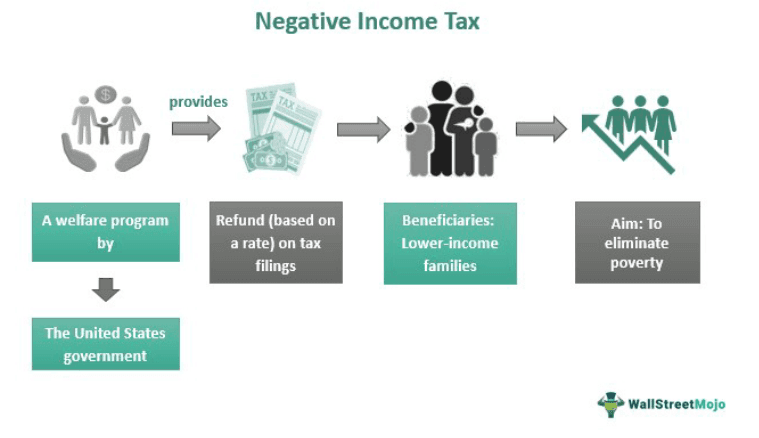
Negative Income Tax, also known as net operation loss (NOL), allows individuals to earn a subsidized amount on taxable earnings. American economist Milton Friedman first proposed this system in 1962. According to the system, only certain income groups can access this income. Individuals qualifying for the negative income tax program will receive the benefit. However, it discouraged people from working.
The idea of this tax is traceable back to the 1960s. In 1962, economist Milton Friedman proposed the concept in the book "Capitalism and Freedom." Later, in 1965, another economist, Robert Lampman, popularized the idea of a net operation loss rate. Lampman argued that the government should provide welfare benefits to two-parent families and single people.
By the end of the 20th century, economists Vilfredo Pareto, James Tobin, Joseph A. Pechman, Peter M. Mieszkowski, and Abram Bergson supported it. Likewise, Michael Boskin, Christopher Green, and Paul Samuelson clearly defined the negative income tax graph. As a result, U.S. President Richard Nixon, along with the support of economists, added a negative income levy as a part of the Family Assistance Plan in 1969. Likewise, along with the United States, even Canada became a part of a net operating loss (NOL) program.
This theory is a mirror reflection of the existing tax system. For example, Friedman's negative income tax theory states a few benefits that can influence the global economy. Let us look at them:
- Provides financial assistance to the individuals
- Targets low-income groups and minimizes the poverty gaps
- This program can replace all other supporting programs.
- Better than other welfare as the cost involved is relatively lower.