Table Of Contents
Novation Meaning
Novation, in contract law, refers to the agreement between current parties to replace one party or obligation with another alternative. The main purpose of this law is to substitute one party with another so that the rights and obligations of the contract now reside between the new parties.
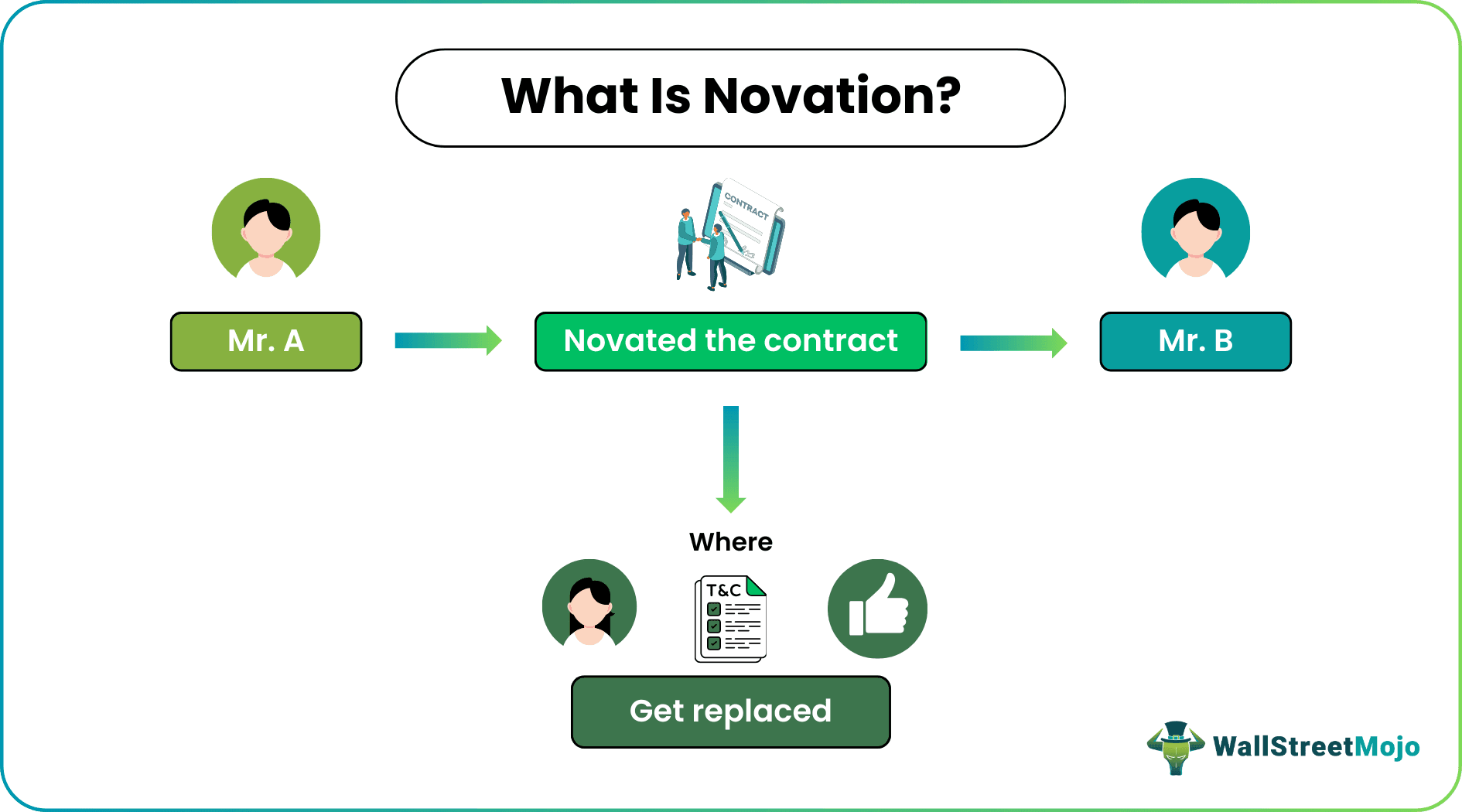
Novation law includes several kinds of replacements. Here, mutual consent serves as the essence of this process. It enables transferring the benefits and liabilities of one person to another. Also, the parties agree to dissolve the existing agreement and replace it with another one. However, the novation process is incomplete without its essentials.
