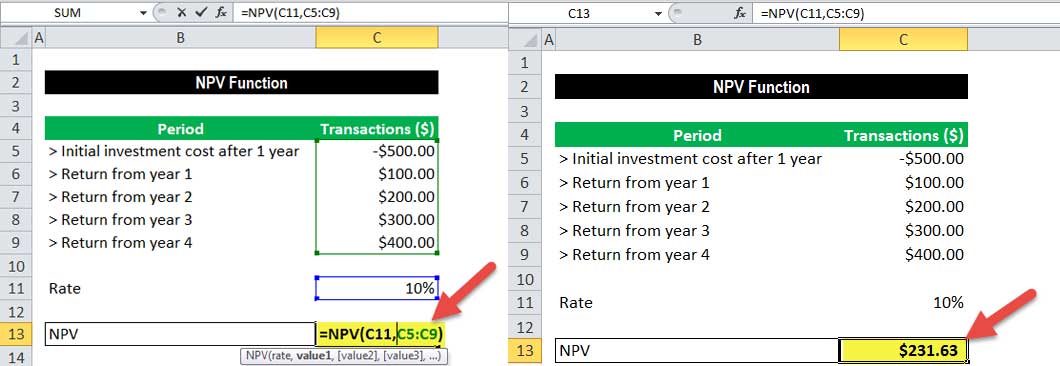
In this example, we made the initial investment of $500 (shown in cell C5) at the end of the first period. This value is considered the first argument (value1) to the NPV function in Excel.
Example #2
The below spreadsheet shows a further example in which the first payment is made at the start of the first period and how this payment should be considered in the NPV function in Excel.
Again, the rate of 10% is stored in cell C11, and cash flow value arguments of the transactions are held between the range C5-C9 of the spreadsheet. NPV in Excel is inserted in cell C11.

The function gives the result of $2,54.80.

Note that, as the initial investment of $500 (shown in cell C5) was done at the start of the first period, this value is not included in the arguments to the NPV function in Excel. Instead, the first cash flow is added to the NPV Excel result.
As described in example # 2, the NPV formula in excel is established on future cash flows. Therefore, if the first cash flow happens at the start of the first period, we must add the first cash flow value to the NPV Excel result. We should not include it in the values arguments.
Things to note about the NPV in Excel
- The NPV investment begins one period ahead of the date of the value1 cash flow and ends with the last cash flow in the list. The NPV calculation in Excel is based upon future cash flows. Therefore, if the first cash flow is made at the beginning of the first period, the first value must be explicitly added to the NPV Excel result, excluded in the values arguments. For more information, see the examples below.
- Let us say n is the number of cash flows in the list of values; the formula for NPV (Net Present Value) in Excel would be:
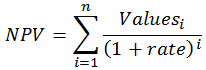
- If the arguments are supplied individually, numbers, logical values, blank cells, and text representations of numbers are evaluated as numeric values. At the same time, the function ignores other values of cells in text and error form.
- If the arguments are supplied in a range, all non-numeric values in the range are ignored.
- We need to enter transactions, payments, and income values in the right sequence as NPV functions use the order of the 2nd argument, i.e., value1, value2, …, to evaluate the ranking of cash flows.
- The key difference between NPV functions and PV function is that PV allows cash flows to begin either at the beginning or at the end of the period.
- NVP (Net Present Value)function in the latest versions of Excel can accept up to 254 value arguments, but with Excel 2003, only up to 29 values can be supplied.

