Table Of Contents
What Is Non-Profit Accounting?
Non-profit accounting refers to the accounting arrangement that helps record and retrieve the financial details of a not-for-profit organization. Such organizations run not for profit but for the betterment of society. Hence, recording accounts used in favor of relevant causes is significant.
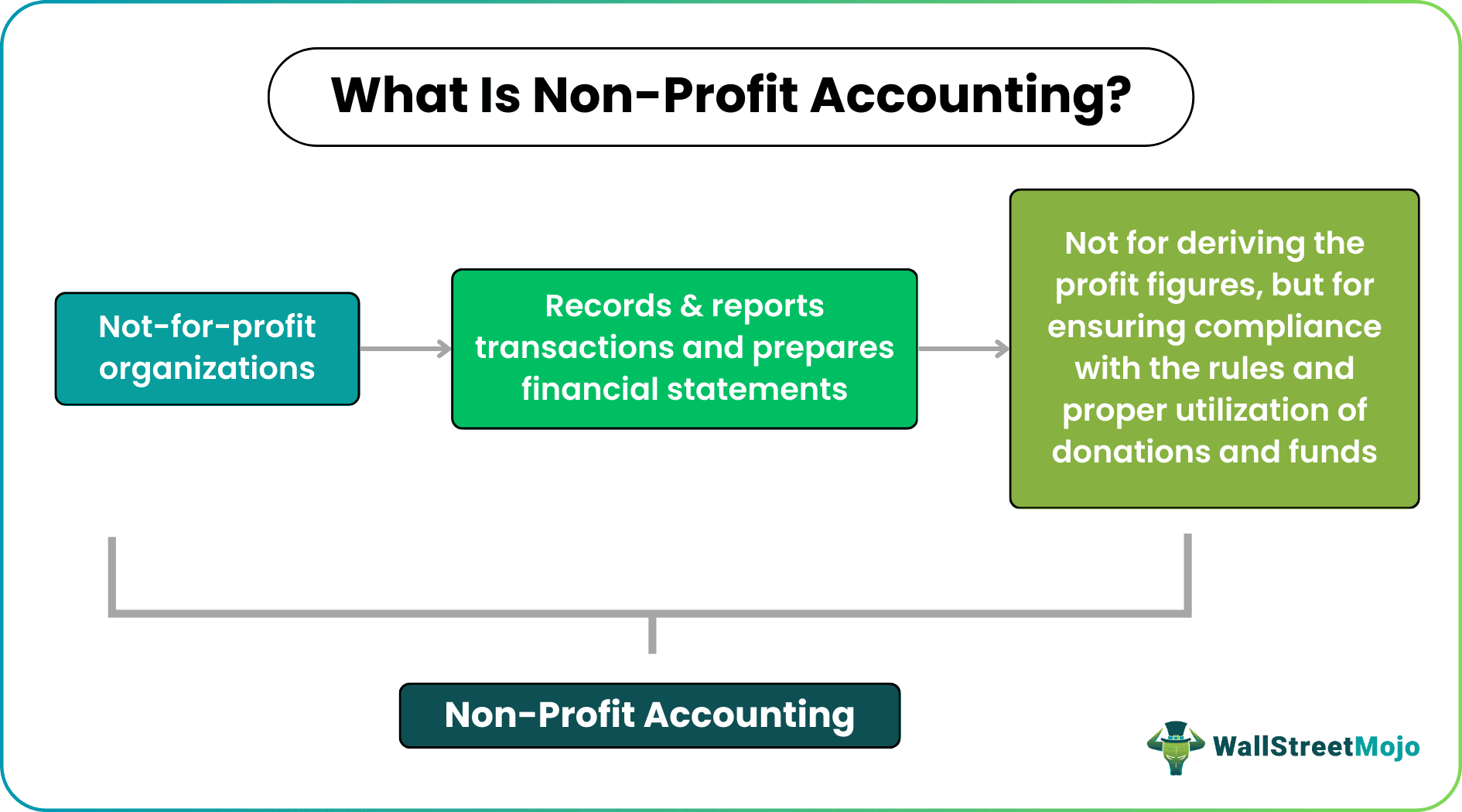
The accounting process, in this case, doesn't remain confined to checking the profits made but to ensuring that the businesses have been operating in compliance with the rules and industry standards. In addition, accountability with non-profit accounting enables contributors and donors to get details of the utilization of their resources.