Key Takeaways
- Novation, in legal terms, refers to substituting a person, term, or set of obligations with another. It enables the replacement with the mutual consent of all.
- In financial markets, it refers to trading the securities to a third party on the buyer's behalf. It has major applications in banking, real estate, and contractual projects.
- The major types of Novation include standard, expromissio, and delegation.
- The essentials of this law include mutual consent between all, the validity of the new contract, and no breaching of the old contract.
Novation Agreement Explained
Novation agreement has two different meanings in different contexts. While in contract law, it refers to replacing an existing party or obligation with another. However, in financial markets, it refers to an agreement where the clearing house acts as a medium to trade securities for the buyers.
In contract law, a deed of novation is an agreement where all the parties agree to substitute either of them with a third person. However, they need to fulfill the essentials of the contract. First, all parties must have mutual consent for this replacement. In addition, no party should breach the original contract. Also, the new contract should be valid and enforceable. Finally, the old parties need to compensate (indemnify) for losses during the novation process.
As the novation happens, the old contract gets discharged, and no parties are required to bind this contract. Thus, the replacing party's rights and liabilities get transferred to the new party. So, the old party will not be accountable (liable) for any losses arising after novation.
History
The concept of the deed of novation dates back to Roman law, derived from the word "Novati," meaning substitution. Later, in Bracton, the emergence of assignment enabled the substitution of a new debtor and creditor.
For example, the creditor will instruct the debtor to pay their family or friends. Thus, there was a delegation of responsibilities to another person. Later, in the 19th century, Federal and Scottish laws adopted it.
Types
Let us look at the types of novation law to comprehend the concept better:
#1 - Standard
It happens when the parties agree to new terms and create a new contract. Here, the parties renovate the existing conditions and novate a new agreement. They are free to do so, which is called the standard novation.
#2 - Expromissio
Expromissio (Roman word) means inviting a new person into the agreement. A new person enters the contract, thereby releasing the old party. Here, mutual consent of all the parties is a must. Otherwise, there can be a breach of the contract.
#3 - Delegation
A delegation is the transfer of responsibilities from one person to another. As a result, the rights and obligations of the exiting party get transferred to the third party.
For example, if Alex were liable to pay $200 to Sam after delegated novation, Sam would exit, and Mitchell will replace him in the contract. Thus, Alex will now pay $200 to Mitchell.
Examples
Although it has several uses, the main influence of novation is in the financial, real estate, and banking sector. For better understanding, let us look at some real-time examples of the doctrine of novation:
Example #1
Suppose Sam and Jessy have legally bound a contract. According to the agreement, Sam will purchase a house from Jessy on December 5, 2022. However, due to uncertainty, Jessy will not be available to execute the contract. Thus, she, along with Sam, goes for novation. As per the doctrine of novation, Jessy will delegate all her rights and liabilities to Musk (her husband). So, Musk took over Jessy's position instead of Jessy, resulting in a new contract. Thus, Sam needs to pay Musk as he has replaced Jessy.
Example #2
On November 5, 2022, the court resolved the two-year issue between the maritime companies Trafigura Maritime Logistics Pte Ltd and Clearlake Shipping Pte Ltd. According to the judge, the novation between Clearlake Chartering and Clearlake Shipping discharged the former from its liability. As a result, Clearlake Chartering is no longer liable to pay Trafigura because it had delegated its obligations to Clearlake Shipping.
Novation vs Assignment
Although novation is an alternative to the assignment, they both have differences. The former allows all the parties to substitute any of them with another person. The terms, benefits, and obligations can also get transferred. In contrast, the latter only transfers the benefits to the other person. There is no transfer of liabilities and obligations to other people. The major difference is that a person can get replaced in the former, but in the latter, it is impossible. However, both transfer benefits to a new party.
| Novation | Assignment | |
| Meaning | It is an act of substituting one party or obligation with another. | A defined process of transferring interest and benefits from one person to another. |
| Purpose | To replace one party, terms, or obligation with another. | To transfer the benefits from one person to another. |
| Transfer of liabilities | Yes | No transfer of obligations |
| Replacing a person | Yes | No |
