Table Of Contents
What is the Mortgage Interest Deduction?
The mortgage interest deduction is an itemized deduction from personal tax when a person takes a loan to buy home. Here, the loan should be to build, buy or to improve a property and related to personal Real-Estate.
Explanation
The mortgage interest deduction is a lucrative tax exemption given to persons who have taken a loan to finance their homes. This exemption has motivated many individuals to buy their homes instead of renting it. Renting doesn’t generate any wealth. The total amount paid as rent is wasted. So instead of renting, if individuals buy properties to live and get tax exemption on the interest paid, then it encourages citizens to buy more personal properties.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
How Does it Work?
To get such a deduction, few rules need to be followed:
- You will have to itemize your taxes, that means if you have applied for the standard deduction, then you can’t apply for Interest Deduction.
- The Real estate that you are planning to buy should be your primary or secondary residence. So basically, the Mortgage Interest deduction can be enjoyed on two properties simultaneously. The property should be strictly residential. So properties that you buy for investments are not applicable.
- It is not that the exemption is given on property of any value. So there is a cap on the principal value. Earlier, that is before 16th December 2017. The cap was $1 million. Now the cap is revised, and it got changed to $750,000
- Any particular investment that the IRS qualifies to be a residential property can avail of this exemption. So it is not necessary that it has to be a house.
- Any ordinary loan which doesn’t have any mortgaged-backed with it will not qualify for the exemption. So personal loans will not qualify for the exemption. A personal loan doesn’t have mortgages, so they are not secured.
Calculate Mortgage Interest Tax Deduction
Let us understand with an example.
Mr. X took two loans from two different sources.
1st Loan – This is a secured loan from a bank. Loan amount $1,000,000. A mortgage is a residential house that Mr. X bought to stay. The interest charged on loan is 5% per annum.
2nd Loan – This is an unsecured loan taken for the renovation of Mr. X’s first residential property. The loan amount is $500,000, and the interest rate is 5%.
Solution:
Calculate Interest payment, as shown below:

Mr. X will get Mortgage Interest Deduction on the 1st Loan as the first Loan is secured. So the total Interest that is $1,000,000 * 5% = $50,000 will be deducted from the total personal income of Mr. X and then tax will be charged on the remaining balance. This will lead to a lower tax charged for Mr. X.
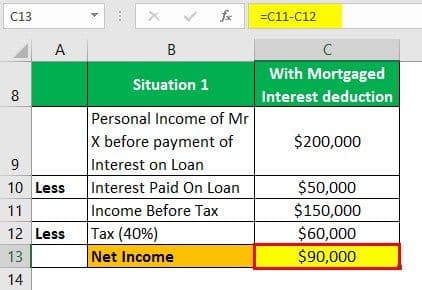
Situation 1

Net Income = $150,000 - $60,000 = $90,000
Situation 2

Net Income = $200,000 - $80,000 = $120,000
Conclusion: The Tax charged in situation 1 is $60,000 and Tax charged in situation 2 is $80,000. So it is seen that without the Mortgage Interest deduction exemption, the tax that Mr. X has to pay is high.
Mortgage Interest Deduction Amount
There is a cap on the principal value of the loan on which the Mortgage Interest Deduction Exemption will be applicable. Before 16th December 2017, the cap on the principal value of the loan was $1,000,000, and now the cap on principal value is $750,000. Now normal standard deductions are also increased. So an individual will have to check the tax benefit under standard deduction and Mortgage Interest Deduction. After checking benefits under both schemes, then an individual should decide what to do.
Advantages
- This exemption helps individuals to save tax on the interest amount that is charged for the loan taken for residential purposes. As tax is an important cost for individuals, so this exemption helps individuals to save costs.
- This deduction motivates individuals to buy their own house, rather than staying as tenants. As payment of rent has no economic benefit for individuals, so it is always better to buy their own property rather than staying in a rented apartment and paying rent for a lifetime without any economic benefit.
- Interest Payment is felt as a burden by individuals, but when Interest deduction is provided, then that burden is reduced. So it acts as positive psychology for individuals.
Disadvantages
- It is only applicable to the primary and secondary property. So if anyone is planning to buy a third property, then he will not get the benefit.
- Mortgaged Interest Deduction is capped to a principal of $750,000, so any property value above this will not enjoy this benefit.
- Standard deductions have increased a lot now, so actually, the mortgage interest deduction is not so lucrative now. Most of the individuals will find that the standard deductions are more than a deduction from Mortgage Interest. So there is no benefit for individuals to opt for this deduction.
- The deduction is only available for residential property, so if other commercial properties are purchased, then the benefit can’t be taken. So individuals who are planning to set up businesses will not be profitable in this scheme.
Conclusion
Mortgage Interest Deduction used to be a very popular scheme earlier. After the latest amendment, the cap on principal changed, and individuals started enjoying less benefit. The standard deduction has increased a lot now, so the importance of Mortgage Interest fell even more.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.