Key Takeaways
- Non-profit accounting is about recording and reporting a non-profit organization's transactions.
- It involves choosing the best accounting method, understanding various compliances and tax responsibilities, and creating and reporting the figures in the appropriate financial statements.
- Non-profit organizations have a separate statement of the functional expenses to record the funds accounting of the company.
- Funds accounting, restricted distribution, acceptable guidelines, and proper documentation must achieve the best non-profit accounting results.
How Does Non-Profit Accounting Work?
Non-profit accounting makes a non-profit organization reliable and trustworthy. The firms prepare financial statements that let the individuals have details regarding the utilization of the funds. If donors find any tampering with the records, they suspect the misutilization of the funds and resources. On the contrary, if the records are accurate, they continue donating or contributing money and resources to noble causes.
Accounting for non-profit organizations is not about financial statements depicting profits but about the entities utilizing the contributed and donated resources properly. If the financial statements indicate discrepancies, the organizations lose trust. Thus, a non-profit accounting firm must be careful enough to make computations thoroughly to present the figures accurately. For one to perform this type of accounting, completion of the required non-profit accounting certification is recommended.
However, there are three main reports in the financial statement of non-profit organizations:
- A statement of the financial position
- A statement of the activities
- A statement of the functional expenses
In addition, there are specific programs that non-profit organizations conduct, and the accounting for such programs are done separately to know separate surplus/deficit from such a program. Today, organizations use non-profit accounting software that operates efficiently and per all requirements.
