Table Of Contents
What Is The National Futures Association (NFA)?
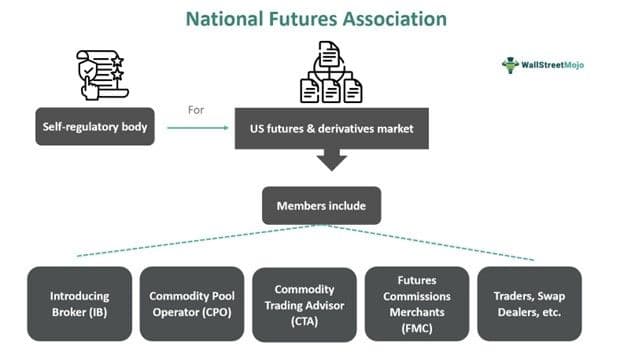
The National Futures Association (NFA) is a self-regulatory organization built to design and implement regulatory programs for the futures and derivatives markets and investors associated with it. The prime purpose of this NFA is to protect the interest of the investors and ensure compliance among the members within the futures and derivatives market.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
NFA began operating officially in 1982. It combines several registration requirements and regulates the derivatives plus futures market. Apart from them, it also takes care of the regulatory needs of the retail off-exchange foreign currency (forex) and OTC derivatives (swaps).
Key Takeaways
- The National Futures Association (NFA) is an independent self-regulatory organization established for the futures and derivatives industry.
- It protects the integrity of the investors and keeps members under supervision against regulatory requirements. It also provides membership to brokers, traders, CPOs, CTA, FMC, and other professionals.
- It became formally operational in 1982 under the provisions of the same act that led to the foundation of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
- There have been various amendments to the NFA rules. Recently, in 2023, they have included digital assets as a part of their regulation.
National Futures Association Explained
National Futures Association is an independent organization established for futures and derivatives. The headquarters of the US National Futures Association is in Chicago, and the main office is located in New York City. It tries to safeguard the interest and integrity of the investors associated with the derivatives and futures platform. In addition, it also monitors the trades but does not control them.
The National Futures Association registration requires brokers, traders, commodity pool operators (CPO), commodity trading advisors (CTA), futures commission merchants (FCM), and other participants to register with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). The CFTC is the body that granted the NFA the formal designation of being a registered futures association, and only the CFTC-registered firms become NFA members.
With the NFA registration, the traders gain the right to conduct their business in the US market. It protects the customers from any unwanted disputes with high-standard guidelines. The associated individuals can also enjoy the educational resources available on the platform. However, the members are expected to comply with the NFA and CFTC regulations and be aware of all the rules thoroughly. Hence, there is the National Futures Association exam, namely the Futures Commission Merchant (FCM) exam, which is periodically conducted to monitor the compliance of all members.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Requirements
There are some NFA rules for customers and investors. Let us look at them:
- Filing financial reports periodically
- Submitting it for regular audits
- Investors cannot trade on the customer's accounts.
- Maintaining minimum capital requirements while using the accounts.
However, if the participants try to refuse to obey them, there is a fine for not complying with the NFA rules. In recent years, the US National Futures Association has fined many financial institutions and brokers. The fines and penalties range from $10,000 to $25,00,000 for violations. Yet, in some cases, like eDeal Market LLC, there was a permanent barring from its NFA membership.
History
Under the provisions of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Act of 1974, the CFTC was founded, followed by the proposal to create NFA. The CFTC designated the latter as a registered futures association, and it formally began operating in 1982. However, it has achieved certain key milestones in recent years. Let us look at them:
- 1998 - The first online registration system (ORS) was implemented for future traders and professionals.
- 2002 - Launched its first online database system, Background Affiliation Status Information Center (BASIC), which has the history of its members.
- 2010 - NFA expanded its responsibilities to swap dealers and other swap market participants.
- 2012 - It adopted forex dealers and traders to include foreign exchange markets under its regulation.
- 2023 - NFA passed a law and added digital assets to their rule compliances.
Rules
Let us look at the National Futures Association rules as per the standards set for members:
1. Articles of Incorporation
Eighteen articles under this section cover various aspects, including name, location, purpose, form of organization, membership, rights, voting quorum, and others.
2. Bylaws
This section of the NFA standards includes bylaws starting from 101 to 1508. However, each part has its chapters. Following is the description of each chapter:
➔ Chapter 1 - Offices
➔ Chapter 2 - Purposes
➔ Chapter 3 - Membership and Association of the Members
➔ Chapter 4 - Meetings of Members and Elections
➔ Chapter 5 - Board of Directors (BOD)
➔ Chapter 6 - Officers (Chairman, Vice Chairman, President, Treasurer, and Secretary).
➔ Chapter 7 - Committees
➔ Chapter 8 - Arbitration and its Code
➔ Chapter 9 - Enforcement and Discipline
➔ Chapter 10 - Financial Requirements
➔ Chapter 11 - Business with Non-Members
➔ Chapter 12 - Property and Investments
➔ Chapter 13 - Schedule of Dues and Assessments
➔ Chapter 14 - Indemnification and Lawsuits Against NFA
➔ Chapter 15 - Miscellaneous Provisions
3. Compliance Rules
It includes the rules required by the members to follow.
4. Code of Arbitration
It refers to the guidelines that must be followed by the NFA while acting as an arbitrator.
5. Member Arbitration Rules
It defines the rules applicable to the members during arbitration. For a claim amount within $250,000, the NFA may appoint one arbitrator. But, exceeding it can lead to the appointment of three arbitrators.
6. Financial Requirement
It refers to the minimum capital requirement the members need as part of the NFA.
7. Registration Rules
This section includes the registration procedure for the members. They must fill out forms and apply for NFA. Some include Form 7-R, Form 8-R, Form 3-R, Form 7-W, Form 8-T and 8-W.
Functions
Let us look at the functions of the NFA to comprehend the concept better:
- Providing Membership - One of the prime roles of the NFA is to provide membership to investors and traders. According to the Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) and CFTC, traders must register their business with the NFA.
- Creating Enforcement Rules - As part of the financial market, the NFA creates practices and regulations for the futures and derivatives industry.
- Protection of Investor's Interest - NFA also tries to protect the traders and investors operating within the market.
- Action against Members - If, at any point, the members try to violate any rules, NFA can take considerable action against them. NFA has the right to issue warning letters to formal complaints to the accused.
- Enabling Educational resources - To aid investors, the NFA provides educational material to its investors. Various webinars, workshops, and conferences are held to spread awareness of their rights.
- Arbitration for Disputes - If the disputes in the derivatives industry exceed the limit, the NFA acts as an arbitrator (medium). It intends to act as a mediator to settle their issues.
Examples
Let us look at the examples for a better understanding:
Example #1
Suppose Kiass Capital Ltd is a firm that acts as a broker on the US stock market. Along with equity, they also dealt with the futures and derivatives market. They were already registered with the NFA. However, the traders attempted to use their customers' accounts to make illegal trades. Through this, they booked a profit of $1 million. However, as NFA detected this act, they charged the broking firm a hefty amount as a fine.
Example #2
In March 2023, the National Futures Association (NFA) adopted and issued new rules for members dealing in digital asset commodities. Rule 2-51, labeled as Requirements for Members and Associates Engaged in Activities Involving Digital Asset Commodities, was an attempt to impose enhanced and stricter supervision requirements in the markets engaged in digital asset trading. This would ensure the customers remain protected against any kind of fraud that might occur because the NFA rules are not being obeyed by the members. The dealings in digital asset commodities, like Bitcoin and Ether, would remain under thorough surveillance, thereby making investments in digital assets more reliable and secure for investors.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

