Table Of Contents
What Is Negative Gearing?
Negative gearing is a phenomenon that occurs when an individual takes a mortgage to purchase an asset and experiencesa loss as the income from the investment is less than the investment expenses. This, however, helps investors utilize the corresponding loss to reduce total taxable income.
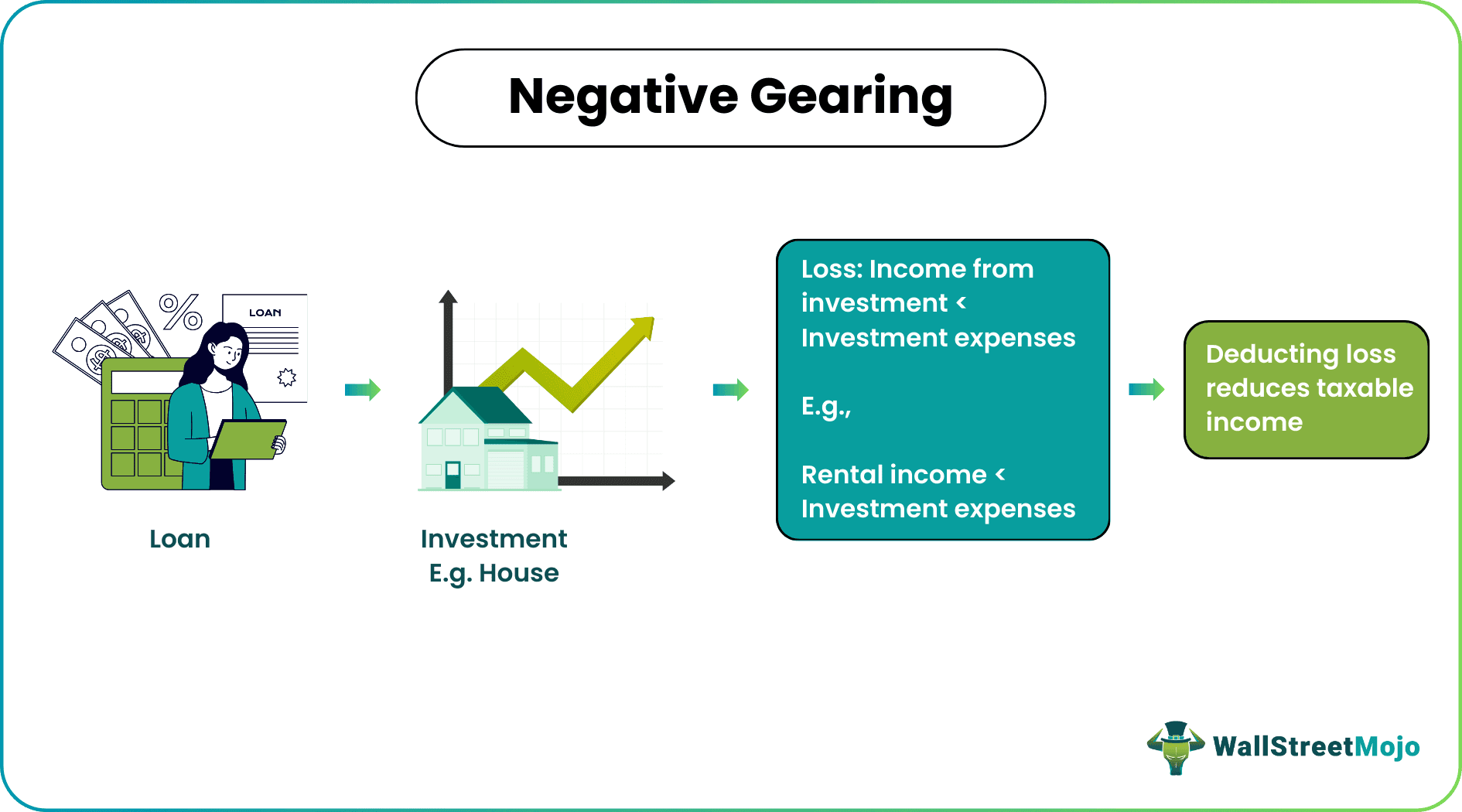
The phenomenon is predominantly evident in real estate and financial markets. Investors use borrowed funds for picking investments like real estate properties and shares. As a result, the possibility of incurring loss is not uncommon; they may receive rental income and dividends inadequate to cover interest expenses. In such cases, the loss offsets the total taxable income.
Key Takeaways
- Negative gearing happens when loss due to income from investment falling below the investment expenses is utilized to reduce total taxable income.
- The investors benefit from reduced tax liability in the short term. In addition, an increase in asset market value will help extract capital gain as a long-term goal covering all initial losses.
- Examples are buying real estate or shares using borrowed funds to reduce taxable income.
- The strategy will not be beneficial, If the mortgage interest rises without a rise in investor income or if real estate value decreases, causing no potential capital gain.