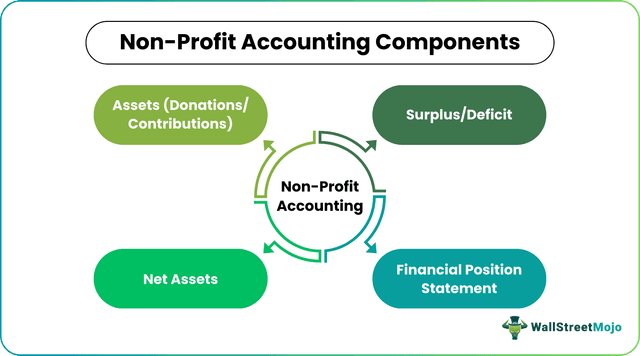
Components
Not-for-profit organizations involve several components for recording and presenting financial details. Some of them include the following:
1. Assets
The organizations receive donations from various sources. These funds or resources can be general and used for general purposes of the organization or specific donations offered for a specific cause. The donations enter the statement of the financial position as assets.
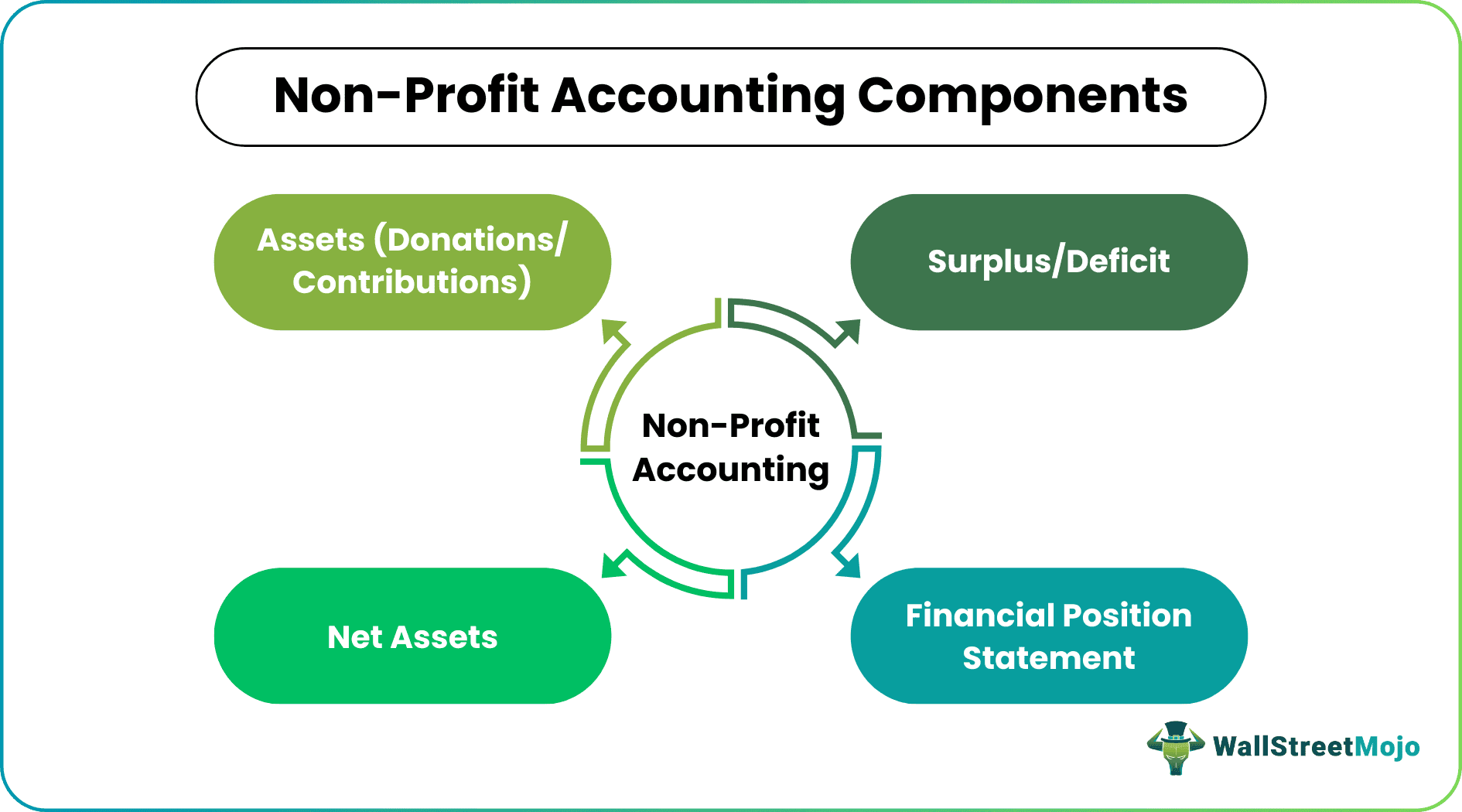
2. Surplus/Deficit
These organizations work for the welfare of society. The specific programs for social welfare fall under a separate category and do not form part of the firm's surplus/deficit. In a profit-making organization, there is a shareholders' equity section, given the presence of the stakeholders in the companies.
3. Net Assets
In a non-profit organization, no stake in equity is there. Hence, such organizations record net assets in the financial position statement.
4. Statement of Financial Position
In non-profit organizations, the accounts department prepares a statement of activities. It calculates surplus/deficit instead of profit and loss account and prepares the statement of financial position in place of the balance sheet. Cash flow statements are, however, common for all.
Principles
The policies, procedures, and best practices differ based on the nations and states in which the not-for-profit organizations operate. Thus, one of the non-profit accounting jobs is to understand the state-specific basics related to conflicts of interest, reasonable compensation, financial transparency, nonpartisan activities, and outcomes and effectiveness of the not-for-profit firms.
1. Funds Accounting
In non-profit organizations, the statement of the functional expenses is prepared to record the funds accounting. Using fund accounting, not-for-profit organizations segregate donations and expenses into restricted, temporarily restricted, and general categories and accordingly use them.