Negative Gearing Explained
Negative gearing is a technique beneficial to many taxpayers as it allows them to subtract the losses they make on their investments from the taxable income. So, it is distinct that it reduces their tax burden in the short run. The strategy's ultimate success lies in asset appreciation. The increase in market value over time and subsequent sale of assets results in the capital gain covering the initial losses.
There are several other advantages to this technique. When it comes to rental income, it is taxed like ordinary income. If the losses are deductible against personal taxable income, the system allows passive investment losses to be written off against labor income. In certain nations, maintaining high home values is vital in the viewpoint of politicians to avoid diminishing the fortunes of the majority of voters, that is, property owners.
Rich and high earners can utilize this strategy because they can easily afford to borrow loans for investment purposes. Therefore, the greatest share of the benefits goes to them – and the biggest growth is to those owning multiple properties. However, it is not perceived as a safe option for low-income people. Furthermore, the strategy which differs from this is positive gearing, in which the investor can use the adequate cash inflow from investment to pay expenses.
The negative gearing process reduces the government's taxation revenue. For example, negative gearing in Australia reduced the nation's income tax revenue significantly. When countries like Japan and Australia allow this technique, countries like Canada, and America, permit it but are constrained by restrictions. Recently, New Zealand has decided to shut down its policies leading to negative gearing in investment property to control its housing market.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to see how to calculate negative gearing:
Example 1
Janice has taken a mortgage loan from a bank to purchase a residential rental property. She rents it to a family, the family pays a rent of $1300 every month, so technically the annual rental income received by Janice is $15600. However, when the cash inflow in the form of rental income is compared to the cash outflow due to expenses incurred for holding or maintaining the property that equals $20,000, Janice incurs an annual loss of $4400. In essence, the expenses exceed rental income.
Janice is also an engineer and works at a private firm. The taxable income of Janice is $36,000. However, Janice claims $4400 in the taxation process as a loss on her negative geared property, and the shortfall is subtracted from her annual income. Earlier, she was paying tax on her annual income of $36000, but after the shortfall is offset, which is $36000 - $4400 = $31600. Therefore, the new taxable income of Janice is $31600. In this way, Janice enjoys tax benefits.
It is a simple example of negative gearing in property, but in complex or real cases, many external and internal factors need to be considered for calculating the taxable income. For instance, one should consider depreciation and check whether the loss is limited according to guidelines.
Example 2
Negative gearing in Australia has become one of the major concerns recently as the authorities decide on tax reforms. According to them, the tax system would be fairer and more consistent if a few measures are incorporated. One of them includes winding back of negative gearing, while the rest is the reduction of capital gain tax discount, etc.
Pros & Cons
Negative gearing, though it sounds a negative concept, has a wide range of benefits when chosen as an investment strategy. At the same time, it has a few limitations as well. To understand the negative gearing meaning better, studying the advantages and disadvantages of the concept becomes necessary.
Benefits
The benefits of negative gearing have been listed below:
- The tax offset is one of the advantages of this type of investment option. However, it is most useful to those with high marginal tax rates.
- The tax advantage is also useful for the one looking up to expand their investment portfolio.
- One can easily deduct the loss from the property involved in negative gearing to receive benefits on the taxable income. The taxpayer may become eligible for a tax refund in this case.
Risks
The limitations surrounding the option are as follows:
- It can cost a lot of money to the investor. For example, if the mortgage interest rises, without a simultaneous increase in rent, and investor income reduces, the investor will find it difficult to pay for liabilities like interest and taxes.
- If the interest rate drops, the cost also decreases, hence loss also reduces.
- A significant decline in real estate values may bring trouble to investors. The investor fails to make a capital gain from the property sale if the housing or real estate market is down.
- For the property to generate cash inflow, the investor must first find a tenant ready to move into the property, agreeing on a considerable rent.
- Governing entities like IRS limits the types and amounts of expenses or losses taxpayer can deduct for a rental property.
- Due to increased unproductive asset speculations, this practice can cause asset or house price inflation.
Negative Gearing Vs Positive Gearing
Both negative and positive gearing have a vital role to play in mortgage-based investment. They offer respective benefits to the people who choose them. Though the objective of these options is the same, i.e., to be fruitful for the investors who choose them, there are differences that one must be aware of before they choose one for them. Let us have a look at a few of them:
- When the income from the investments one makes is more than the interest paid on them and related expenses, the property is said to be positively geared. On the other hand, if the scenario is the opposite and the income from the investment is less than the interest payment and other costs involved, the asset becomes negatively geared.
- Negative gearing helps one save heavily on taxes, especially if the person has high marginal tax rates to bear. On the contrary, positive gearing offers no tax deduction feature.
Tax savings should not be the only reason behind opting for a negative gearing investment. The choice must depend on the current situation of the investor and how they want to benefit from their property.