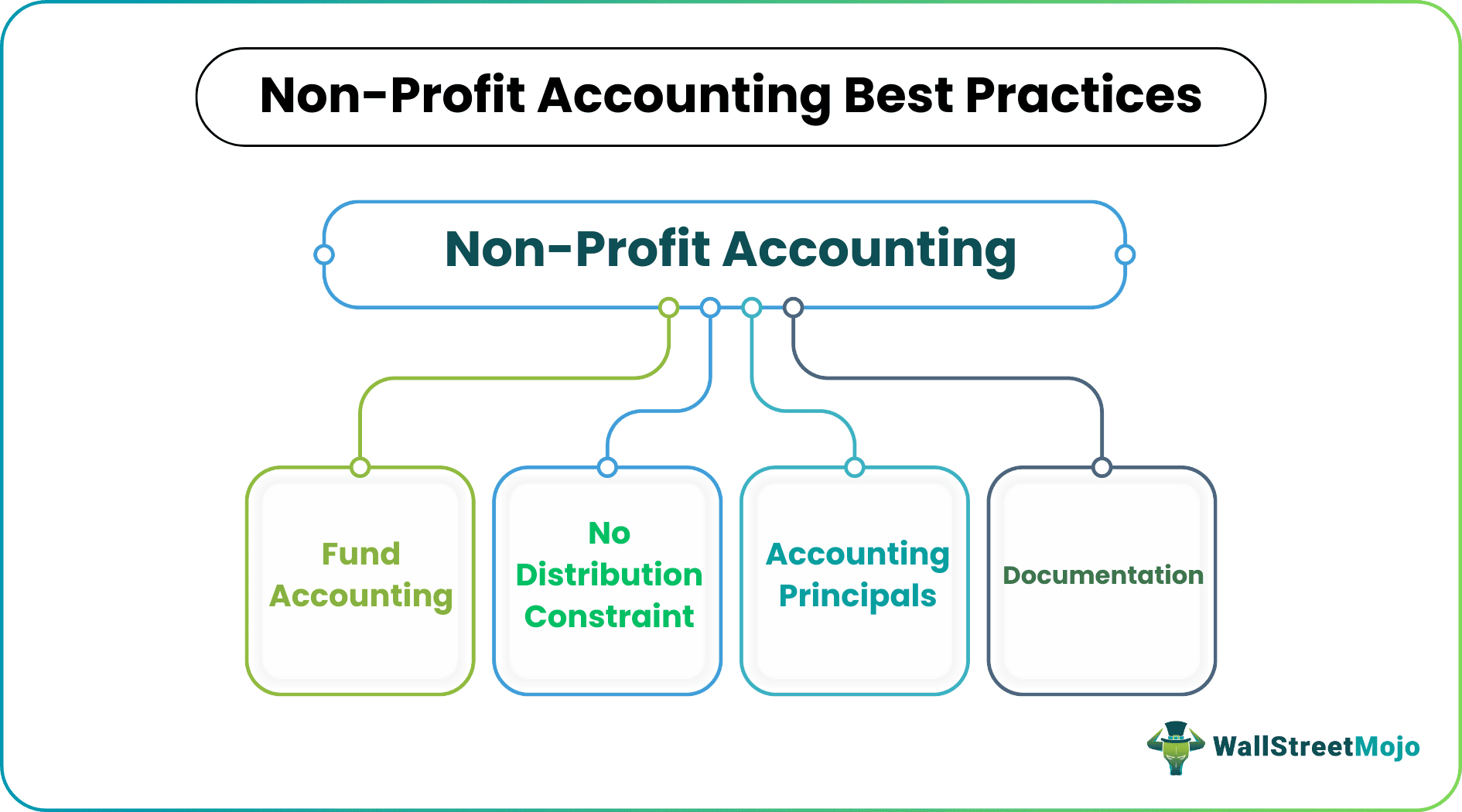
2. No Distribution
In non-profit accounting, accountability in terms of laws and usage of funds is prime. Thus, no organization leader can use the extra funds gathered for noble causes. In short, the extra funds are preserved for future use and cannot be distributed to anyone in the organization.
3. Accounting Guidelines
Non-profit organizations must follow certain accounting guidelines to ensure accuracy and reliability. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has set general guidelines for all organizations. These rules are commonly known as the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
4. Documentation
Last but not least is the documentation. It includes preparing the budget, considering the revenue, and creating the balance sheet, known as the statement of the financial position for not-for-profit organizations.
Example
Below is an example of how to do non-profit accounting:


Non-Profit Accounting vs Profit Accounting
Non-profit and profit accounting differ in various aspects, including the involved intentions. For example, while profit accounting checks the exact profit figures, non-profit accounting ensures the proper utilization of donations and funds. The other differences are as follows:
| Category | Profit Accounting | Non-Profit Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Income statement and statement of operations | Statement of operations |
| Final Document | Balance sheet | Statement of Financial Position |
| Income Credential | Statement of retained earnings | Statement of changes in net assets |